Sustainable investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to generate long-term value while supporting responsible business practices. Green bonds are fixed-income securities specifically issued to finance projects that have positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy or clean transportation. Explore how sustainable investing and green bonds are reshaping the banking industry's approach to responsible finance.
Why it is important
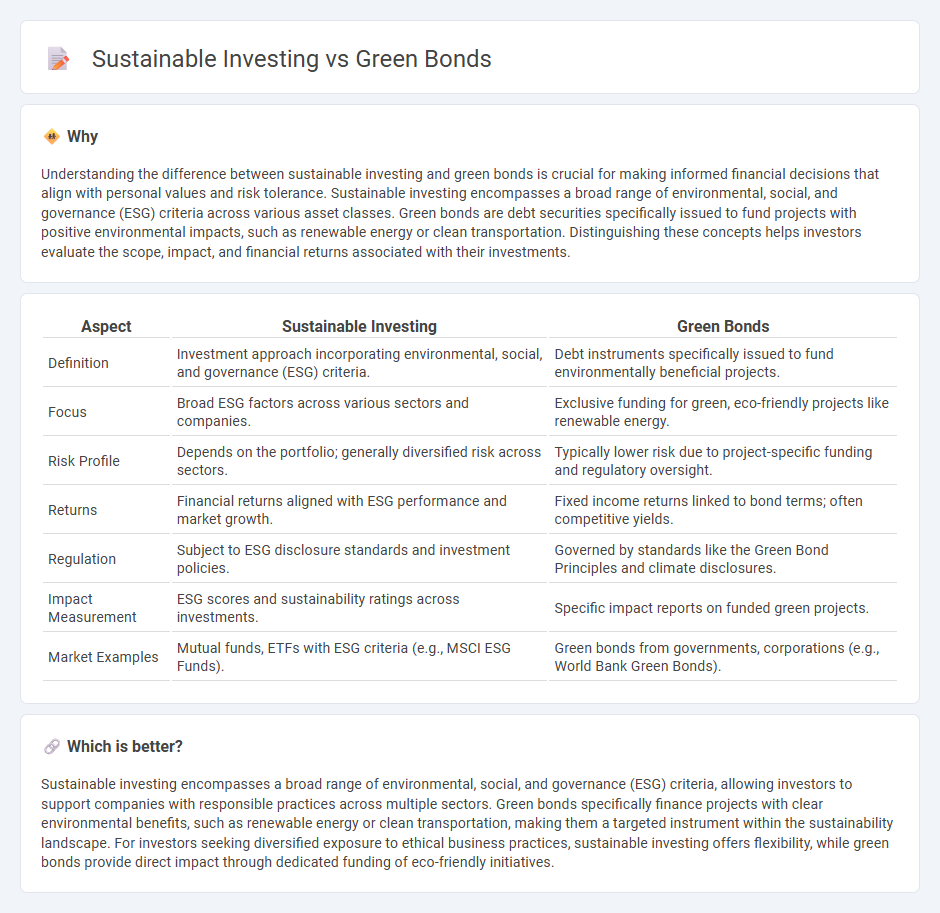
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and green bonds is crucial for making informed financial decisions that align with personal values and risk tolerance. Sustainable investing encompasses a broad range of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria across various asset classes. Green bonds are debt securities specifically issued to fund projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy or clean transportation. Distinguishing these concepts helps investors evaluate the scope, impact, and financial returns associated with their investments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Green Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment approach incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. | Debt instruments specifically issued to fund environmentally beneficial projects. |
| Focus | Broad ESG factors across various sectors and companies. | Exclusive funding for green, eco-friendly projects like renewable energy. |
| Risk Profile | Depends on the portfolio; generally diversified risk across sectors. | Typically lower risk due to project-specific funding and regulatory oversight. |
| Returns | Financial returns aligned with ESG performance and market growth. | Fixed income returns linked to bond terms; often competitive yields. |
| Regulation | Subject to ESG disclosure standards and investment policies. | Governed by standards like the Green Bond Principles and climate disclosures. |
| Impact Measurement | ESG scores and sustainability ratings across investments. | Specific impact reports on funded green projects. |
| Market Examples | Mutual funds, ETFs with ESG criteria (e.g., MSCI ESG Funds). | Green bonds from governments, corporations (e.g., World Bank Green Bonds). |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing encompasses a broad range of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, allowing investors to support companies with responsible practices across multiple sectors. Green bonds specifically finance projects with clear environmental benefits, such as renewable energy or clean transportation, making them a targeted instrument within the sustainability landscape. For investors seeking diversified exposure to ethical business practices, sustainable investing offers flexibility, while green bonds provide direct impact through dedicated funding of eco-friendly initiatives.
Connection
Sustainable investing directs capital toward environmentally responsible companies, aligning financial goals with ecological impact, while green bonds finance projects with measurable environmental benefits such as renewable energy and clean transportation. These financial instruments attract investors seeking returns linked to sustainability metrics, fostering a market that supports climate goals and reduces carbon footprints. Banks play a crucial role by underwriting green bonds and facilitating sustainable investment portfolios, amplifying the flow of capital into the green economy.
Key Terms
Environmental Impact Assessment
Green bonds specifically fund projects with measurable environmental benefits, such as renewable energy or pollution reduction, ensuring targeted impact through Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA). Sustainable investing encompasses a broader strategy, integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria across diverse asset classes, but may not always require EIAs for each investment. Explore detailed comparisons and methodologies to understand how green bonds and sustainable investing contribute to ecological sustainability.
Use of Proceeds
Green bonds allocate funds exclusively to environmentally beneficial projects such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution prevention, ensuring transparent tracking of Use of Proceeds. Sustainable investing encompasses a broader approach, integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria across investment portfolios without limiting capital deployment strictly to green initiatives. Explore the distinctions in fund allocation and impact measurement to better understand how each strategy promotes sustainability.
ESG Criteria
Green bonds specifically finance projects with clear environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and pollution reduction, and are typically verified through rigorous ESG criteria to ensure impact. Sustainable investing encompasses a broader strategy that integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors across various asset classes to promote ethical and long-term value creation. Explore how aligning your portfolio with ESG criteria through both green bonds and sustainable investing can drive impactful and responsible investments.
Source and External Links
Green bond - Wikipedia - A green bond is a fixed-income financial instrument used specifically to fund projects with positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, pollution control, and climate change adaptation, distinguishing it from regular bonds by the exclusive use of proceeds for environmental projects.
What are Green Bonds and what projects do they finance? - Iberdrola - Green bonds are debt instruments issued by public or private entities dedicated to financing sustainable and socially responsible environmental projects like renewable energy and clean transportation, with the European Investment Bank pioneering their issuance in 2007.
Green Bond Principles (GBP) - ICMA - The Green Bond Principles guide issuers in raising capital for environmentally sustainable projects that support a net-zero emissions economy, emphasizing transparency, integrity, and disclosure in the use of proceeds and impact reporting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com