Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term financial returns while promoting responsible business practices. Impact investing specifically targets measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial gains, often focusing on underserved communities or critical global issues. Discover how these investing strategies reshape the banking landscape and drive positive change.
Why it is important
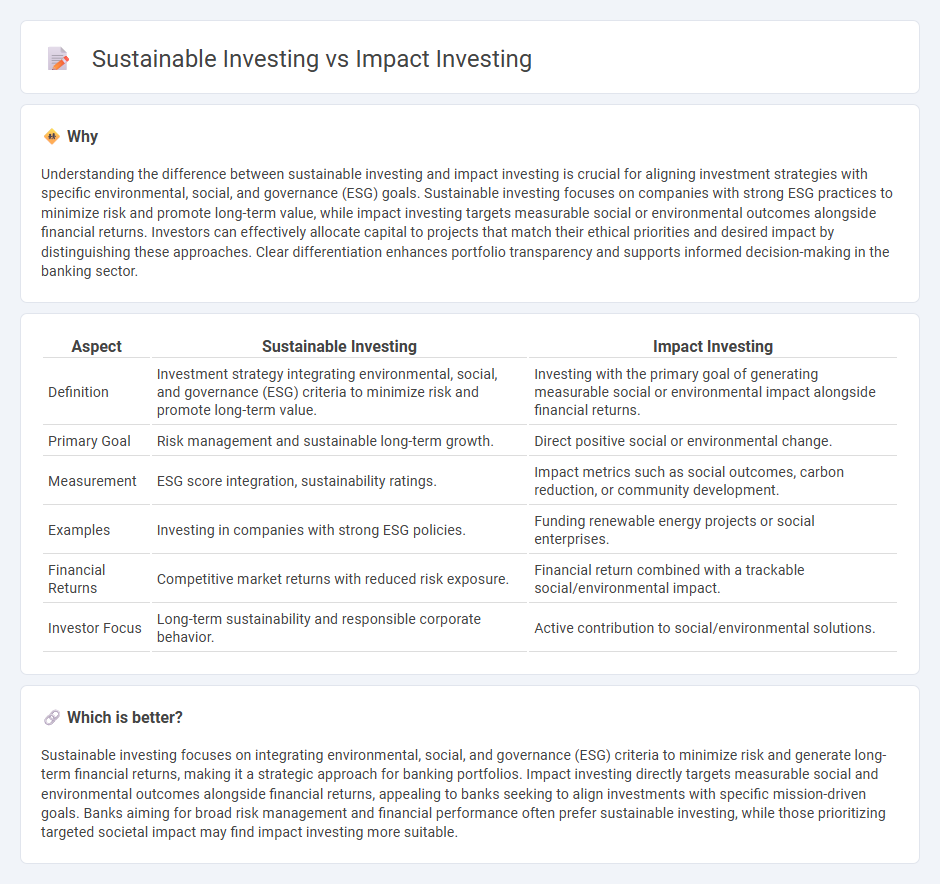
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and impact investing is crucial for aligning investment strategies with specific environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals. Sustainable investing focuses on companies with strong ESG practices to minimize risk and promote long-term value, while impact investing targets measurable social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. Investors can effectively allocate capital to projects that match their ethical priorities and desired impact by distinguishing these approaches. Clear differentiation enhances portfolio transparency and supports informed decision-making in the banking sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Impact Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment strategy integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to minimize risk and promote long-term value. | Investing with the primary goal of generating measurable social or environmental impact alongside financial returns. |
| Primary Goal | Risk management and sustainable long-term growth. | Direct positive social or environmental change. |
| Measurement | ESG score integration, sustainability ratings. | Impact metrics such as social outcomes, carbon reduction, or community development. |
| Examples | Investing in companies with strong ESG policies. | Funding renewable energy projects or social enterprises. |
| Financial Returns | Competitive market returns with reduced risk exposure. | Financial return combined with a trackable social/environmental impact. |
| Investor Focus | Long-term sustainability and responsible corporate behavior. | Active contribution to social/environmental solutions. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to minimize risk and generate long-term financial returns, making it a strategic approach for banking portfolios. Impact investing directly targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, appealing to banks seeking to align investments with specific mission-driven goals. Banks aiming for broad risk management and financial performance often prefer sustainable investing, while those prioritizing targeted societal impact may find impact investing more suitable.
Connection
Sustainable investing and impact investing both prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate positive outcomes alongside financial returns. Banks integrate these strategies by financing projects that reduce carbon emissions, promote social equity, or enhance corporate governance, thereby aligning portfolios with global sustainability goals such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This connection drives capital toward enterprises that create measurable, long-term benefits for society and the environment while managing financial risk.
Key Terms
Social Return
Impact investing prioritizes measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns, targeting projects with direct positive outcomes such as affordable housing or renewable energy. Sustainable investing integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors to minimize risks and support long-term business viability, often emphasizing corporate responsibility and ethical practices. Explore further to understand how each approach drives Social Return on Investment (SROI) differently.
ESG Criteria
Impact investing prioritizes generating measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns, often targeting projects aligned with specific ESG criteria. Sustainable investing integrates ESG factors into investment decisions to promote long-term value and minimize risks related to environmental, social, and governance issues. Explore in-depth comparisons and strategies to understand how each approach supports responsible investment goals.
Financial Performance
Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes while seeking competitive financial returns, often achieving market-rate or above-average performance. Sustainable investing integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria into investment decisions to manage risks and generate long-term financial gains, showing strong correlations with reduced volatility and enhanced portfolio resilience. Explore in-depth analyses and comparative studies to understand how each strategy influences financial performance and investment goals.
Source and External Links
What You Need to Know About Impact Investing - Impact investing involves making investments with the intention to generate both financial returns and positive social or environmental impacts.
What is Impact Investing? - Impact investing is a strategy that aligns investments with personal and philanthropic values while generating financial returns.
Impact Investing - Impact investing refers to investments made with the intention to generate beneficial social or environmental effects alongside financial returns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com