Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) offer secure, government-backed digital money that can streamline cross-border payments and reduce transaction costs. International remittance services traditionally rely on intermediaries, causing delays and high fees, which CBDCs aim to address through faster settlement times and enhanced transparency. Explore how CBDCs are transforming the future of global money transfers.
Why it is important
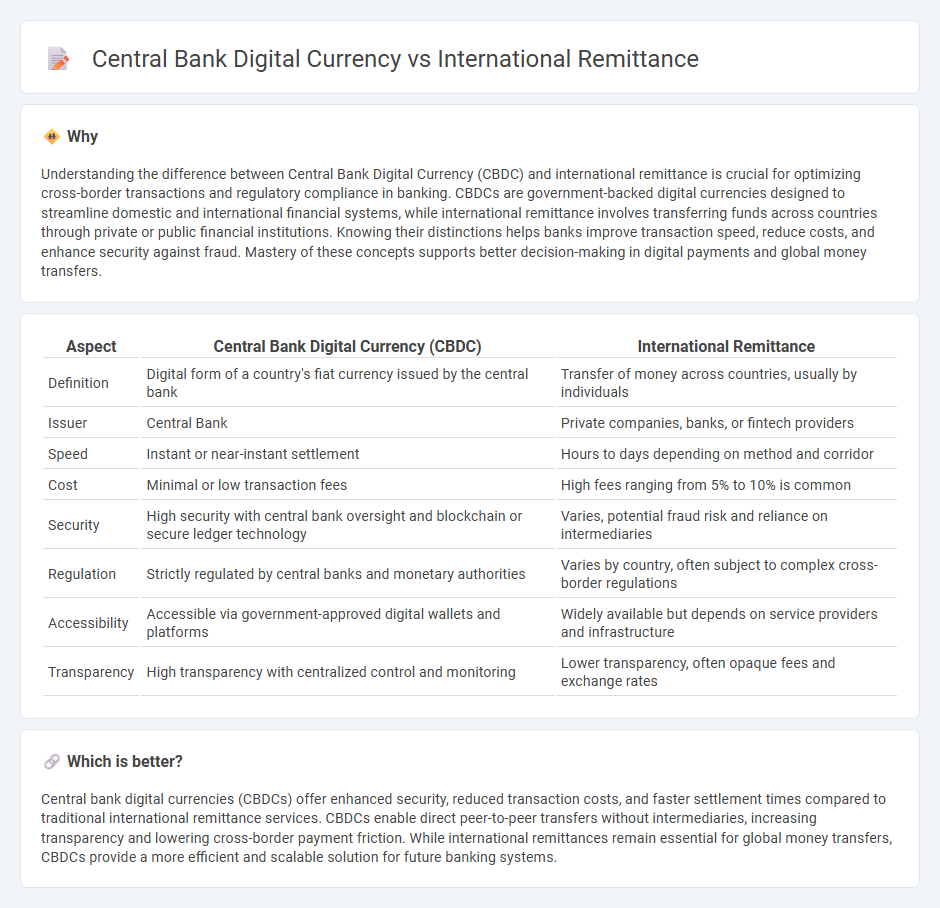
Understanding the difference between Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and international remittance is crucial for optimizing cross-border transactions and regulatory compliance in banking. CBDCs are government-backed digital currencies designed to streamline domestic and international financial systems, while international remittance involves transferring funds across countries through private or public financial institutions. Knowing their distinctions helps banks improve transaction speed, reduce costs, and enhance security against fraud. Mastery of these concepts supports better decision-making in digital payments and global money transfers.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) | International Remittance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital form of a country's fiat currency issued by the central bank | Transfer of money across countries, usually by individuals |
| Issuer | Central Bank | Private companies, banks, or fintech providers |
| Speed | Instant or near-instant settlement | Hours to days depending on method and corridor |
| Cost | Minimal or low transaction fees | High fees ranging from 5% to 10% is common |
| Security | High security with central bank oversight and blockchain or secure ledger technology | Varies, potential fraud risk and reliance on intermediaries |
| Regulation | Strictly regulated by central banks and monetary authorities | Varies by country, often subject to complex cross-border regulations |
| Accessibility | Accessible via government-approved digital wallets and platforms | Widely available but depends on service providers and infrastructure |
| Transparency | High transparency with centralized control and monitoring | Lower transparency, often opaque fees and exchange rates |
Which is better?
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) offer enhanced security, reduced transaction costs, and faster settlement times compared to traditional international remittance services. CBDCs enable direct peer-to-peer transfers without intermediaries, increasing transparency and lowering cross-border payment friction. While international remittances remain essential for global money transfers, CBDCs provide a more efficient and scalable solution for future banking systems.
Connection
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) enhances international remittance by enabling faster, cheaper, and more secure cross-border transactions. CBDCs reduce reliance on intermediaries, lowering transaction costs and minimizing settlement times compared to traditional correspondent banking systems. Integration of CBDCs into remittance corridors improves transparency, traceability, and financial inclusion for unbanked populations globally.
Key Terms
**International Remittance:**
International remittance involves the transfer of funds across borders, primarily facilitated by money transfer operators, banks, and digital wallets, with global flows estimated at over $700 billion annually. These transactions often face high fees, fluctuating exchange rates, and regulatory hurdles, making them less efficient for migrants and their families. Explore how emerging technologies and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are set to transform the landscape of cross-border payments.
SWIFT
International remittance systems primarily rely on SWIFT messaging for secure cross-border money transfers, enabling real-time communication between financial institutions globally. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) holds potential to streamline remittance processes by reducing reliance on intermediaries like SWIFT, offering faster settlement, lower fees, and enhanced transparency. Explore the evolving impact of CBDCs on SWIFT-based remittance infrastructure to understand future trends in global payments.
Foreign Exchange (FX)
International remittance relies heavily on Foreign Exchange (FX) markets to convert currencies, often incurring high fees and delays due to multiple intermediaries and exchange rate markups. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) streamlines cross-border payments by enabling direct, secure, and near-instant FX transactions between participating central banks, reducing costs and increasing transparency. Explore how CBDCs are reshaping FX dynamics and transforming the future of international money transfers.
Source and External Links
Remittances: Funds for the Folks Back Home - International remittance involves migrants sending part of their earnings back home typically through a sending agent who transfers money via a paying agent in the recipient country, with fees and currency conversion costs often involved, especially impacting smaller remittances under $200.
Remittances - World Bank - The World Bank emphasizes reducing remittance costs and increasing volumes, supporting transparency, consumer protection, and better payment system infrastructures, with remittance flows crucial for developing economies.
Remittance - Wikipedia - Remittances are money transfers by foreign workers or diaspora to their home countries, with the US being the largest sending country, and key recipients including India, China, and the Philippines, often sent via official agents or increasingly through online and mobile transfers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com