Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) represents a digital form of central bank money, stored electronically and accessible to the public, contrasting with traditional bank reserves that are records of commercial banks' deposits held at the central bank, used primarily for interbank settlements. CBDCs offer the potential for enhanced payment efficiency, financial inclusion, and reduced transaction costs compared to reserves which function mainly within the banking system. Explore further to understand how CBDCs could transform monetary policy and banking operations.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between central bank digital currency (CBDC) and bank reserves is crucial for grasping their distinct roles in monetary policy and financial stability. CBDCs represent a digital form of central bank money accessible to the public, while bank reserves are electronic deposits held by commercial banks at the central bank used primarily for interbank settlements. This distinction impacts how digital currencies influence money supply, banking operations, and consumer transactions. Clarity on these concepts aids policymakers and consumers in navigating the evolving digital financial landscape.
Comparison Table
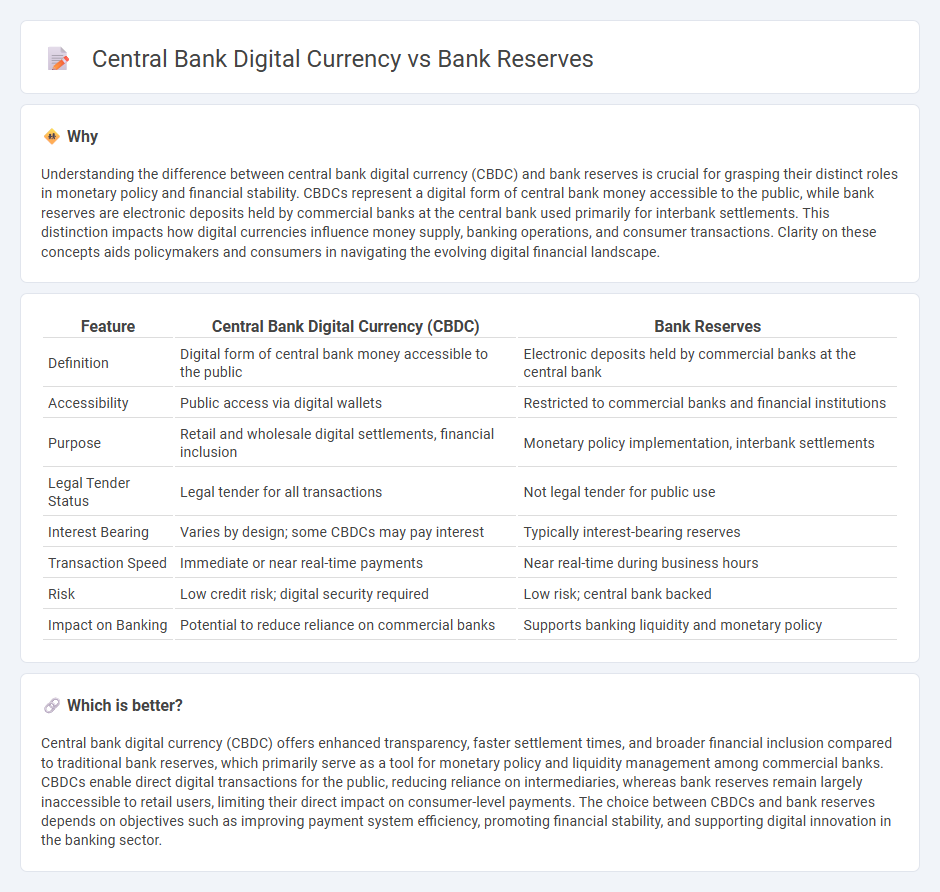
| Feature | Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) | Bank Reserves |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital form of central bank money accessible to the public | Electronic deposits held by commercial banks at the central bank |
| Accessibility | Public access via digital wallets | Restricted to commercial banks and financial institutions |
| Purpose | Retail and wholesale digital settlements, financial inclusion | Monetary policy implementation, interbank settlements |
| Legal Tender Status | Legal tender for all transactions | Not legal tender for public use |
| Interest Bearing | Varies by design; some CBDCs may pay interest | Typically interest-bearing reserves |
| Transaction Speed | Immediate or near real-time payments | Near real-time during business hours |
| Risk | Low credit risk; digital security required | Low risk; central bank backed |
| Impact on Banking | Potential to reduce reliance on commercial banks | Supports banking liquidity and monetary policy |
Which is better?
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) offers enhanced transparency, faster settlement times, and broader financial inclusion compared to traditional bank reserves, which primarily serve as a tool for monetary policy and liquidity management among commercial banks. CBDCs enable direct digital transactions for the public, reducing reliance on intermediaries, whereas bank reserves remain largely inaccessible to retail users, limiting their direct impact on consumer-level payments. The choice between CBDCs and bank reserves depends on objectives such as improving payment system efficiency, promoting financial stability, and supporting digital innovation in the banking sector.
Connection
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) directly influences bank reserves by representing a digital form of central bank liabilities, effectively expanding the base money supply. CBDCs enable instant settlement and can alter the demand for traditional reserves held by commercial banks at the central bank. The integration of CBDCs with existing reserve systems enhances monetary policy implementation and payment system efficiency.
Key Terms
Fractional Reserve Banking
Bank reserves represent the cash that commercial banks hold either in their vaults or as deposits at the central bank, crucial for meeting withdrawal demands and regulatory requirements under the fractional reserve banking system. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) introduces a new form of reserve asset that could alter liquidity dynamics by providing a risk-free, digital claim on the central bank, potentially impacting money creation and reserve management. Explore more about how CBDCs could transform traditional fractional reserve banking and financial stability mechanisms.
Monetary Base
Bank reserves represent the deposits commercial banks hold at the central bank, forming a crucial part of the monetary base that underpins the money supply. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) introduces a new layer to the monetary base by offering digital liabilities directly to the public, potentially altering liquidity dynamics and monetary policy transmission. Explore the evolving interaction between bank reserves and CBDCs to understand future monetary base composition and policy implications.
Digital Fiat Currency
Bank reserves represent commercial banks' holdings of funds deposited at the central bank, used to meet liquidity requirements and facilitate interbank settlements. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), a form of digital fiat currency issued directly by the central bank, offers a secure, instantly accessible, and programmable alternative to traditional reserves and cash. Explore the transformative impact of CBDCs on monetary policy and financial ecosystems by learning more.
Source and External Links
Bank Reserves - Overview, Requirements, Guidelines - Bank reserves are the minimum cash reserves that financial institutions must keep in their vaults or on deposit at the central bank, set as a fixed percentage of deposits to ensure liquidity for withdrawals and obligations, with central banks like the Federal Reserve establishing specific reserve requirements.
Bank reserves - Bank reserves include cash physically held by commercial banks and deposits held with the central bank, comprising required reserves (mandated minimum) and excess reserves, intended to maintain liquidity and support withdrawals, and they form part of the bank's assets rather than equity.
How the Federal Reserve Got So Huge, and Why and How It Can Shrink - Banks keep money on deposit at the Federal Reserve as reserve balances, which serve as their checking accounts at the Fed and provide liquidity and contingency funding; reserve requirements previously mandated minimum levels, but banks now hold large amounts of reserves partly for liquidity management and payment activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com