Open banking enables secure sharing of financial data between banks and third-party providers, fostering innovative financial services and personalized customer experiences. Payment gateways facilitate the authorization and processing of online transactions, ensuring seamless and secure payments between merchants and customers. Explore the differences and benefits of open banking and payment gateways to optimize your financial strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between open banking and payment gateways is crucial for leveraging secure, seamless financial transactions and enhancing customer experience. Open banking allows third-party providers to access banking data securely via APIs, fostering innovation and personalized financial services. Payment gateways facilitate the authorization and processing of online payments, acting as intermediaries between merchants and financial institutions. Distinguishing these concepts enables businesses to select optimal solutions for payment processing and data integration.
Comparison Table
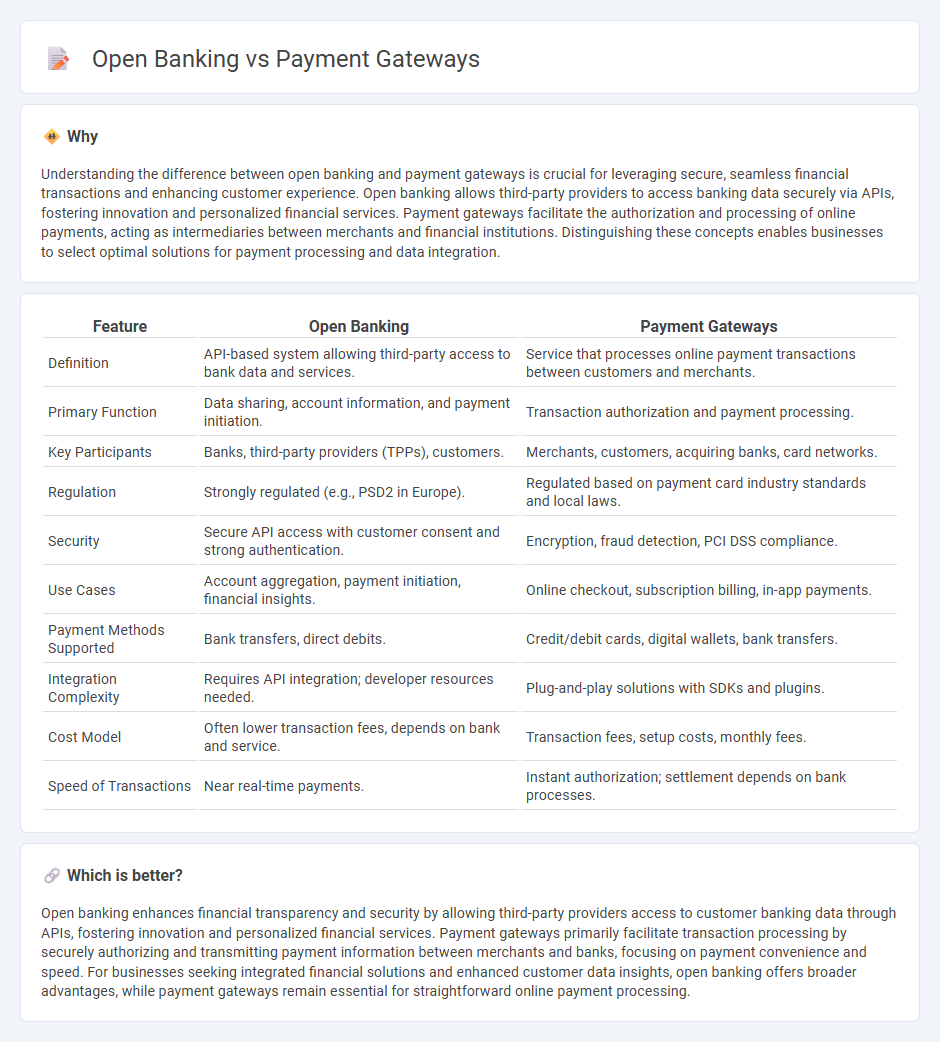
| Feature | Open Banking | Payment Gateways |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | API-based system allowing third-party access to bank data and services. | Service that processes online payment transactions between customers and merchants. |
| Primary Function | Data sharing, account information, and payment initiation. | Transaction authorization and payment processing. |
| Key Participants | Banks, third-party providers (TPPs), customers. | Merchants, customers, acquiring banks, card networks. |
| Regulation | Strongly regulated (e.g., PSD2 in Europe). | Regulated based on payment card industry standards and local laws. |
| Security | Secure API access with customer consent and strong authentication. | Encryption, fraud detection, PCI DSS compliance. |
| Use Cases | Account aggregation, payment initiation, financial insights. | Online checkout, subscription billing, in-app payments. |
| Payment Methods Supported | Bank transfers, direct debits. | Credit/debit cards, digital wallets, bank transfers. |
| Integration Complexity | Requires API integration; developer resources needed. | Plug-and-play solutions with SDKs and plugins. |
| Cost Model | Often lower transaction fees, depends on bank and service. | Transaction fees, setup costs, monthly fees. |
| Speed of Transactions | Near real-time payments. | Instant authorization; settlement depends on bank processes. |
Which is better?
Open banking enhances financial transparency and security by allowing third-party providers access to customer banking data through APIs, fostering innovation and personalized financial services. Payment gateways primarily facilitate transaction processing by securely authorizing and transmitting payment information between merchants and banks, focusing on payment convenience and speed. For businesses seeking integrated financial solutions and enhanced customer data insights, open banking offers broader advantages, while payment gateways remain essential for straightforward online payment processing.
Connection
Open banking enables secure data sharing between banks and third-party providers, facilitating seamless integration with payment gateways. Payment gateways leverage this access to authenticate transactions and provide real-time payment processing, enhancing customer experience. The collaboration supports innovative financial services, boosting efficiency and transparency in digital payments.
Key Terms
Transaction Processing
Payment gateways facilitate transaction processing by securely capturing and transmitting cardholder data to payment processors, enabling seamless credit and debit card payments. Open banking enhances transaction processing by providing direct access to consumers' bank accounts through APIs, promoting faster fund transfers, reduced transaction fees, and improved transparency. Explore how these technologies transform digital payments and optimize transaction efficiency.
API Integration
Payment gateways facilitate secure online transactions by connecting merchants directly with banks and card networks through standardized APIs, ensuring seamless payment processing. Open banking APIs provide access to consumer financial data and enable payment initiation, promoting enhanced transparency and innovative financial services beyond traditional gateways. Explore detailed insights on how API integration shapes the future of digital payments and fintech innovation.
Customer Authentication
Payment gateways rely heavily on traditional customer authentication methods such as passwords, OTPs, and 3D Secure protocols to validate transactions securely. Open banking enhances customer authentication by leveraging APIs to enable real-time access to bank-verified identity data and multi-factor authentication using biometric or device-based signals. Explore the evolving landscape of customer authentication in payment gateways and open banking to understand their impact on transaction security and user experience.
Source and External Links
Payment Gateways in 2025: Main Types + How They Work - Payment gateways are merchant services that process credit card payments for e-commerce and physical stores, with popular providers including PayPal, Square, Stripe, and Apple Pay, each offering different features and security protections for transactions.
Payment Gateways: What They Are And How To Choose One - A payment gateway serves as an intermediary technology in online transactions, securely transmitting payment data between customers, merchants, banks, and processors, often using encryption protocols like SSL and ensuring compliance with PCI DSS standards.
Payment gateway - Wikipedia - Payment gateways facilitate payment transactions by transferring information between payment portals (websites, mobile, POS) and banks or processors, enabling merchants to accept a variety of payment methods without directly handling the money flow.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com