Sustainable banking focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial services to promote responsible investment and long-term economic development. Universal banking offers a wide range of financial services, including commercial and investment banking, under one roof to maximize efficiency and customer convenience. Explore the key differences and benefits of sustainable banking versus universal banking to understand their impact on the financial industry.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainable banking and universal banking is crucial for aligning financial decisions with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals versus broad financial services. Sustainable banking prioritizes ethical investments, green financing, and corporate responsibility to promote long-term ecological and social impact. Universal banking offers a wide range of financial services including retail, investment, and commercial banking under one roof, focusing on profitability and market coverage. Knowing these distinctions helps investors and consumers choose banking options that match their values and financial needs.
Comparison Table
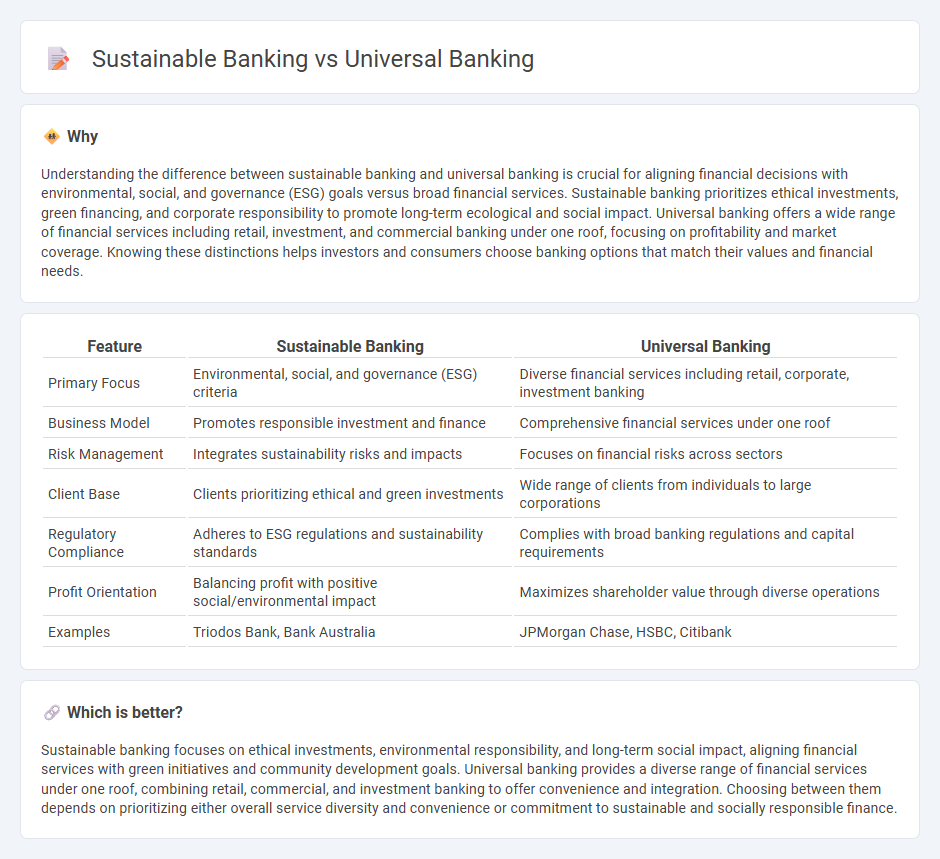
| Feature | Sustainable Banking | Universal Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria | Diverse financial services including retail, corporate, investment banking |
| Business Model | Promotes responsible investment and finance | Comprehensive financial services under one roof |
| Risk Management | Integrates sustainability risks and impacts | Focuses on financial risks across sectors |
| Client Base | Clients prioritizing ethical and green investments | Wide range of clients from individuals to large corporations |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adheres to ESG regulations and sustainability standards | Complies with broad banking regulations and capital requirements |
| Profit Orientation | Balancing profit with positive social/environmental impact | Maximizes shareholder value through diverse operations |
| Examples | Triodos Bank, Bank Australia | JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, Citibank |
Which is better?
Sustainable banking focuses on ethical investments, environmental responsibility, and long-term social impact, aligning financial services with green initiatives and community development goals. Universal banking provides a diverse range of financial services under one roof, combining retail, commercial, and investment banking to offer convenience and integration. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing either overall service diversity and convenience or commitment to sustainable and socially responsible finance.
Connection
Sustainable banking integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial services, promoting responsible investments aligned with long-term ecological stability. Universal banking combines commercial and investment banking services, offering a diverse portfolio that can support sustainable finance initiatives through comprehensive capital allocation. The synergy between sustainable banking and universal banking enables holistic risk management and fosters innovation in green financial products.
Key Terms
Diversification
Universal banking integrates a wide range of financial services, including commercial, investment, and insurance activities, to maximize diversification and risk management, whereas sustainable banking emphasizes investments in environmentally and socially responsible projects to achieve long-term impact alongside financial returns. The diversification in universal banking helps mitigate sector-specific risks through a broad asset portfolio, while sustainable banking diversifies by balancing financial goals with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. Explore further to understand how these banking models address diversification in evolving financial landscapes.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
Universal banking integrates diverse financial services including investment, retail, and corporate banking, but often faces criticism for lacking targeted Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) commitments. Sustainable banking prioritizes ESG criteria by channeling investments into eco-friendly projects, promoting social equity, and implementing transparent governance frameworks to mitigate risks and enhance long-term value. Explore how sustainable banking drives ESG transformation in the financial sector for deeper insights.
Financial Inclusion
Universal banking integrates diverse financial services, offering extensive credit, deposit, and investment products to a broad customer base, thereby driving economic growth through comprehensive financial access. Sustainable banking prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, actively supporting underserved communities and promoting financial inclusion through responsible lending and social impact investments. Explore how these banking models foster inclusive economies and empower marginalized populations with equitable financial opportunities.
Source and External Links
Universal bank - Wikipedia - A universal bank is a bank that combines commercial banking, investment banking, and other financial services like insurance under one institution, allowing it to offer a full range of services and foster long-term customer relationships.
What is Universal Banking? | Metropolitan Capital Bank & Trust - Universal banking integrates a wide variety of financial services on a single platform to create efficiencies and synergies, typically serving larger organizations but increasingly focused also on small to medium-sized businesses.
Universal banking - EBF - Universal banks provide comprehensive services across retail, commercial, and investment banking, and maintaining the model is argued to support competitiveness and economic financing advantages in Europe.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com