Green financing focuses on funding sustainable projects that promote environmental conservation and renewable energy, while microfinance provides small loans and financial services to low-income individuals or entrepreneurs lacking access to conventional banking. Both approaches aim to foster economic development and social impact, but target different sectors and objectives within the financial ecosystem. Discover more about how green financing and microfinance are transforming modern banking.
Why it is important
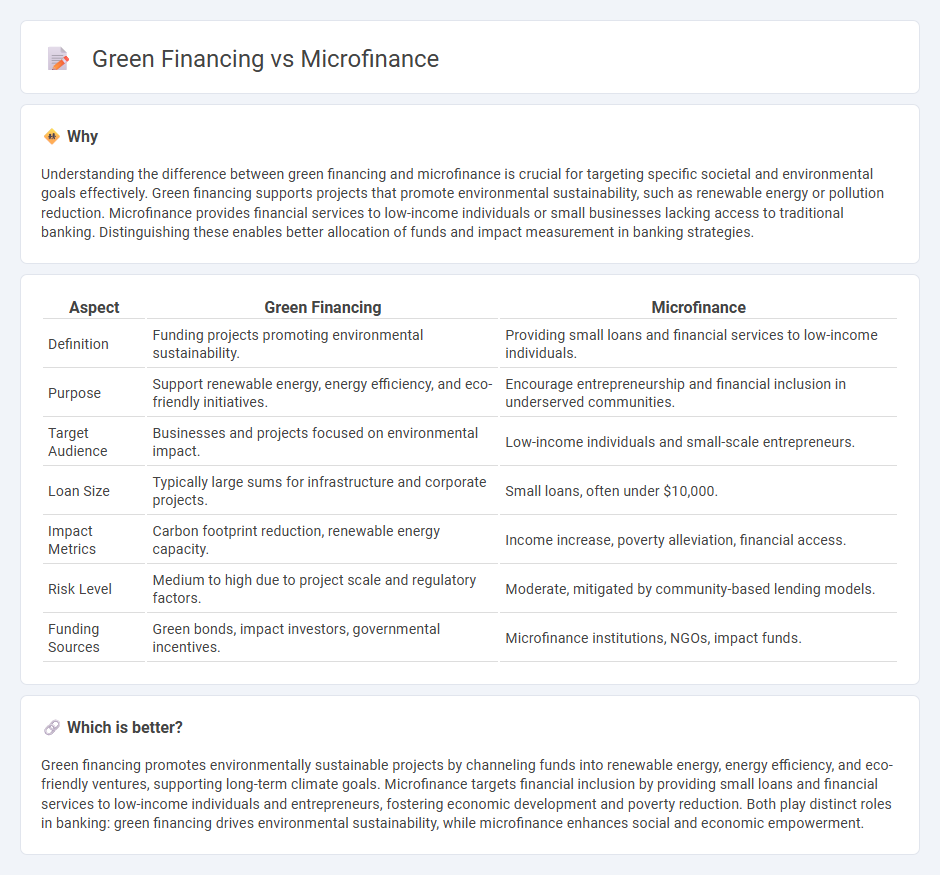
Understanding the difference between green financing and microfinance is crucial for targeting specific societal and environmental goals effectively. Green financing supports projects that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy or pollution reduction. Microfinance provides financial services to low-income individuals or small businesses lacking access to traditional banking. Distinguishing these enables better allocation of funds and impact measurement in banking strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Financing | Microfinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funding projects promoting environmental sustainability. | Providing small loans and financial services to low-income individuals. |
| Purpose | Support renewable energy, energy efficiency, and eco-friendly initiatives. | Encourage entrepreneurship and financial inclusion in underserved communities. |
| Target Audience | Businesses and projects focused on environmental impact. | Low-income individuals and small-scale entrepreneurs. |
| Loan Size | Typically large sums for infrastructure and corporate projects. | Small loans, often under $10,000. |
| Impact Metrics | Carbon footprint reduction, renewable energy capacity. | Income increase, poverty alleviation, financial access. |
| Risk Level | Medium to high due to project scale and regulatory factors. | Moderate, mitigated by community-based lending models. |
| Funding Sources | Green bonds, impact investors, governmental incentives. | Microfinance institutions, NGOs, impact funds. |
Which is better?
Green financing promotes environmentally sustainable projects by channeling funds into renewable energy, energy efficiency, and eco-friendly ventures, supporting long-term climate goals. Microfinance targets financial inclusion by providing small loans and financial services to low-income individuals and entrepreneurs, fostering economic development and poverty reduction. Both play distinct roles in banking: green financing drives environmental sustainability, while microfinance enhances social and economic empowerment.
Connection
Green financing promotes sustainable environmental projects by providing capital for renewable energy, conservation, and eco-friendly technologies, often targeting underserved communities. Microfinance offers small loans and financial services to low-income individuals, enabling their participation in green projects such as clean energy adoption and sustainable agriculture. Together, green financing and microfinance foster inclusive economic growth by supporting environmentally responsible initiatives at the grassroots level.
Key Terms
**Microfinance:**
Microfinance provides small loans and financial services to low-income individuals and entrepreneurs who lack access to traditional banking, fostering economic empowerment and poverty alleviation globally. It targets underserved communities to promote sustainable development by enabling small business growth and improving livelihoods. Explore more about how microfinance drives inclusive financial access and social impact.
Microcredit
Microcredit, a key component of microfinance, provides small loans to underserved individuals or communities to foster entrepreneurship and alleviate poverty, enabling access to essential resources without traditional collateral. In contrast, green financing targets projects aimed at environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and climate resilience initiatives. Explore the distinct impacts and opportunities within microcredit and green financing to better understand their roles in economic and environmental development.
Financial Inclusion
Microfinance enhances financial inclusion by providing small loans and financial services to underserved populations, particularly in developing regions, facilitating entrepreneurship and poverty alleviation. Green financing directs capital towards environmentally sustainable projects, promoting eco-friendly development while also aiming to improve access to clean energy and sustainable resources for marginalized communities. Explore how these financial models intersect to drive inclusive growth and environmental sustainability.
Source and External Links
Microfinance - Definition, Benefits, Drawbacks, Models - Microfinance provides financial services, including microcredit, savings, and insurance, to individuals and small businesses lacking access to traditional financial services.
Microfinance 101: All you need to know - This guide explains microfinance, its benefits, and how it helps individuals and small businesses without access to traditional banking services.
Microfinancing Basics - This resource provides an overview of microfinance, including its emergence, types, and how it assists entrepreneurs needing less capital than traditional banks offer.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com