Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) represent state-backed digital money issued by national monetary authorities, offering regulated, stable value and widespread acceptance as legal tender. In contrast, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on decentralized blockchain networks, with values driven by market demand and varying levels of volatility. Explore the distinctions and impacts of CBDCs versus cryptocurrencies to understand their roles in the future of digital finance.
Why it is important
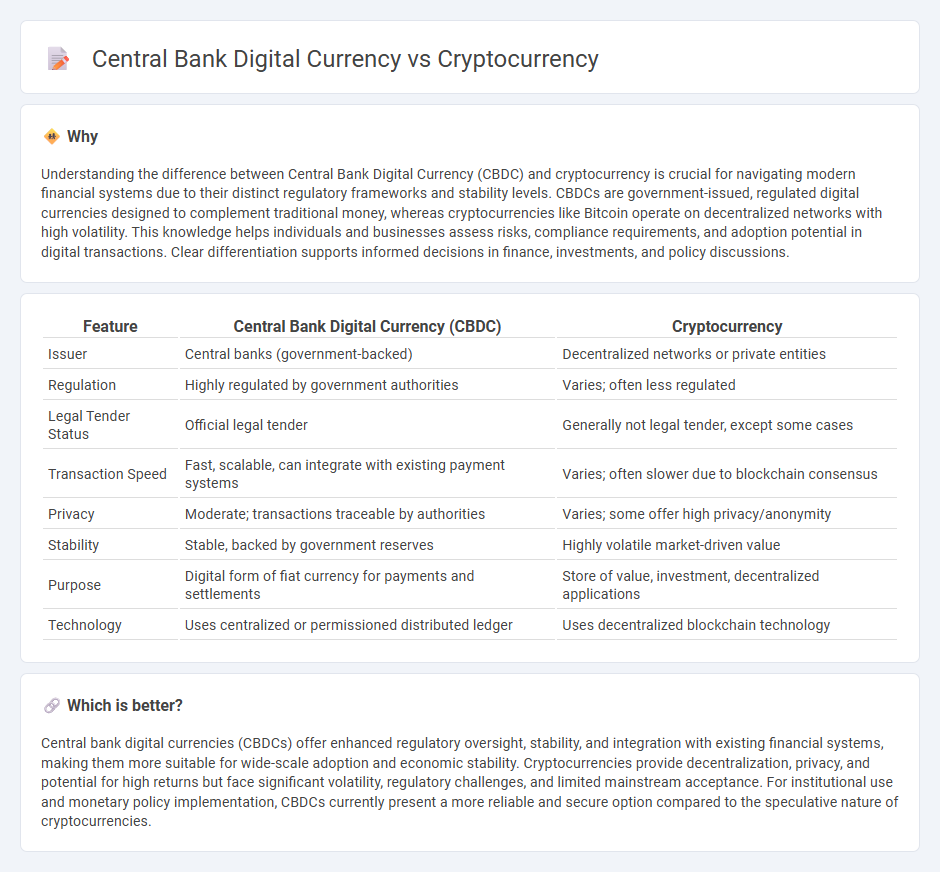
Understanding the difference between Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and cryptocurrency is crucial for navigating modern financial systems due to their distinct regulatory frameworks and stability levels. CBDCs are government-issued, regulated digital currencies designed to complement traditional money, whereas cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin operate on decentralized networks with high volatility. This knowledge helps individuals and businesses assess risks, compliance requirements, and adoption potential in digital transactions. Clear differentiation supports informed decisions in finance, investments, and policy discussions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) | Cryptocurrency |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Central banks (government-backed) | Decentralized networks or private entities |
| Regulation | Highly regulated by government authorities | Varies; often less regulated |
| Legal Tender Status | Official legal tender | Generally not legal tender, except some cases |
| Transaction Speed | Fast, scalable, can integrate with existing payment systems | Varies; often slower due to blockchain consensus |
| Privacy | Moderate; transactions traceable by authorities | Varies; some offer high privacy/anonymity |
| Stability | Stable, backed by government reserves | Highly volatile market-driven value |
| Purpose | Digital form of fiat currency for payments and settlements | Store of value, investment, decentralized applications |
| Technology | Uses centralized or permissioned distributed ledger | Uses decentralized blockchain technology |
Which is better?
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) offer enhanced regulatory oversight, stability, and integration with existing financial systems, making them more suitable for wide-scale adoption and economic stability. Cryptocurrencies provide decentralization, privacy, and potential for high returns but face significant volatility, regulatory challenges, and limited mainstream acceptance. For institutional use and monetary policy implementation, CBDCs currently present a more reliable and secure option compared to the speculative nature of cryptocurrencies.
Connection
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and cryptocurrencies both utilize blockchain technology to enable secure, transparent digital transactions. While CBDCs are government-backed digital currencies issued by central banks to enhance monetary policy efficiency and financial inclusion, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks independent of traditional banking systems. Their convergence influences the evolution of digital finance, driving innovation in payment systems and regulatory frameworks.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Cryptocurrency operates on a decentralized network where transactions are verified by distributed nodes, eliminating the need for a central authority and enhancing transparency and security. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is issued and regulated by a nation's central bank, maintaining centralized control over monetary policy and transaction oversight. Explore the nuanced impact of decentralization on financial systems by learning more about the distinctions between cryptocurrency and CBDCs.
Sovereign Control
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) represents sovereign control by enabling governments to issue digital currency backed by the state, ensuring regulatory oversight, monetary policy implementation, and financial stability. Cryptocurrency operates on decentralized blockchain technology, lacking centralized authority, which grants users privacy and autonomy but limits government intervention. Discover how sovereign control shapes the future of digital currencies and impacts the global financial system.
Blockchain
Cryptocurrency operates on decentralized blockchain technology, enabling secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, while Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) uses a centralized blockchain or distributed ledger managed by a regulatory authority to maintain monetary stability. Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, emphasize transparency and immutability, whereas CBDCs prioritize regulatory compliance and controlled issuance to enhance financial system efficiency. Explore the distinct roles of blockchain in cryptocurrency and CBDC development to understand their impact on the future of digital finance.
Source and External Links
What is Cryptocurrency and How Does it Work? - Cryptocurrency is a digital payment system that operates on a decentralized blockchain, secured by cryptography, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without banks or central authorities, with Bitcoin being the first and most well-known cryptocurrency launched in 2009.
Cryptocurrency - Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies that function through decentralized computer networks using blockchain technology and consensus mechanisms like proof of work or proof of stake, with over 25,000 different cryptocurrencies existing as of 2023 and the market capitalization estimated at $2.76 trillion in 2025.
Digital Currencies | Explainer | Education - Cryptocurrencies, exemplified by Bitcoin, use blockchain technology and cryptography to securely record and verify transactions that are processed by miners solving complex mathematical problems, rewarded with new coins, thus ensuring system integrity and decentralization.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com