Alternative credit data offers financial institutions unique insights into creditworthiness through non-traditional sources such as utility payments, rental history, and employment records, enhancing risk assessment beyond standard credit reports. Social media data leverages behavioral patterns, online interactions, and network information to predict financial reliability and personalize banking services, though it raises privacy concerns. Explore how integrating these data types transforms credit evaluation and customer engagement in modern banking.
Why it is important
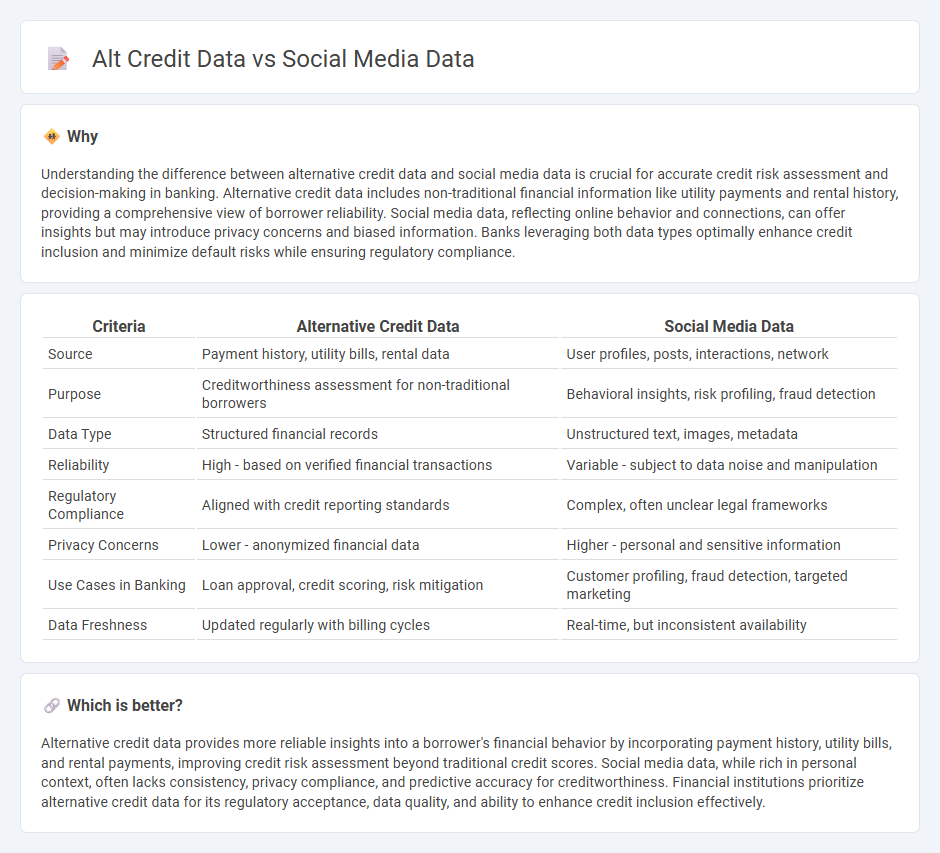
Understanding the difference between alternative credit data and social media data is crucial for accurate credit risk assessment and decision-making in banking. Alternative credit data includes non-traditional financial information like utility payments and rental history, providing a comprehensive view of borrower reliability. Social media data, reflecting online behavior and connections, can offer insights but may introduce privacy concerns and biased information. Banks leveraging both data types optimally enhance credit inclusion and minimize default risks while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Alternative Credit Data | Social Media Data |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Payment history, utility bills, rental data | User profiles, posts, interactions, network |
| Purpose | Creditworthiness assessment for non-traditional borrowers | Behavioral insights, risk profiling, fraud detection |
| Data Type | Structured financial records | Unstructured text, images, metadata |
| Reliability | High - based on verified financial transactions | Variable - subject to data noise and manipulation |
| Regulatory Compliance | Aligned with credit reporting standards | Complex, often unclear legal frameworks |
| Privacy Concerns | Lower - anonymized financial data | Higher - personal and sensitive information |
| Use Cases in Banking | Loan approval, credit scoring, risk mitigation | Customer profiling, fraud detection, targeted marketing |
| Data Freshness | Updated regularly with billing cycles | Real-time, but inconsistent availability |
Which is better?
Alternative credit data provides more reliable insights into a borrower's financial behavior by incorporating payment history, utility bills, and rental payments, improving credit risk assessment beyond traditional credit scores. Social media data, while rich in personal context, often lacks consistency, privacy compliance, and predictive accuracy for creditworthiness. Financial institutions prioritize alternative credit data for its regulatory acceptance, data quality, and ability to enhance credit inclusion effectively.
Connection
Alternative credit data and social media data intersect by providing non-traditional insights into a person's creditworthiness beyond conventional credit reports. Banks leverage social media data, such as user behavior, network relationships, and online activities, to enhance risk assessment models and predict repayment reliability. Integrating these datasets helps financial institutions improve credit scoring accuracy and extend lending to underserved or thin-file customers.
Key Terms
Digital Footprint
Social media data captures user interactions, preferences, and online behavior, revealing a rich digital footprint valuable for credit risk assessment and marketing strategies. Alternative credit data, including utility payments and mobile phone usage, complements traditional credit reports by providing insights into financial habits often missed by conventional scoring models. Explore how integrating these diverse datasets enhances predictive accuracy and broadens access to credit opportunities.
Alternative Credit Scoring
Alternative credit scoring leverages non-traditional data sources such as social media activity and alternative credit data to enhance credit risk assessment for underserved populations. Social media data provides insights into behavioral patterns and social connections, while alternative credit data includes utility payments, rental history, and other non-credit financial behaviors that traditional credit scoring often overlooks. Discover how integrating these diverse data points refines credit scoring accuracy and expands financial inclusion.
Risk Assessment
Social media data provides real-time insights into consumer behavior and sentiment, enabling dynamic risk assessment models that capture non-traditional indicators of creditworthiness. Alternative credit data, such as utility payments and rental history, enhances risk evaluation by incorporating financial behaviors often missed by standard credit scores. Explore how integrating these data sources can revolutionize risk assessment strategies.
Source and External Links
The What, Why, and How of Social Media Data - Social media data refers to raw insights and information collected from users' social media activity, including metrics like engagement rate, reach, video views, audience demographics, and sentiment analysis, which help businesses measure and refine their social media strategies.
What Is Social Media Data? (Plus How To Use It) - Social media data is user information that reveals behaviors on social networks, enabling businesses to segment audiences, nurture leads, tailor sales outreach, and guide content creation based on how users interact with posts and profiles.
Social Media Statistics Details - There are 4.8 billion social media users worldwide, representing 59.9% of the global population and 92.7% of all internet users, highlighting the massive scale and reach of social media platforms as data sources.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com