Composable banking leverages modular components and APIs to create flexible, scalable financial services tailored to specific customer needs. Legacy banking relies on monolithic systems with rigid architectures that limit innovation and adaptation in a rapidly evolving market. Discover how composable banking is transforming the financial landscape and enhancing customer experiences.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between composable banking and legacy banking is crucial for financial institutions aiming to enhance agility, reduce operational costs, and accelerate innovation cycles. Composable banking leverages modular, API-driven components allowing rapid customization and integration, whereas legacy banking relies on monolithic, inflexible systems with slower adaptation to market demands. This knowledge enables banks to strategically invest in scalable technology that improves customer experience and competitive advantage. Recognizing these distinctions drives informed decision-making for digital transformation and regulatory compliance in the evolving financial landscape.
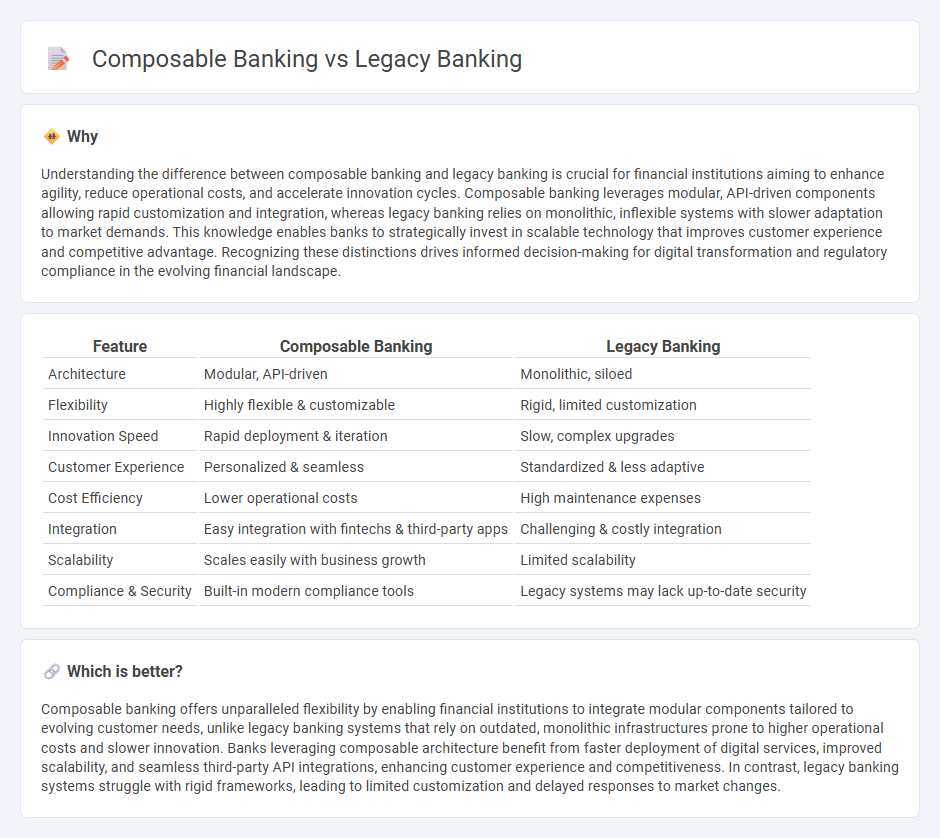
Comparison Table
| Feature | Composable Banking | Legacy Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Modular, API-driven | Monolithic, siloed |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible & customizable | Rigid, limited customization |
| Innovation Speed | Rapid deployment & iteration | Slow, complex upgrades |
| Customer Experience | Personalized & seamless | Standardized & less adaptive |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs | High maintenance expenses |
| Integration | Easy integration with fintechs & third-party apps | Challenging & costly integration |
| Scalability | Scales easily with business growth | Limited scalability |
| Compliance & Security | Built-in modern compliance tools | Legacy systems may lack up-to-date security |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers unparalleled flexibility by enabling financial institutions to integrate modular components tailored to evolving customer needs, unlike legacy banking systems that rely on outdated, monolithic infrastructures prone to higher operational costs and slower innovation. Banks leveraging composable architecture benefit from faster deployment of digital services, improved scalability, and seamless third-party API integrations, enhancing customer experience and competitiveness. In contrast, legacy banking systems struggle with rigid frameworks, leading to limited customization and delayed responses to market changes.
Connection
Composable banking integrates modular APIs and microservices that enable financial institutions to modernize Legacy banking systems without complete replacement. Legacy banking infrastructures, often characterized by monolithic architectures, gain agility and scalability through composable banking frameworks that facilitate seamless integration of new digital services. This connection allows banks to enhance customer experience, reduce operational costs, and quickly adapt to market changes while leveraging existing legacy investments.
Key Terms
Monolithic Architecture
Legacy banking systems rely heavily on monolithic architecture, where a single integrated platform handles all banking services, leading to limited flexibility and slower innovation. Composable banking embraces modular, API-driven components, enabling banks to rapidly adapt and customize services while improving scalability. Explore how composable banking revolutionizes financial services by overcoming the constraints of monolithic systems.
API Integration
Legacy banking systems rely on monolithic structures with limited API integration, leading to slower innovation and reduced flexibility. Composable banking embraces modular APIs, enabling seamless connectivity between services and rapid customization for personalized customer experiences. Explore how adopting composable banking can revolutionize API strategies and drive digital transformation.
Core Banking Systems
Legacy banking relies on monolithic core banking systems that often hinder agility, limit scalability, and increase operational costs due to rigid architectures. Composable banking leverages modular, API-driven core banking platforms enabling rapid innovation, seamless integration with fintech services, and enhanced customer experiences. Discover how composable core banking transforms financial institutions by optimizing efficiency and adaptability.
Source and External Links
Legacy Banking Systems: Why and how to Modernize - OpenLegacy - Legacy banking systems are typically outdated mainframe-based platforms that hinder flexibility and scalability, and modernizing them via cloud technologies and microservices can reduce costs and improve services.
Welcome to Legacy Bank - Legacy Bank is an established traditional bank with a long history, offering standard banking products and online services as part of its ongoing operations.
What Are Legacy Core Banking Systems? - Cognizant - Legacy core banking systems are often decades-old mainframe platforms that limit banks' agility and innovation, prompting many banks to adopt cloud-based digital core systems to enhance customer experience and accelerate product delivery.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com