Instant settlement processes payments immediately upon initiation, ensuring real-time fund transfers and improved liquidity management for businesses and consumers. Gross settlement involves transactions being settled individually on a transaction-by-transaction basis, typically at scheduled intervals, which may lead to delayed fund availability but reduces settlement risk. Explore the detailed differences and benefits of instant versus gross settlement to optimize your banking transactions.
Why it is important
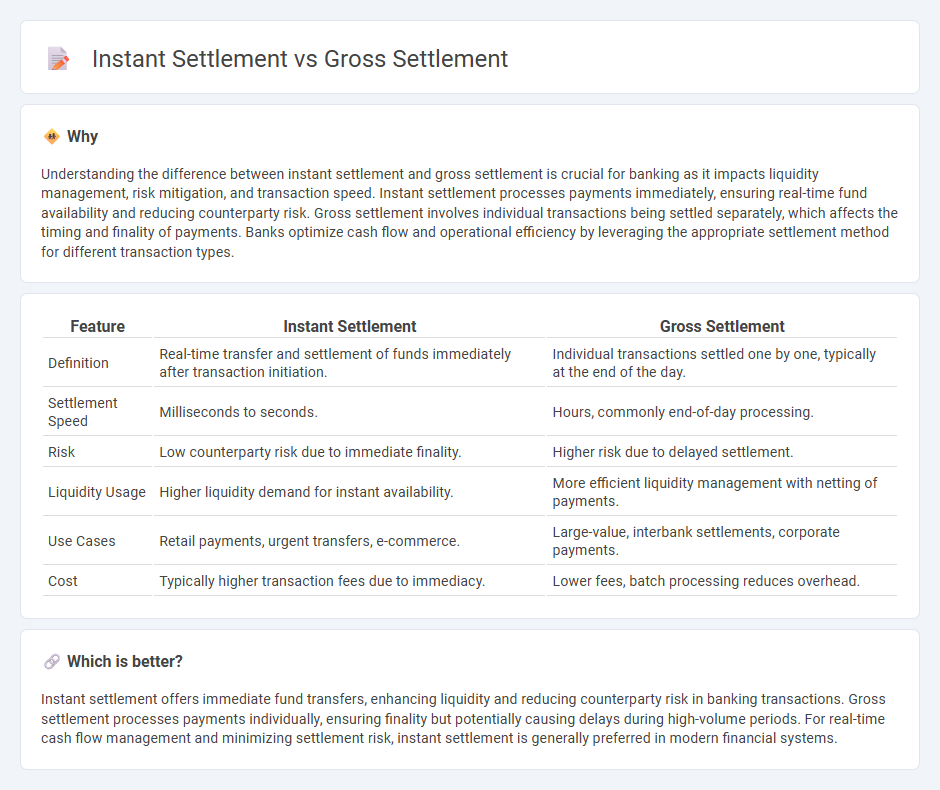
Understanding the difference between instant settlement and gross settlement is crucial for banking as it impacts liquidity management, risk mitigation, and transaction speed. Instant settlement processes payments immediately, ensuring real-time fund availability and reducing counterparty risk. Gross settlement involves individual transactions being settled separately, which affects the timing and finality of payments. Banks optimize cash flow and operational efficiency by leveraging the appropriate settlement method for different transaction types.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Instant Settlement | Gross Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time transfer and settlement of funds immediately after transaction initiation. | Individual transactions settled one by one, typically at the end of the day. |
| Settlement Speed | Milliseconds to seconds. | Hours, commonly end-of-day processing. |
| Risk | Low counterparty risk due to immediate finality. | Higher risk due to delayed settlement. |
| Liquidity Usage | Higher liquidity demand for instant availability. | More efficient liquidity management with netting of payments. |
| Use Cases | Retail payments, urgent transfers, e-commerce. | Large-value, interbank settlements, corporate payments. |
| Cost | Typically higher transaction fees due to immediacy. | Lower fees, batch processing reduces overhead. |
Which is better?
Instant settlement offers immediate fund transfers, enhancing liquidity and reducing counterparty risk in banking transactions. Gross settlement processes payments individually, ensuring finality but potentially causing delays during high-volume periods. For real-time cash flow management and minimizing settlement risk, instant settlement is generally preferred in modern financial systems.
Connection
Instant settlement and gross settlement are connected through their roles in payment processing systems, where instant settlement facilitates real-time transfer and finality of funds on a transaction-by-transaction basis, while gross settlement refers to the direct, individual clearing of payments without netting. Both systems aim to enhance liquidity management and reduce settlement risk in banking operations. Integration of instant settlement mechanisms within gross settlement frameworks optimizes speed and security for high-value transactions processed by central banks.
Key Terms
Finality
Gross settlement processes transactions individually, ensuring finality by settling each payment without netting, which reduces counterparty risk but may require more liquidity. Instant settlement offers immediate finality by processing transactions in real-time, enhancing efficiency and minimizing settlement exposure. Discover how each method impacts financial systems and transaction security in greater detail.
Processing Time
Gross settlement processes transactions individually with settlement occurring at designated times, leading to longer processing times often spanning hours. Instant settlement completes fund transfers in real-time, ensuring immediate availability and significantly reducing processing delays to seconds. Explore our detailed comparison to understand which settlement method best suits your needs.
Liquidity
Gross settlement processes transfer each transaction individually, requiring firms to maintain higher liquidity reserves to cover multiple unsettled payments simultaneously. Instant settlement, often enabled by real-time payment systems, minimizes liquidity needs by settling payments immediately and reducing counterparty risk. Explore the advantages and implications of both settlement methods for efficient liquidity management.
Source and External Links
What is Gross Settlement? - Gross settlement is the process of transferring funds or securities on an individual order basis where each transaction is settled immediately and separately without bundling or netting with others, exemplified by the Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system used for high-value, time-critical payments.
Settlement (Net vs. Gross) - Gross settlement involves continuously settling transactions individually and in real-time as they occur, making these transactions irrevocable and well-suited for large, urgent transfers typically managed by central banks.
Gross Settlement vs. Net Settlement in Banking - Gross settlement systems process each payment independently and in real time without netting or batching, ensuring finality and security, commonly used for high-value payments through systems operated by central banks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com