Banking as a Service (BaaS) enables third-party providers to access banking infrastructure via APIs, offering financial products without holding a banking license. Platform banking integrates multiple financial services into a unified ecosystem, enhancing customer experience through seamless digital interactions. Explore further to understand how these models revolutionize the financial industry.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Banking as a Service (BaaS) and platform banking is crucial for financial institutions aiming to innovate efficiently and comply with regulatory standards. BaaS allows third parties to offer banking services through APIs without full banking licenses, accelerating product deployment and market reach. Platform banking provides an integrated framework enabling banks to offer a suite of digital services internally and externally, enhancing customer experience and operational agility. Clear differentiation helps in selecting appropriate technology stacks, partnership models, and compliance strategies for business growth.
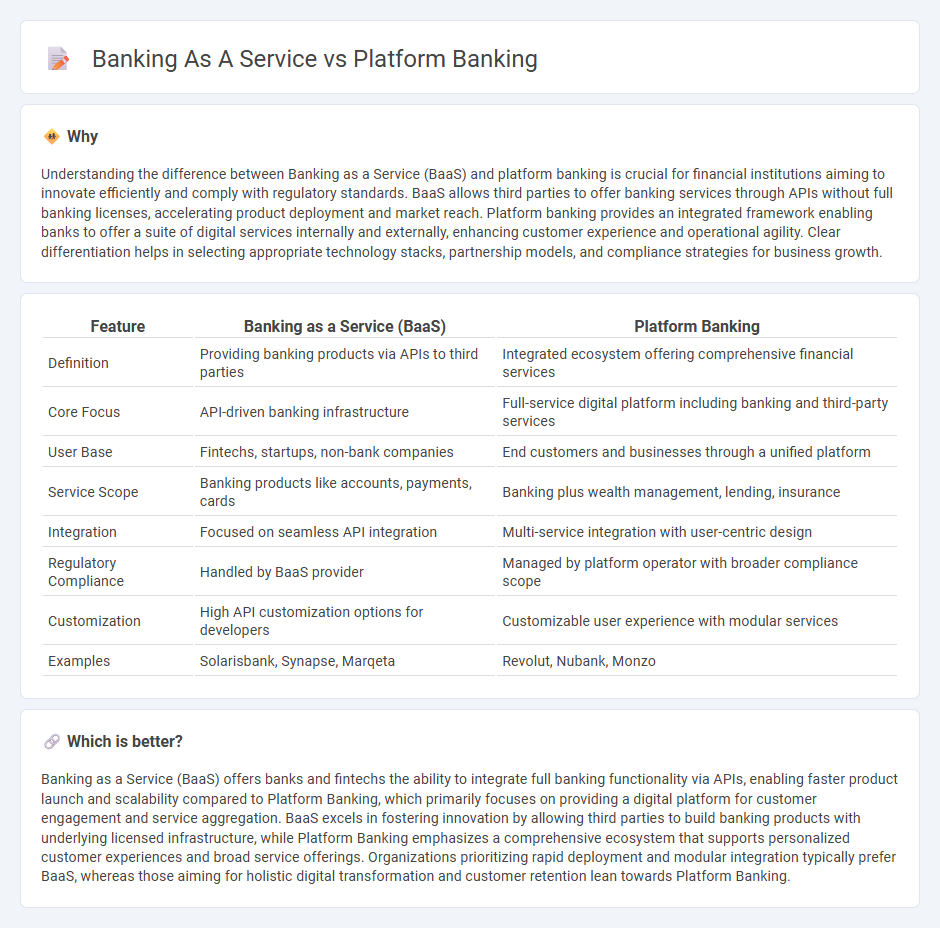
Comparison Table
| Feature | Banking as a Service (BaaS) | Platform Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing banking products via APIs to third parties | Integrated ecosystem offering comprehensive financial services |
| Core Focus | API-driven banking infrastructure | Full-service digital platform including banking and third-party services |
| User Base | Fintechs, startups, non-bank companies | End customers and businesses through a unified platform |
| Service Scope | Banking products like accounts, payments, cards | Banking plus wealth management, lending, insurance |
| Integration | Focused on seamless API integration | Multi-service integration with user-centric design |
| Regulatory Compliance | Handled by BaaS provider | Managed by platform operator with broader compliance scope |
| Customization | High API customization options for developers | Customizable user experience with modular services |
| Examples | Solarisbank, Synapse, Marqeta | Revolut, Nubank, Monzo |
Which is better?
Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers banks and fintechs the ability to integrate full banking functionality via APIs, enabling faster product launch and scalability compared to Platform Banking, which primarily focuses on providing a digital platform for customer engagement and service aggregation. BaaS excels in fostering innovation by allowing third parties to build banking products with underlying licensed infrastructure, while Platform Banking emphasizes a comprehensive ecosystem that supports personalized customer experiences and broad service offerings. Organizations prioritizing rapid deployment and modular integration typically prefer BaaS, whereas those aiming for holistic digital transformation and customer retention lean towards Platform Banking.
Connection
Banking as a Service (BaaS) enables third-party providers to access banking infrastructure through APIs, seamlessly integrating financial services into various platforms. Platform banking centralizes multiple financial products within a single digital ecosystem, enhancing customer experience by offering diverse services under one interface. The connection lies in BaaS providing the technical foundation that powers platform banking's unified and scalable service delivery.
Key Terms
API Integration
Platform banking leverages APIs to integrate diverse financial services seamlessly, enabling banks to offer personalized, modular products directly through digital platforms. Banking as a Service (BaaS) provides third-party companies with standardized API access to core banking functions, accelerating product development and market entry without building full banking infrastructure. Explore the distinctions in API integration strategies between platform banking and BaaS to optimize digital financial service offerings.
White-label Solutions
Platform banking offers customizable digital infrastructure allowing financial institutions to integrate third-party services seamlessly, enhancing customer experience without the need for full-scale development. Banking as a Service (BaaS) provides white-label solutions enabling non-bank companies to offer branded financial products through API-based access to licensed banking capabilities. Explore comprehensive comparisons and use cases to understand how white-label solutions drive innovation in financial services.
Third-party Providers
Platform banking enables Third-Party Providers (TPPs) to access banking services through open APIs, facilitating seamless integration and enhancing customer experience via customizable financial products. Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers an end-to-end infrastructure that allows TPPs to build and scale embedded banking solutions without managing regulatory compliance or backend operations. Explore the key differences and benefits of platform banking versus BaaS for Third-Party Providers.
Source and External Links
Platform banking...and how it enhances financial services - Platform banking refers to banks integrating fintech services into their offerings via APIs, allowing customers to access a broader or more specialized range of financial products through the bank's digital channels.
Platform Banking: Revolutionizing Financial Services in Digital Age - Platform banking is a digital marketplace, often app-based, where banks collaborate with fintechs and partners to deliver a wide variety of integrated financial and non-financial services through a single interface, focusing on customer experience and personalization.
What Is a Banking Platform and Why Is It the Key to SME Growth in ... - A banking platform is a digital ecosystem connecting banks, fintechs, and customers via unified technology, enabling seamless, personalized financial services--much like an app store where users select the services that best fit their needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com