Behavioral biometrics analyzes unique patterns in user behavior, such as typing rhythm and touchscreen interactions, to enhance banking security by continuously verifying identity. Token-based authentication uses physical or digital devices generating one-time passwords to provide a secure method for accessing banking services. Discover how these technologies transform authentication and protect your financial assets.
Why it is important
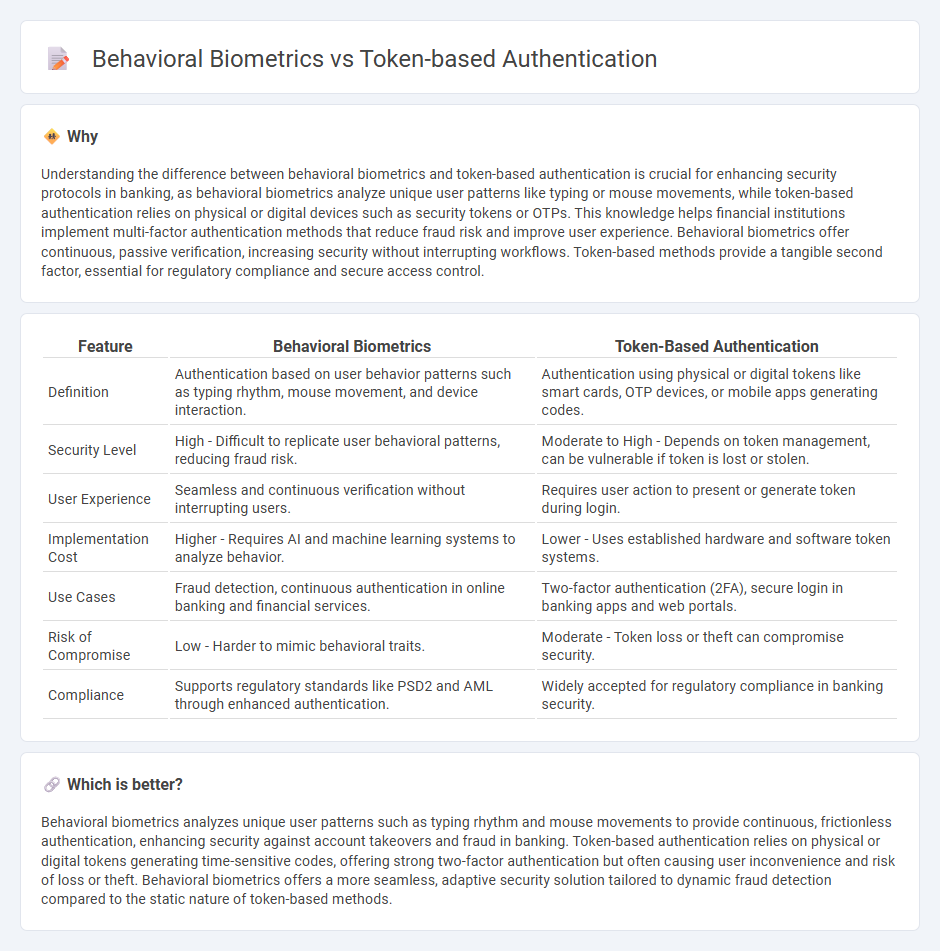
Understanding the difference between behavioral biometrics and token-based authentication is crucial for enhancing security protocols in banking, as behavioral biometrics analyze unique user patterns like typing or mouse movements, while token-based authentication relies on physical or digital devices such as security tokens or OTPs. This knowledge helps financial institutions implement multi-factor authentication methods that reduce fraud risk and improve user experience. Behavioral biometrics offer continuous, passive verification, increasing security without interrupting workflows. Token-based methods provide a tangible second factor, essential for regulatory compliance and secure access control.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Behavioral Biometrics | Token-Based Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authentication based on user behavior patterns such as typing rhythm, mouse movement, and device interaction. | Authentication using physical or digital tokens like smart cards, OTP devices, or mobile apps generating codes. |
| Security Level | High - Difficult to replicate user behavioral patterns, reducing fraud risk. | Moderate to High - Depends on token management, can be vulnerable if token is lost or stolen. |
| User Experience | Seamless and continuous verification without interrupting users. | Requires user action to present or generate token during login. |
| Implementation Cost | Higher - Requires AI and machine learning systems to analyze behavior. | Lower - Uses established hardware and software token systems. |
| Use Cases | Fraud detection, continuous authentication in online banking and financial services. | Two-factor authentication (2FA), secure login in banking apps and web portals. |
| Risk of Compromise | Low - Harder to mimic behavioral traits. | Moderate - Token loss or theft can compromise security. |
| Compliance | Supports regulatory standards like PSD2 and AML through enhanced authentication. | Widely accepted for regulatory compliance in banking security. |
Which is better?
Behavioral biometrics analyzes unique user patterns such as typing rhythm and mouse movements to provide continuous, frictionless authentication, enhancing security against account takeovers and fraud in banking. Token-based authentication relies on physical or digital tokens generating time-sensitive codes, offering strong two-factor authentication but often causing user inconvenience and risk of loss or theft. Behavioral biometrics offers a more seamless, adaptive security solution tailored to dynamic fraud detection compared to the static nature of token-based methods.
Connection
Behavioral biometrics enhance token-based authentication by analyzing unique user patterns such as typing rhythm and mouse movements to verify identity continuously. Token-based authentication relies on temporary, dynamic credentials like OTPs or hardware tokens, while behavioral biometrics provide an additional layer of security by detecting anomalies in user behavior. Combining these technologies significantly reduces fraud and unauthorized access in banking systems by ensuring both possession and behavioral verification.
Key Terms
One-Time Password (OTP)
Token-based authentication using One-Time Passwords (OTP) relies on generating a unique, time-sensitive code sent to users via SMS, email, or authenticator apps, enhancing security through a secondary verification layer. Behavioral biometrics, on the other hand, authenticate users by analyzing patterns in their interactions, such as typing rhythm or navigation habits, providing continuous, passive verification without requiring explicit input. Explore the nuances of these authentication methods to strengthen your cybersecurity measures efficiently.
Keystroke Dynamics
Token-based authentication relies on physical devices like smart cards or USB tokens to verify user identity, whereas behavioral biometrics analyzes unique patterns such as keystroke dynamics--typing rhythm, speed, and pressure--to continuously authenticate users. Keystroke dynamics offers enhanced security by detecting anomalies in typing behavior that static token systems might miss, reducing fraud and unauthorized access risks. Explore how integrating keystroke dynamics can revolutionize authentication security in your systems.
Session Token
Session tokens serve as a critical component in token-based authentication by securely maintaining user sessions without repeatedly requesting credentials. Unlike behavioral biometrics, which analyze unique user patterns such as typing rhythm or mouse movements for identity verification, session tokens provide a straightforward, server-issued identifier that ensures seamless access control during active sessions. Explore more about how integrating session tokens can enhance security efficiency in modern authentication systems.
Source and External Links
What is Token Authentication and How Does It Work? - Token-based authentication generates encrypted tokens to verify user identities, enhancing security and user experience by reducing the need for repeated login credentials.
What Is Token-Based Authentication & How It Works - Token-based authentication is a passwordless method that uses tokens to validate user identity, simplifying the authentication process by doing away with traditional credential verification for every request.
What is Token Authentication and How Does It Work? - Token-based authentication uses digital tokens to validate user identities instead of traditional username and password combinations, often implemented using standards like JWT and OAuth2 for secure access to resources.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com