Negative interest rates, implemented by central banks to stimulate economic activity, push borrowing costs below zero, compelling lenders to pay borrowers. Floating interest rates fluctuate based on market conditions and central bank policies, affecting loan repayments and financial planning. Explore the differences between these interest rate mechanisms to understand their impact on banking and personal finance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between negative interest rates and floating interest rates is crucial for effective financial planning and risk management in banking. Negative interest rates imply that depositors pay to keep money in the bank, encouraging borrowing and spending, while floating interest rates fluctuate with market conditions, affecting loan repayments and investment returns. This knowledge helps investors and borrowers optimize decisions based on economic trends and interest rate forecasts. Banks rely on this distinction to set competitive rates and maintain profitability in dynamic financial environments.
Comparison Table
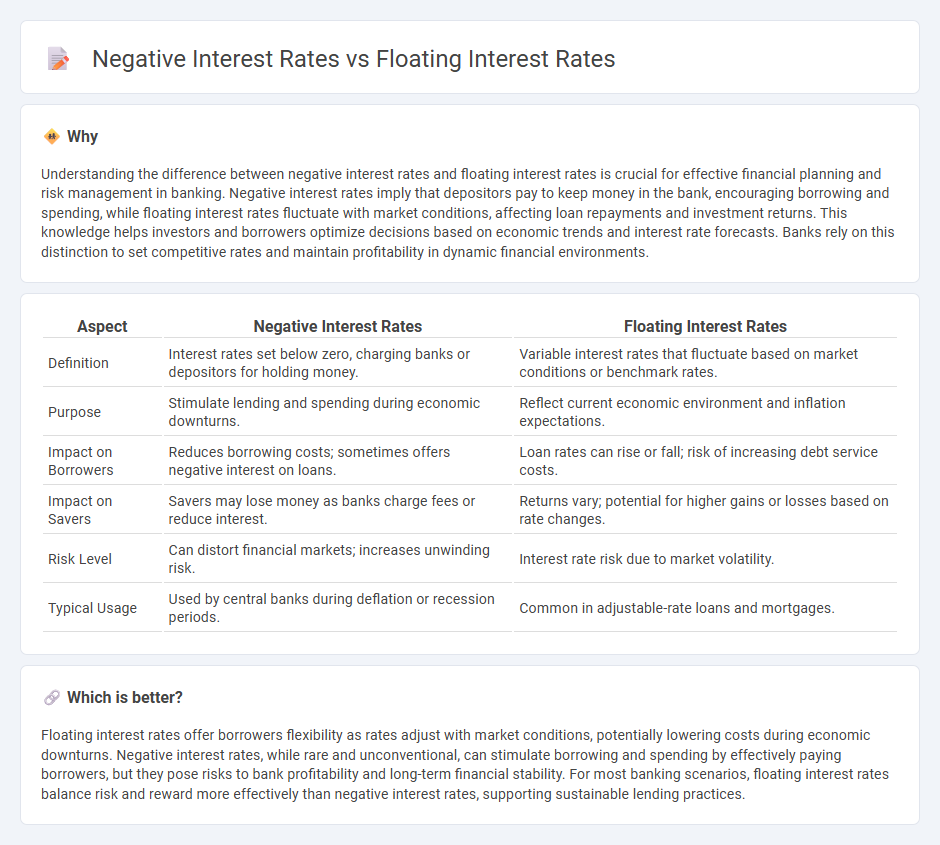
| Aspect | Negative Interest Rates | Floating Interest Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interest rates set below zero, charging banks or depositors for holding money. | Variable interest rates that fluctuate based on market conditions or benchmark rates. |
| Purpose | Stimulate lending and spending during economic downturns. | Reflect current economic environment and inflation expectations. |
| Impact on Borrowers | Reduces borrowing costs; sometimes offers negative interest on loans. | Loan rates can rise or fall; risk of increasing debt service costs. |
| Impact on Savers | Savers may lose money as banks charge fees or reduce interest. | Returns vary; potential for higher gains or losses based on rate changes. |
| Risk Level | Can distort financial markets; increases unwinding risk. | Interest rate risk due to market volatility. |
| Typical Usage | Used by central banks during deflation or recession periods. | Common in adjustable-rate loans and mortgages. |
Which is better?
Floating interest rates offer borrowers flexibility as rates adjust with market conditions, potentially lowering costs during economic downturns. Negative interest rates, while rare and unconventional, can stimulate borrowing and spending by effectively paying borrowers, but they pose risks to bank profitability and long-term financial stability. For most banking scenarios, floating interest rates balance risk and reward more effectively than negative interest rates, supporting sustainable lending practices.
Connection
Negative interest rates influence floating interest rates by pushing benchmark rates below zero, which directly impacts variable-rate loans and deposits linked to these benchmarks. Floating interest rates adjust periodically based on central bank policies, and when negative rates are implemented, they cause the floating rates to shift downward, affecting borrowing costs and savings returns. This interconnected dynamic shapes monetary policy transmission and financial market behavior in economies experiencing unconventional interest rate environments.
Key Terms
LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate)
Floating interest rates, often tied to benchmarks like LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate), fluctuate based on market conditions and reflect the cost of borrowing over time. Negative interest rates, a rare monetary policy tool, push rates below zero, effectively charging lenders to hold money, impacting traditional floating rate mechanisms like LIBOR. Explore how these interest rate frameworks influence global financial markets and lending practices for deeper insights.
ECB Deposit Rate
The European Central Bank (ECB) Deposit Rate is a key benchmark influencing both floating interest rates and negative interest rates within the Eurozone's monetary policy framework. Floating interest rates fluctuate based on market conditions and central bank policies, while negative interest rates, such as those applied by the ECB, push borrowing costs below zero to stimulate economic activity. Explore how these interest rate mechanisms impact lending, borrowing, and investment decisions across European financial markets.
Interest Rate Swap
Interest Rate Swaps (IRS) are financial derivatives used to exchange fixed interest rate payments for floating interest rate payments, typically linked to benchmark rates like LIBOR or SOFR, allowing parties to hedge against interest rate volatility. Negative interest rates, though rare in swaps, impact the valuation and payment flows by causing unusual cash flow scenarios where lenders pay borrowers, which complicates traditional IRS strategies. Explore detailed mechanics and risk management techniques to master the implications of floating and negative rates in interest rate swaps.
Source and External Links
Floating interest rate - A floating interest rate, also known as a variable or adjustable rate, is a debt instrument's interest rate that changes over time based on a reference or benchmark rate like SOFR, often resulting in lower initial costs but with the risk of rising rates for the borrower.
Floating Interest Rate - Definition, Use, Pros, Cons - Floating interest rates vary over the debt duration according to external benchmarks such as the prime rate, offering generally lower costs but exposing borrowers to interest rate risk if rates increase.
Floating Interest Rate | Formula + Calculator - A floating interest rate fluctuates with market benchmark rates, benefiting borrowers when rates fall but creating higher costs and risks when rates rise, often including protective features like rate floors for lenders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com