Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to support long-term economic growth and climate resilience. Ethical banking focuses on transparency, social responsibility, and avoiding investments in harmful industries like fossil fuels or weapons manufacturing. Explore more to understand how these approaches reshape modern banking practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainable finance and ethical banking is crucial for making informed investment decisions that align with personal values and long-term financial goals. Sustainable finance focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote economic growth while minimizing negative impacts. Ethical banking prioritizes transparency, social justice, and community development by avoiding investments in harmful industries. Recognizing these distinctions empowers consumers to support financial institutions that reflect their commitment to social responsibility and environmental stewardship.
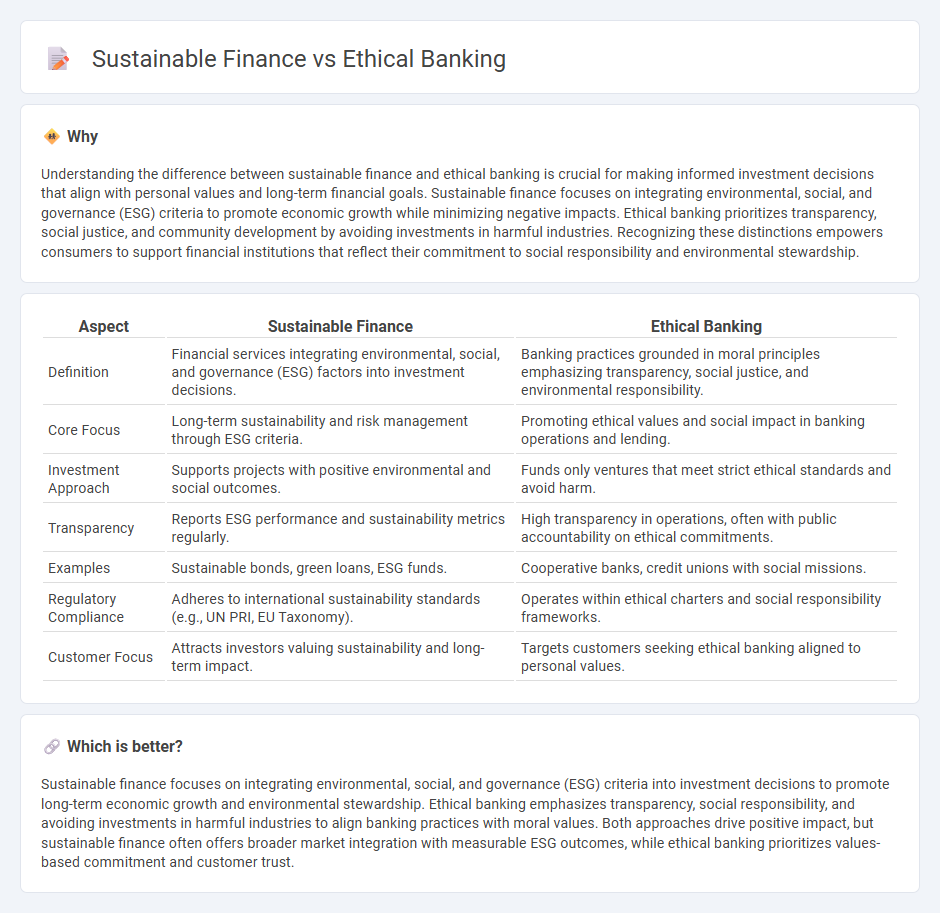
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Finance | Ethical Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial services integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions. | Banking practices grounded in moral principles emphasizing transparency, social justice, and environmental responsibility. |
| Core Focus | Long-term sustainability and risk management through ESG criteria. | Promoting ethical values and social impact in banking operations and lending. |
| Investment Approach | Supports projects with positive environmental and social outcomes. | Funds only ventures that meet strict ethical standards and avoid harm. |
| Transparency | Reports ESG performance and sustainability metrics regularly. | High transparency in operations, often with public accountability on ethical commitments. |
| Examples | Sustainable bonds, green loans, ESG funds. | Cooperative banks, credit unions with social missions. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adheres to international sustainability standards (e.g., UN PRI, EU Taxonomy). | Operates within ethical charters and social responsibility frameworks. |
| Customer Focus | Attracts investors valuing sustainability and long-term impact. | Targets customers seeking ethical banking aligned to personal values. |
Which is better?
Sustainable finance focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to promote long-term economic growth and environmental stewardship. Ethical banking emphasizes transparency, social responsibility, and avoiding investments in harmful industries to align banking practices with moral values. Both approaches drive positive impact, but sustainable finance often offers broader market integration with measurable ESG outcomes, while ethical banking prioritizes values-based commitment and customer trust.
Connection
Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into banking decisions, ensuring investments promote long-term ecological balance and social welfare. Ethical banking prioritizes transparency, fair lending practices, and community development, aligning financial services with moral and societal values. Both concepts drive the transition towards responsible finance, fostering economic growth while addressing global sustainability challenges.
Key Terms
Transparency
Ethical banking prioritizes transparency by openly communicating lending practices, investment criteria, and social impact commitments to build trust with customers. Sustainable finance emphasizes transparent reporting on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics to ensure accountability and drive long-term value creation. Explore how transparency shapes decision-making in both sectors for a deeper understanding.
Social Responsibility
Ethical banking prioritizes transparency, fair practices, and positive social impact by avoiding industries that harm society, while sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term economic and social benefits. Both approaches emphasize social responsibility, with ethical banking focusing more on values-driven investment decisions and sustainable finance supporting projects aligned with global sustainability goals. Explore how these financial models contribute to responsible economic growth and social equity.
Environmental Impact
Ethical banking prioritizes transparency, social responsibility, and avoiding investments in harmful industries, which often leads to positive environmental outcomes such as reduced carbon emissions and support for renewable energy projects. Sustainable finance specifically targets investments that actively promote environmental sustainability, including green bonds and climate-focused funds designed to mitigate environmental risks and support eco-friendly innovation. Explore how both approaches uniquely contribute to environmental impact and drive the future of responsible investing.
Source and External Links
Ethical Banking - Ethical banks avoid funding toxic industries like fossil fuels and weapons, instead supporting positive sectors such as renewable energy and sustainable farming, while also considering issues like tax fairness and pay equality.
Ethical banking - Ethical banks, also known as social or sustainable banks, consider the social and environmental impact of their investments and operations, though their ethical policies and screening processes often lack full transparency for depositors.
Ethical banks in the UK: List of 10 providers (2025) - UK ethical banks, such as Triodos and Charity Bank, are focused on positive environmental and social impact, funding renewable energy, community projects, charities, and sustainable housing, with some being certified B Corps or owned by their members.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com