Instant settlement enables financial transactions to be completed within seconds, ensuring faster fund availability compared to traditional batch processing methods. Real-time settlement processes transactions continuously throughout the business day, minimizing delays and enhancing liquidity management for banks and customers. Explore the key differences and benefits of instant versus real-time settlement to optimize your banking operations.
Why it is important
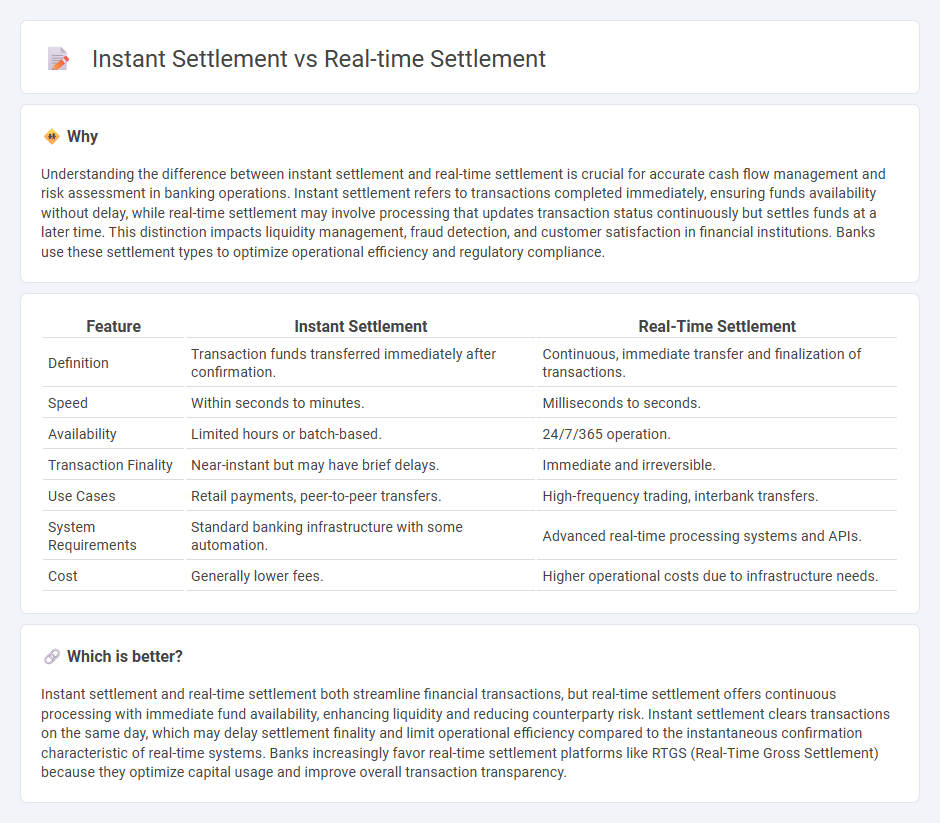
Understanding the difference between instant settlement and real-time settlement is crucial for accurate cash flow management and risk assessment in banking operations. Instant settlement refers to transactions completed immediately, ensuring funds availability without delay, while real-time settlement may involve processing that updates transaction status continuously but settles funds at a later time. This distinction impacts liquidity management, fraud detection, and customer satisfaction in financial institutions. Banks use these settlement types to optimize operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Instant Settlement | Real-Time Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transaction funds transferred immediately after confirmation. | Continuous, immediate transfer and finalization of transactions. |
| Speed | Within seconds to minutes. | Milliseconds to seconds. |
| Availability | Limited hours or batch-based. | 24/7/365 operation. |
| Transaction Finality | Near-instant but may have brief delays. | Immediate and irreversible. |
| Use Cases | Retail payments, peer-to-peer transfers. | High-frequency trading, interbank transfers. |
| System Requirements | Standard banking infrastructure with some automation. | Advanced real-time processing systems and APIs. |
| Cost | Generally lower fees. | Higher operational costs due to infrastructure needs. |
Which is better?
Instant settlement and real-time settlement both streamline financial transactions, but real-time settlement offers continuous processing with immediate fund availability, enhancing liquidity and reducing counterparty risk. Instant settlement clears transactions on the same day, which may delay settlement finality and limit operational efficiency compared to the instantaneous confirmation characteristic of real-time systems. Banks increasingly favor real-time settlement platforms like RTGS (Real-Time Gross Settlement) because they optimize capital usage and improve overall transaction transparency.
Connection
Instant settlement and real-time settlement both refer to the immediate processing of financial transactions, minimizing delays between initiation and completion. Instant settlement ensures funds are transferred and reflected in accounts without waiting periods, while real-time settlement emphasizes continuous, immediate updating of transaction status across systems. Together, they enhance liquidity management and reduce counterparty risk in modern banking infrastructure.
Key Terms
Clearing
Real-time settlement processes transactions immediately as they are cleared, reducing counterparty risk and enhancing liquidity management. Instant settlement completes the transfer of funds and securities seconds after trade confirmation, aiming to eliminate settlement lag entirely. Explore deeper insights into clearing mechanisms to understand the nuances between real-time and instant settlement systems.
Settlement
Real-time settlement processes financial transactions immediately as they occur, ensuring funds are transferred without delay and reducing counterparty risk. Instant settlement delivers funds within seconds, emphasizing speed but sometimes involving batch processing that might not confirm final settlement instantly. Explore detailed comparisons to understand the nuances of settlement technologies in modern finance.
Finality
Real-time settlement ensures that the transfer of funds between parties occurs continuously throughout the day, while instant settlement emphasizes immediate finality where transactions are irrevocably settled at the moment of execution. Finality in instant settlement reduces counterparty risk by confirming that transactions cannot be revoked, contrasting with real-time settlement systems that may still involve some delay or netting processes before funds are considered final. Explore the distinctions between these settlement mechanisms to understand their impact on payment systems and financial risk management.
Source and External Links
A brief introduction to the Real-Time Gross Settlement system and CHAPS - Bank of England - Real-time settlement refers to the process where payment obligations between participants are settled individually and immediately on a gross basis throughout the business day, eliminating settlement risk and providing finality in payments.
Make the move: Real-time settlement for card-based payments - Cognizant - Real-time settlement enables instant fund availability for merchants and acquirers, zero settlement risk, and better liquidity control for issuers by processing card payments immediately rather than via deferred batch settlement.
What is Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)? - Modern Treasury - RTGS is an electronic payment system where transactions between banks are processed and settled immediately, not in batches, ensuring fast, secure transfer of funds for large-value payments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com