Synthetic identity fraud involves creating a fictitious identity by combining real and fabricated information to bypass banking security systems, while identity theft uses someone's actual personal data without consent to commit fraud. Financial institutions face increased challenges detecting synthetic identities due to their partially authentic elements, complicating prevention and recovery efforts. Explore further to understand how banks combat these evolving fraud techniques.
Why it is important
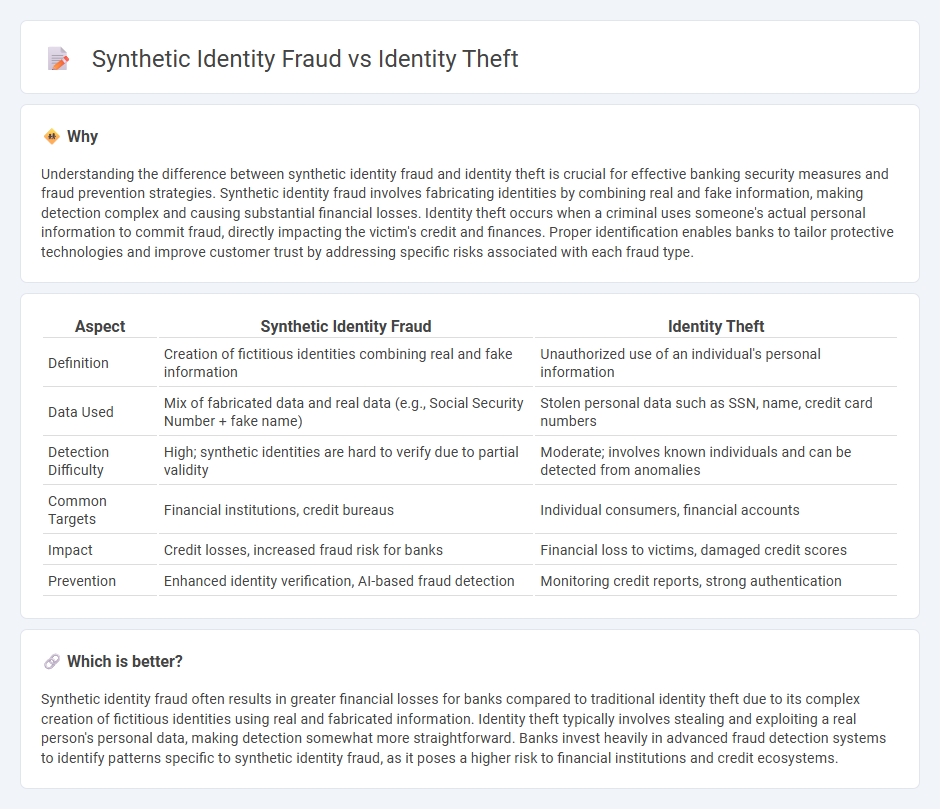
Understanding the difference between synthetic identity fraud and identity theft is crucial for effective banking security measures and fraud prevention strategies. Synthetic identity fraud involves fabricating identities by combining real and fake information, making detection complex and causing substantial financial losses. Identity theft occurs when a criminal uses someone's actual personal information to commit fraud, directly impacting the victim's credit and finances. Proper identification enables banks to tailor protective technologies and improve customer trust by addressing specific risks associated with each fraud type.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Identity Fraud | Identity Theft |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creation of fictitious identities combining real and fake information | Unauthorized use of an individual's personal information |
| Data Used | Mix of fabricated data and real data (e.g., Social Security Number + fake name) | Stolen personal data such as SSN, name, credit card numbers |
| Detection Difficulty | High; synthetic identities are hard to verify due to partial validity | Moderate; involves known individuals and can be detected from anomalies |
| Common Targets | Financial institutions, credit bureaus | Individual consumers, financial accounts |
| Impact | Credit losses, increased fraud risk for banks | Financial loss to victims, damaged credit scores |
| Prevention | Enhanced identity verification, AI-based fraud detection | Monitoring credit reports, strong authentication |
Which is better?
Synthetic identity fraud often results in greater financial losses for banks compared to traditional identity theft due to its complex creation of fictitious identities using real and fabricated information. Identity theft typically involves stealing and exploiting a real person's personal data, making detection somewhat more straightforward. Banks invest heavily in advanced fraud detection systems to identify patterns specific to synthetic identity fraud, as it poses a higher risk to financial institutions and credit ecosystems.
Connection
Synthetic identity fraud and identity theft are interconnected as both involve the misuse of personal information to create fraudulent identities for financial gain. Identity theft typically uses stolen real data, while synthetic identity fraud combines real and fabricated information to evade detection by banking systems. Financial institutions face increased risks from these crimes, necessitating advanced identity verification and fraud detection technologies.
Key Terms
Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Identity theft involves the unauthorized use of someone's existing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) such as Social Security numbers, addresses, or birthdates to commit fraud. Synthetic identity fraud, however, combines real and fabricated PII elements to create a new, fictitious identity that is harder to detect through conventional means. Explore deeper insights into how these security threats leverage PII and protect your information effectively.
Social Security Number (SSN)
Identity theft involves the unauthorized use of a real individual's Social Security Number (SSN) to commit fraud or theft, while synthetic identity fraud combines real SSNs with fabricated personal information to create entirely new identities. The misuse of SSNs in synthetic identity fraud is particularly challenging to detect because the SSN is valid, making it harder for financial institutions and governments to identify fraudulent activities. Explore the latest methods to protect your SSN and prevent both identity theft and synthetic identity fraud.
Fraudulent Account Creation
Fraudulent account creation in identity theft involves using stolen personal information, such as Social Security numbers or credit card details, to open unauthorized accounts and make transactions under the victim's name. Synthetic identity fraud, however, constructs entirely new, fictitious identities by combining real and fabricated data, often evading traditional detection systems and enabling long-term fraudulent activities. Explore more to understand the nuances and detection strategies of these critical financial security threats.
Source and External Links
Identity theft - Identity theft occurs when someone uses another person's personal identifying information without permission to commit fraud or other crimes, often to gain financial advantages or credit; this can include stealing names, social security numbers, credit card information, and more.
What To Know About Identity Theft - Identity theft involves unauthorized use of personal or financial information, such as credit card or social security numbers, which can lead to fraudulent purchases, opening new accounts, or even stealing tax refunds.
Criminal Division | Identity Theft - Identity theft and fraud involve wrongfully obtaining and using someone's personal data through methods like mail theft, shoulder surfing, phishing, or computer hacking, often for economic gain.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com