Green financing focuses on funding projects that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy and pollution reduction. Impact investing targets investments in companies or organizations that generate measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns. Explore how these finance strategies drive positive change and create opportunities for responsible growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between green financing and impact investing is crucial for making informed decisions in sustainable finance; green financing primarily funds projects that reduce environmental impact, such as renewable energy, while impact investing targets both measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns. This distinction helps banks and investors allocate capital effectively, comply with regulatory frameworks like the EU Taxonomy, and meet stakeholder expectations for transparency and accountability in sustainability practices. Awareness of these differences enhances risk management and aligns investment strategies with specific ESG goals to drive long-term value creation. Recognizing the nuances ensures that financial institutions support initiatives aligned with their mission and client values.
Comparison Table
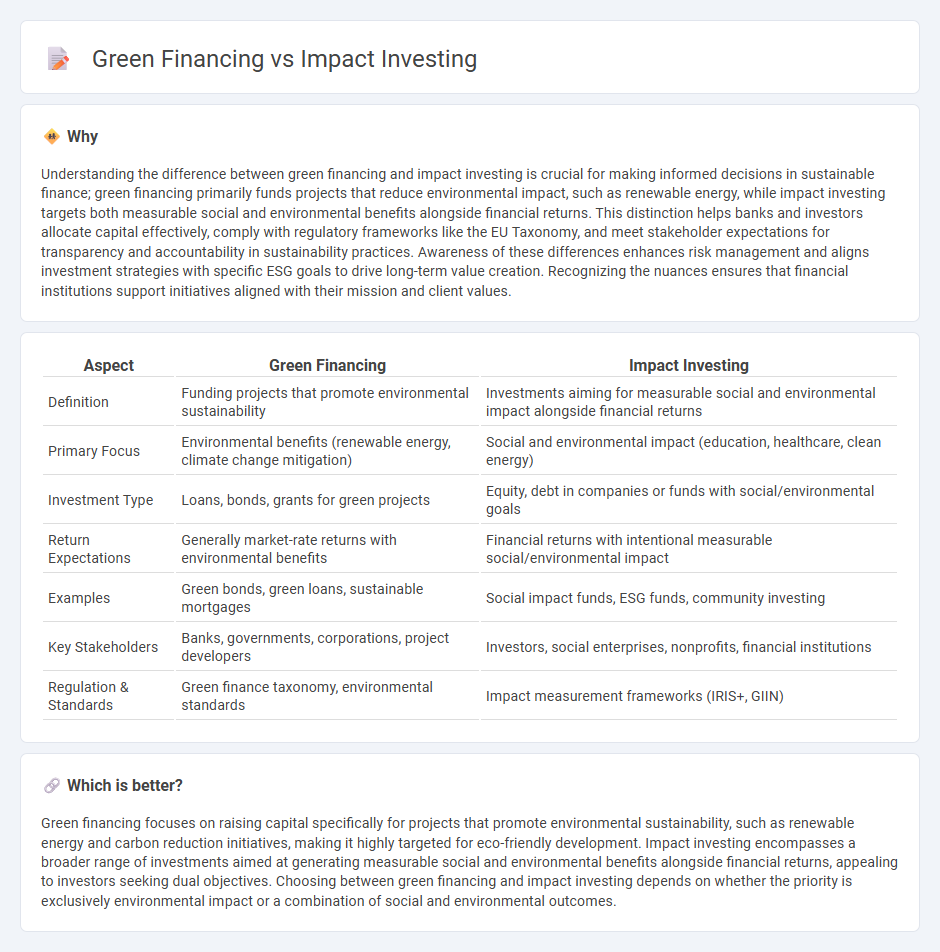
| Aspect | Green Financing | Impact Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funding projects that promote environmental sustainability | Investments aiming for measurable social and environmental impact alongside financial returns |
| Primary Focus | Environmental benefits (renewable energy, climate change mitigation) | Social and environmental impact (education, healthcare, clean energy) |
| Investment Type | Loans, bonds, grants for green projects | Equity, debt in companies or funds with social/environmental goals |
| Return Expectations | Generally market-rate returns with environmental benefits | Financial returns with intentional measurable social/environmental impact |
| Examples | Green bonds, green loans, sustainable mortgages | Social impact funds, ESG funds, community investing |
| Key Stakeholders | Banks, governments, corporations, project developers | Investors, social enterprises, nonprofits, financial institutions |
| Regulation & Standards | Green finance taxonomy, environmental standards | Impact measurement frameworks (IRIS+, GIIN) |
Which is better?
Green financing focuses on raising capital specifically for projects that promote environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy and carbon reduction initiatives, making it highly targeted for eco-friendly development. Impact investing encompasses a broader range of investments aimed at generating measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns, appealing to investors seeking dual objectives. Choosing between green financing and impact investing depends on whether the priority is exclusively environmental impact or a combination of social and environmental outcomes.
Connection
Green financing and impact investing both prioritize environmental sustainability by directing capital towards projects that reduce carbon emissions, conserve resources, and promote renewable energy. Banks and financial institutions increasingly integrate these strategies to support eco-friendly infrastructure, clean technology, and sustainable businesses, creating measurable environmental and social benefits. This connection enhances the transition to a low-carbon economy while generating returns aligned with ethical and sustainability goals.
Key Terms
Social Return
Impact investing prioritizes measurable social returns alongside financial gains, targeting projects that address social challenges such as poverty and education. Green financing concentrates on environmental benefits, funding initiatives aimed at reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainability. Explore how these approaches balance social impact and environmental goals to drive holistic development.
Environmental Criteria
Impact investing prioritizes measurable environmental benefits by channeling capital into projects that generate positive ecological outcomes, such as renewable energy and sustainable agriculture. Green financing provides funds specifically for initiatives that reduce carbon footprints and promote environmental sustainability, often through green bonds or loans targeting clean technology development. Explore further to understand how these approaches drive environmental change through financial mechanisms.
Sustainable Projects
Impact investing directs capital to projects that generate measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns, often targeting renewable energy, affordable housing, and sustainable agriculture. Green financing specifically supports initiatives aimed at reducing environmental impacts, such as clean energy infrastructure, energy efficiency improvements, and pollution control technologies. Explore how these approaches uniquely contribute to sustainable development and which aligns best with your investment goals.
Source and External Links
What you need to know about impact investing - The GIIN - Impact investing involves intentionally investing to generate positive, measurable social or environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, spanning various sectors like energy, healthcare, and housing, and using evidence and data to drive investment design and management.
What is Impact Investing? | Fidelity Charitable - Impact investing is a strategy of making investments that align with personal values by achieving social or environmental benefits while generating financial returns, and is growing particularly among Millennials and women investors.
Impact Investing | United Nations Development Programme - Impact investing is the deployment of capital with the goal of measurable social or environmental benefits plus financial returns, serving as a tool to boost private sector contributions to sustainable development and backed by platforms like GIFIIP to connect investors with impact enterprises.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com