Sustainable finance focuses on investments that generate environmental and social benefits alongside financial returns, promoting long-term economic growth with minimal ecological impact. Microfinance provides financial services such as small loans and savings options to low-income individuals or small businesses lacking access to traditional banking, enabling economic inclusion and poverty reduction. Explore more about how sustainable finance and microfinance reshape the future of ethical banking.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainable finance and microfinance is crucial for aligning financial strategies with environmental, social, and economic goals. Sustainable finance focuses on funding projects that promote long-term ecological balance and social equity, while microfinance targets providing financial services to underserved low-income individuals or small businesses. Recognizing these distinctions enables banks and investors to appropriately allocate resources and measure impact. This knowledge supports better decision-making in promoting inclusive growth and responsible investment in the banking sector.
Comparison Table
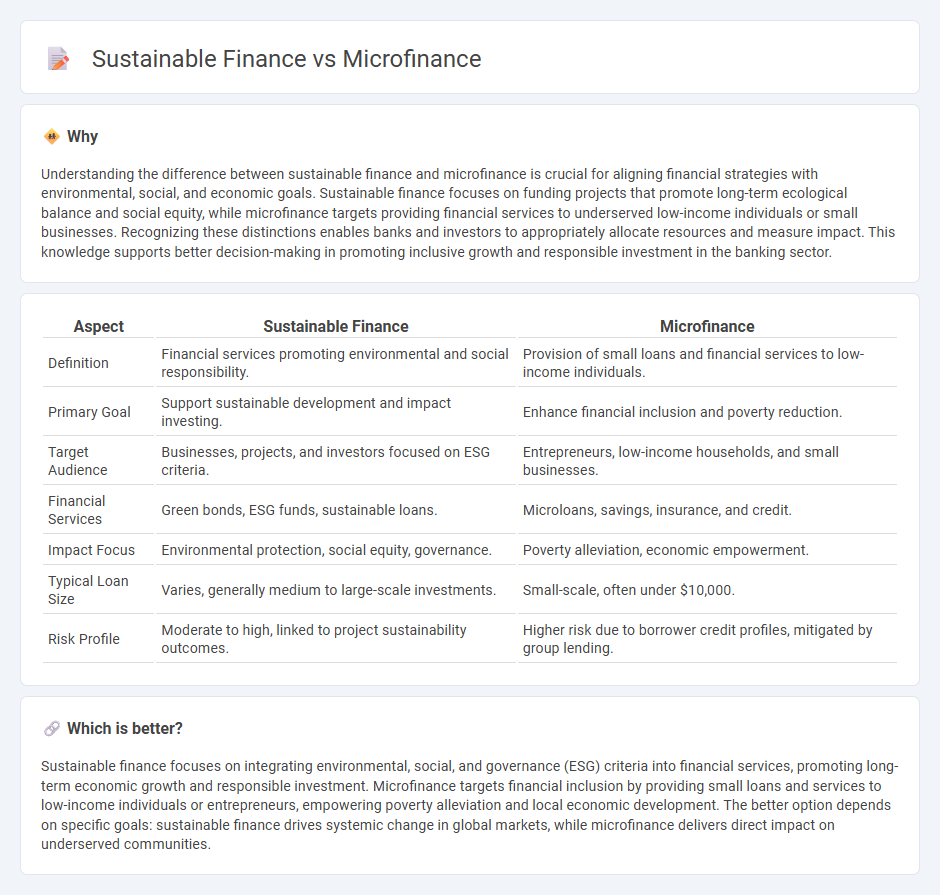
| Aspect | Sustainable Finance | Microfinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial services promoting environmental and social responsibility. | Provision of small loans and financial services to low-income individuals. |
| Primary Goal | Support sustainable development and impact investing. | Enhance financial inclusion and poverty reduction. |
| Target Audience | Businesses, projects, and investors focused on ESG criteria. | Entrepreneurs, low-income households, and small businesses. |
| Financial Services | Green bonds, ESG funds, sustainable loans. | Microloans, savings, insurance, and credit. |
| Impact Focus | Environmental protection, social equity, governance. | Poverty alleviation, economic empowerment. |
| Typical Loan Size | Varies, generally medium to large-scale investments. | Small-scale, often under $10,000. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate to high, linked to project sustainability outcomes. | Higher risk due to borrower credit profiles, mitigated by group lending. |
Which is better?
Sustainable finance focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial services, promoting long-term economic growth and responsible investment. Microfinance targets financial inclusion by providing small loans and services to low-income individuals or entrepreneurs, empowering poverty alleviation and local economic development. The better option depends on specific goals: sustainable finance drives systemic change in global markets, while microfinance delivers direct impact on underserved communities.
Connection
Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial services, promoting investments that support long-term societal benefits. Microfinance provides essential capital to underserved populations, fostering economic inclusion and poverty alleviation while aligning with sustainable development goals (SDGs). The connection lies in microfinance's role as a tool within sustainable finance frameworks, driving social impact through financial empowerment and responsible lending.
Key Terms
Microfinance:
Microfinance involves providing small loans and financial services to low-income individuals or entrepreneurs lacking access to traditional banking, fostering financial inclusion and entrepreneurship in underserved communities. It plays a critical role in poverty alleviation by enabling micro-entrepreneurs to start or expand businesses, generate income, and improve livelihoods. Explore how microfinance drives economic empowerment and sustainable development through tailored financial solutions.
Financial Inclusion
Microfinance provides small loans and financial services to underserved populations, directly enhancing financial inclusion by enabling low-income individuals to access capital. Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial services, promoting long-term economic growth while addressing social equity and environmental sustainability. Explore how combining microfinance and sustainable finance strategies can drive comprehensive financial inclusion and equitable development.
Microcredit
Microcredit, a core component of microfinance, provides small loans to low-income individuals or groups lacking access to traditional banking services, fostering entrepreneurship and financial inclusion. Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial decision-making, promoting investments that contribute to long-term economic and ecological resilience. Explore deeper insights into how microcredit aligns with sustainable finance goals for impactful economic development.
Source and External Links
Microfinance - Microfinance refers to financial services, such as microloans and savings accounts, provided to individuals with limited access to traditional banking services.
Microfinance 101 - This guide explains what microfinance is, its benefits, and how it helps individuals without access to traditional banking.
Microfinance - FINCA International - Microfinance involves providing financial services, especially small loans, to low-income individuals excluded from traditional banking systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com