Behavioral biometrics analyze unique patterns such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, and device usage to enhance banking security by continuously verifying user identity. Facial recognition employs advanced image processing and AI algorithms to authenticate individuals based on facial features, offering fast and contactless access to banking services. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies are transforming secure banking experiences worldwide.
Why it is important
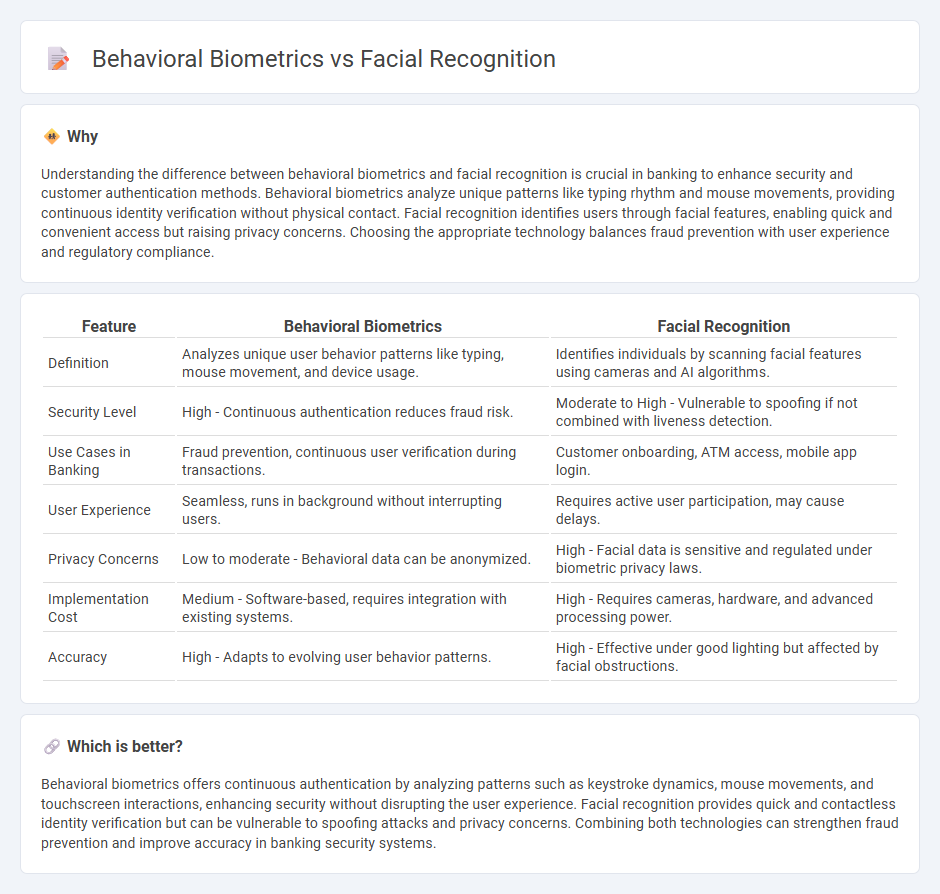
Understanding the difference between behavioral biometrics and facial recognition is crucial in banking to enhance security and customer authentication methods. Behavioral biometrics analyze unique patterns like typing rhythm and mouse movements, providing continuous identity verification without physical contact. Facial recognition identifies users through facial features, enabling quick and convenient access but raising privacy concerns. Choosing the appropriate technology balances fraud prevention with user experience and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Behavioral Biometrics | Facial Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes unique user behavior patterns like typing, mouse movement, and device usage. | Identifies individuals by scanning facial features using cameras and AI algorithms. |
| Security Level | High - Continuous authentication reduces fraud risk. | Moderate to High - Vulnerable to spoofing if not combined with liveness detection. |
| Use Cases in Banking | Fraud prevention, continuous user verification during transactions. | Customer onboarding, ATM access, mobile app login. |
| User Experience | Seamless, runs in background without interrupting users. | Requires active user participation, may cause delays. |
| Privacy Concerns | Low to moderate - Behavioral data can be anonymized. | High - Facial data is sensitive and regulated under biometric privacy laws. |
| Implementation Cost | Medium - Software-based, requires integration with existing systems. | High - Requires cameras, hardware, and advanced processing power. |
| Accuracy | High - Adapts to evolving user behavior patterns. | High - Effective under good lighting but affected by facial obstructions. |
Which is better?
Behavioral biometrics offers continuous authentication by analyzing patterns such as keystroke dynamics, mouse movements, and touchscreen interactions, enhancing security without disrupting the user experience. Facial recognition provides quick and contactless identity verification but can be vulnerable to spoofing attacks and privacy concerns. Combining both technologies can strengthen fraud prevention and improve accuracy in banking security systems.
Connection
Behavioral biometrics and facial recognition complement each other in banking by enhancing multi-factor authentication through continuous identity verification. Behavioral biometrics analyze patterns such as typing rhythm and device interaction, while facial recognition confirms user identity via unique facial features, reducing fraud and improving security. Integrating both technologies creates robust, real-time authentication systems that protect sensitive financial transactions.
Key Terms
Authentication
Facial recognition leverages unique facial features for identity verification, offering a fast, non-invasive authentication method widely used in smartphones and security systems. Behavioral biometrics analyzes patterns such as typing rhythm, gait, and mouse movement, providing continuous authentication that adapts to user behavior and enhances fraud detection. Explore the advantages and use cases of both technologies to determine the best fit for secure authentication solutions.
Liveness Detection
Liveness detection in facial recognition uses techniques such as blink analysis, 3D depth mapping, and infrared sensing to verify that the subject is a real, live person, not a photograph or mask. Behavioral biometrics enhances security by analyzing patterns like typing rhythm, mouse movements, and gait dynamics, which are inherently difficult to replicate or spoof. Explore advanced liveness detection methods to understand how these technologies improve identity verification accuracy and fraud prevention.
Continuous Monitoring
Facial recognition technology identifies individuals by analyzing unique facial features, offering quick authentication but often limited to static points of access. Behavioral biometrics continuously monitor patterns such as typing rhythms, mouse movements, and gait, providing real-time identity verification crucial for ongoing security. Discover how continuous behavioral biometrics enhance authentication beyond traditional facial recognition methods.
Source and External Links
What is facial recognition and how does it work? - Norton - Facial recognition uses AI and biometrics to map facial features from photos or videos, creating a unique facial signature that is compared against large databases to verify identity or find matches, but it raises privacy concerns.
What Is Face Recognition? | Microsoft Azure - Facial recognition technology uses AI to analyze the geometry of facial features in images or videos, creating templates that are compared to databases for identification, verification, or grouping of individuals.
Facial recognition system - Wikipedia - Facial recognition systems match human faces from digital images or video frames against databases to authenticate identity, functioning as a biometric technology widely used in devices, surveillance, and law enforcement despite lower accuracy than some other biometrics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com