Neo banking offers fully digital banking services without traditional brick-and-mortar branches, focusing on user-friendly mobile apps and seamless online experiences. Challenger banks, on the other hand, are licensed financial institutions that directly compete with traditional banks by providing innovative products, often targeting niche markets. Explore the distinct features and advantages of neo banks versus challenger banks to understand how each is transforming the financial industry.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between neo banking and challenger banks is crucial for selecting the right banking solution that aligns with your needs and preferences. Neo banks operate entirely online without physical branches, offering streamlined digital services and lower fees. Challenger banks may combine online platforms with some branch presence and often hold full banking licenses, providing a broader range of financial services. This knowledge helps consumers make informed decisions about security, service scope, and regulatory protections.
Comparison Table
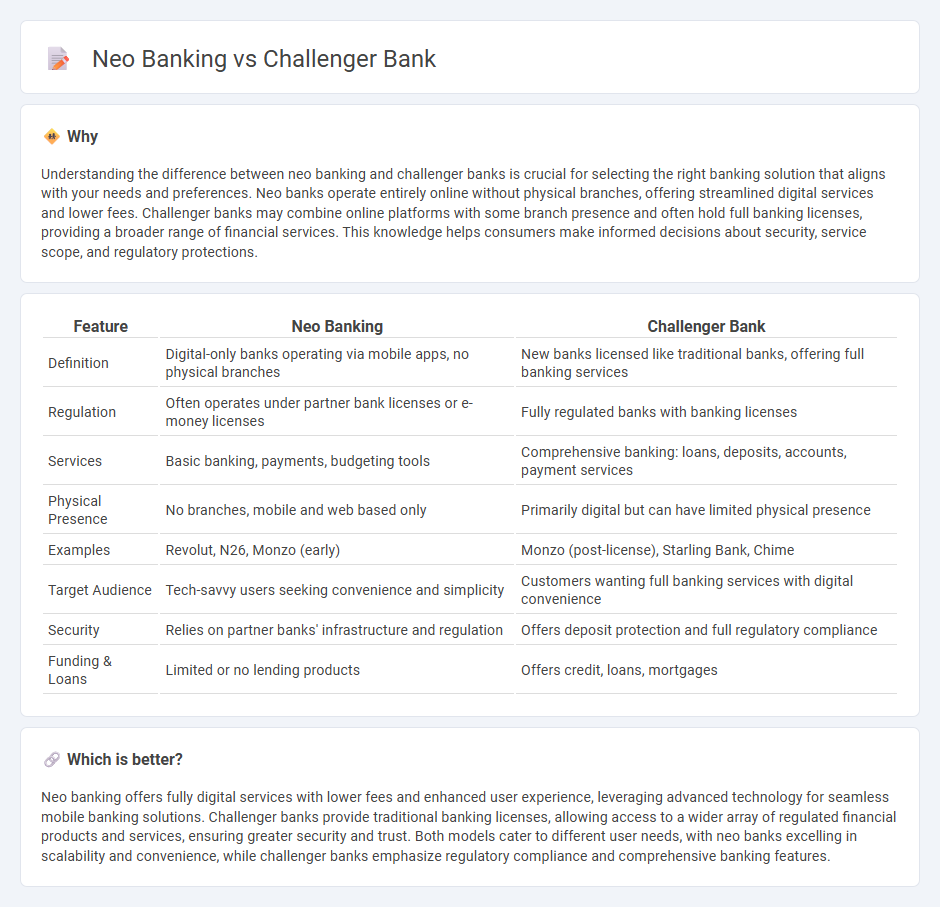
| Feature | Neo Banking | Challenger Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital-only banks operating via mobile apps, no physical branches | New banks licensed like traditional banks, offering full banking services |
| Regulation | Often operates under partner bank licenses or e-money licenses | Fully regulated banks with banking licenses |
| Services | Basic banking, payments, budgeting tools | Comprehensive banking: loans, deposits, accounts, payment services |
| Physical Presence | No branches, mobile and web based only | Primarily digital but can have limited physical presence |
| Examples | Revolut, N26, Monzo (early) | Monzo (post-license), Starling Bank, Chime |
| Target Audience | Tech-savvy users seeking convenience and simplicity | Customers wanting full banking services with digital convenience |
| Security | Relies on partner banks' infrastructure and regulation | Offers deposit protection and full regulatory compliance |
| Funding & Loans | Limited or no lending products | Offers credit, loans, mortgages |
Which is better?
Neo banking offers fully digital services with lower fees and enhanced user experience, leveraging advanced technology for seamless mobile banking solutions. Challenger banks provide traditional banking licenses, allowing access to a wider array of regulated financial products and services, ensuring greater security and trust. Both models cater to different user needs, with neo banks excelling in scalability and convenience, while challenger banks emphasize regulatory compliance and comprehensive banking features.
Connection
Neo banking and challenger banks both represent innovative financial institutions that leverage digital technology to offer banking services, often without traditional brick-and-mortar branches. Neo banks primarily operate as digital-only platforms providing streamlined, user-friendly experiences through mobile apps, whereas challenger banks challenge established banks by offering competitive rates and modern features, sometimes holding full banking licenses. Both aim to disrupt traditional banking by enhancing accessibility, reducing fees, and improving customer service through technology-driven solutions.
Key Terms
Digital-only
Challenger banks are fully licensed financial institutions offering digital-only services with a focus on traditional banking features enhanced by technology. Neo banks operate exclusively online without a banking license, partnering with licensed banks to provide streamlined, user-friendly digital financial solutions. Explore the key differences, benefits, and risks to understand which digital-only banking model suits your needs.
Banking license
Challenger banks operate with full banking licenses, allowing them to offer a wide range of regulated services such as deposits, loans, and payment processing under strict regulatory oversight. Neo banks often function without traditional banking licenses, relying on partnerships with licensed banks to provide financial services, which can limit their product offerings and regulatory scope. Explore the distinctions in licensing and regulatory requirements to understand their impact on service capabilities.
Regulatory framework
Challenger banks operate under full banking licenses regulated by authorities such as the FCA in the UK or the OCC in the US, ensuring compliance with stringent capital and consumer protection requirements. Neo banks often function without full banking licenses, partnering with traditional banks to offer services, which subjects them to a different regulatory scope focused on fintech regulations and data security. Explore further to understand how these regulatory differences impact security, customer trust, and operational flexibility.
Source and External Links
Challenger Banks Explained: Trends and Opportunities - Ulam Labs - Challenger banks are digital-first financial institutions that compete with traditional banks by offering no physical branches, lower fees, faster services, and innovative digital features, largely driven by regulatory changes like Open Banking in the UK.
Challenger Banks: What You Need to Know | Jenius Bank - Challenger banks prioritize modern, digital banking experiences with customer-centric services and emerged after the 2008 financial crisis as agile alternatives to traditional banking models.
Challenger Bank Definition - A definition by FinTech Weekly - Challenger banks, also called neobanks, are typically smaller, tech-focused retail banks that provide modern financial services designed to challenge the dominance of long-established traditional banks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com