Income streaming in banking refers to the continuous revenue generated from interest on loans, fees on account management, and recurring service charges, providing financial stability and predictable cash flow. Commission income, however, arises from one-time transactions such as loan origination fees, investment product sales, and insurance brokerage, often fluctuating with market activity. Discover how these distinct revenue models impact bank profitability and customer engagement.
Why it is important
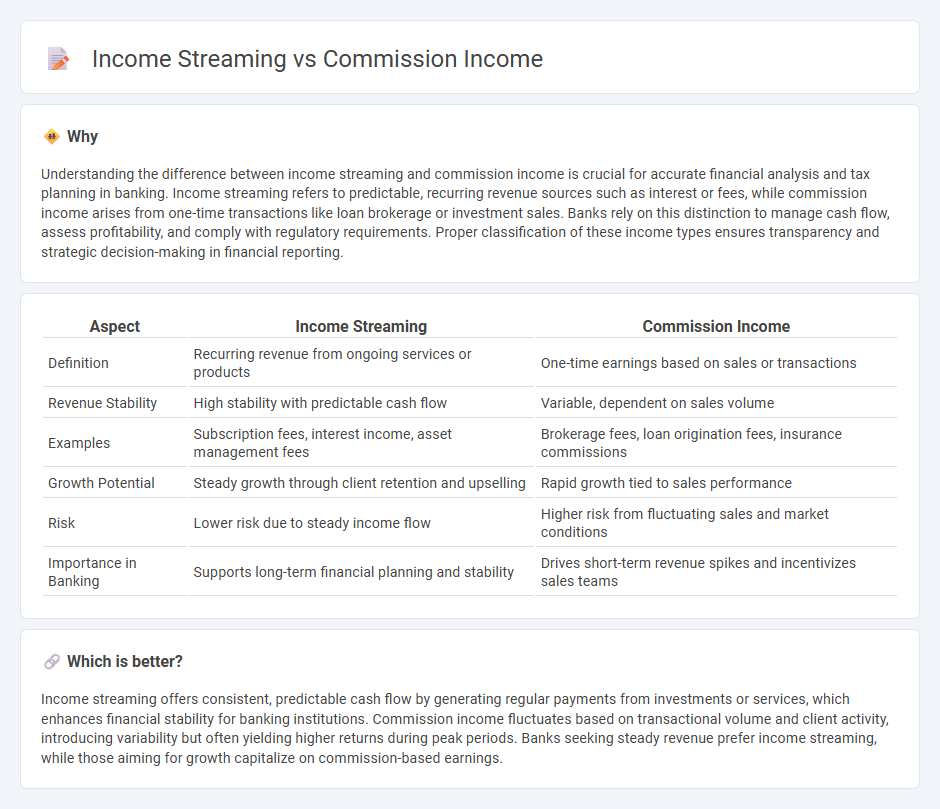
Understanding the difference between income streaming and commission income is crucial for accurate financial analysis and tax planning in banking. Income streaming refers to predictable, recurring revenue sources such as interest or fees, while commission income arises from one-time transactions like loan brokerage or investment sales. Banks rely on this distinction to manage cash flow, assess profitability, and comply with regulatory requirements. Proper classification of these income types ensures transparency and strategic decision-making in financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Income Streaming | Commission Income |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recurring revenue from ongoing services or products | One-time earnings based on sales or transactions |
| Revenue Stability | High stability with predictable cash flow | Variable, dependent on sales volume |
| Examples | Subscription fees, interest income, asset management fees | Brokerage fees, loan origination fees, insurance commissions |
| Growth Potential | Steady growth through client retention and upselling | Rapid growth tied to sales performance |
| Risk | Lower risk due to steady income flow | Higher risk from fluctuating sales and market conditions |
| Importance in Banking | Supports long-term financial planning and stability | Drives short-term revenue spikes and incentivizes sales teams |
Which is better?
Income streaming offers consistent, predictable cash flow by generating regular payments from investments or services, which enhances financial stability for banking institutions. Commission income fluctuates based on transactional volume and client activity, introducing variability but often yielding higher returns during peak periods. Banks seeking steady revenue prefer income streaming, while those aiming for growth capitalize on commission-based earnings.
Connection
Income streaming in banking involves generating steady revenue through diversified financial products and services, directly influencing commission income which banks earn from facilitating transactions such as loans, asset management, and insurance sales. Robust income streams from commission-based activities enhance overall profitability by creating multiple channels for fee-based revenue. Effective management of income streaming optimizes commission income growth, driving sustainable financial performance in competitive banking markets.
Key Terms
Fee-Based Revenue
Fee-based revenue primarily stems from advisory or management fees charged on assets under management, offering a stable and recurring income stream compared to commission income, which is earned per transaction and can fluctuate with market activity. While commission income depends heavily on trading volume and can be irregular, fee-based revenue aligns incentives with client portfolio growth, enhancing long-term business sustainability. Explore more insights on fee-based revenue models and their impact on financial services profitability.
Transaction Charges
Commission income primarily derives from fees charged per completed transaction, serving as a direct revenue stream linked to sales activities. Income streaming, particularly through transaction charges, encompasses a broader approach by continuously generating revenue from multiple ongoing transactions across various platforms or services. Explore how businesses optimize transaction charges to maximize commission income and create sustainable income streams.
Subscription Model
Commission income refers to earnings generated through a percentage-based fee on sales or transactions, commonly seen in affiliate marketing or brokerage services. Income streaming from a subscription model involves recurring revenue obtained from customers who pay a regular fee, ensuring predictable cash flow and long-term customer retention. Explore how subscription models maximize income stability and compare strategic benefits with commission-based revenue streams.
Source and External Links
Commission Income: Definition, Types, Pros & Cons - FreshBooks - Commission income is the earnings an employee receives from making sales, commonly structured as salary plus commission or tiered commissions, such as in real estate or merchandise sales where the commission is a percentage of sales made.
Commission Income - Definition and Explanation - Accountingverse - Commission income refers to fees earned by brokers and agents for closing sales or deals, recorded as a revenue account in financial statements and typical for businesses like real estate, insurance, or stock brokerage.
What Is Commission Pay and How Does It Work? | Indeed.com - Employees paid by commission earn income either exclusively by sales (straight commission) or alongside a base salary, with common roles including sales representatives and real estate agents, where commission structures can impact income stability and motivation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com