Open banking transforms financial services by enabling third-party developers to build applications and services around a financial institution through APIs, fostering innovation and customer-centric solutions. Core banking refers to the back-end system that processes daily banking transactions and updates accounts in real-time, serving as the foundation for traditional banking operations. Explore how open banking and core banking systems together reshape the future of financial services.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between open banking and core banking is crucial for leveraging modern financial technologies and enhancing customer experience. Open banking enables third-party developers to build apps and services around the financial institution, promoting innovation through API integrations. Core banking refers to the traditional back-end systems that process daily banking transactions and maintain customer accounts securely. Awareness of both helps businesses and consumers navigate the evolving banking landscape effectively.
Comparison Table
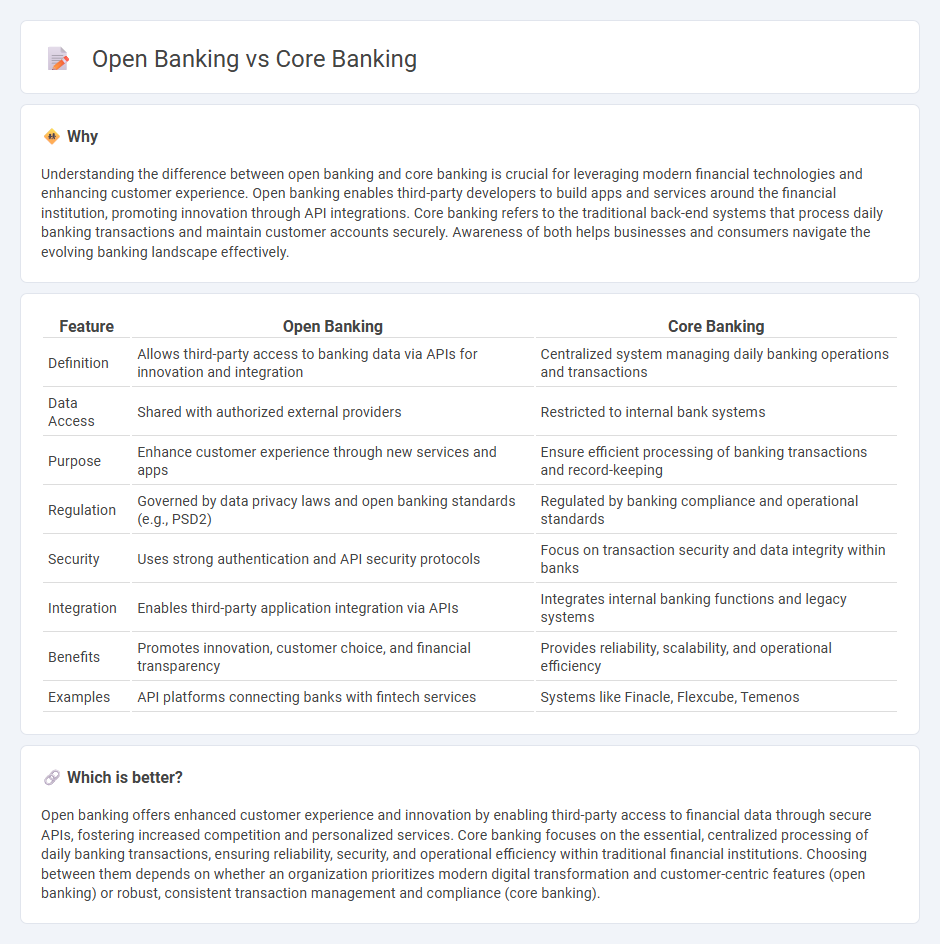
| Feature | Open Banking | Core Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allows third-party access to banking data via APIs for innovation and integration | Centralized system managing daily banking operations and transactions |
| Data Access | Shared with authorized external providers | Restricted to internal bank systems |
| Purpose | Enhance customer experience through new services and apps | Ensure efficient processing of banking transactions and record-keeping |
| Regulation | Governed by data privacy laws and open banking standards (e.g., PSD2) | Regulated by banking compliance and operational standards |
| Security | Uses strong authentication and API security protocols | Focus on transaction security and data integrity within banks |
| Integration | Enables third-party application integration via APIs | Integrates internal banking functions and legacy systems |
| Benefits | Promotes innovation, customer choice, and financial transparency | Provides reliability, scalability, and operational efficiency |
| Examples | API platforms connecting banks with fintech services | Systems like Finacle, Flexcube, Temenos |
Which is better?
Open banking offers enhanced customer experience and innovation by enabling third-party access to financial data through secure APIs, fostering increased competition and personalized services. Core banking focuses on the essential, centralized processing of daily banking transactions, ensuring reliability, security, and operational efficiency within traditional financial institutions. Choosing between them depends on whether an organization prioritizes modern digital transformation and customer-centric features (open banking) or robust, consistent transaction management and compliance (core banking).
Connection
Open banking leverages APIs to enable third-party financial service providers to access core banking systems securely and efficiently. Core banking systems store and manage customers' account information, transaction data, and banking operations, serving as the backbone for open banking services. By integrating with core banking platforms, open banking enhances interoperability, customer experience, and innovation in financial products.
Key Terms
Centralized Database (Core Banking)
Core banking systems rely on a centralized database that stores all customer account information, transaction history, and banking operations in a secure, unified platform. This centralized architecture enables banks to maintain consistent data integrity, streamline internal processes, and deliver seamless customer experiences across multiple branches. Explore the advantages and limitations of centralized databases within core banking to understand their role in modern financial services.
API (Open Banking)
Core banking systems centralize financial transactions and customer data, providing a unified platform for banks to manage accounts, deposits, loans, and payments securely. Open banking leverages APIs to enable third-party developers to build applications that access banking data and services, promoting innovation, personalized financial products, and enhanced customer experience. Explore how APIs in open banking transform traditional core banking models and drive financial technology advancements.
Third-party Integration (Open Banking)
Third-party integration in open banking enables external developers to access banking data and services via APIs, promoting innovation and personalized financial solutions beyond traditional core banking systems. Core banking focuses on centralized, internal processing of financial transactions and customer accounts, while open banking's API-driven approach facilitates secure data sharing with authorized third-party providers. Explore how third-party integration transforms customer experiences and drives financial technology advancements today.
Source and External Links
What is Core Banking? - Core banking is a centralized, online real-time system connecting multiple branches of a bank to allow seamless transactions like loans, deposits, and withdrawals from any branch or channel, supported by software managing database, application, and security systems either on-premises or cloud-based.
Core banking - Wikipedia - Core banking enables customers to access accounts and perform basic transactions from any networked branch, made possible by centralized data centers and real-time processing that replaced earlier batch systems, covering retail banking services such as payments, loans, and deposits.
What Is Core Banking: Definition, Features, Benefits - Core banking systems improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experience with online access, increase revenue through innovative products, and reduce risk via advanced data security, making them vital for modern banking solutions and competition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com