Open banking enables third-party developers to access bank data through APIs, fostering innovation and personalized financial services. Embedded finance integrates financial products directly into non-financial platforms, enhancing user experience by offering seamless transactions within everyday apps. Discover how these evolving models are reshaping the financial landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between open banking and embedded finance is crucial for optimizing financial services and enhancing customer experience. Open banking enables secure data sharing between banks and third-party providers, fostering innovation through APIs. Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, streamlining access for users. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses leverage the right model for improved efficiency and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
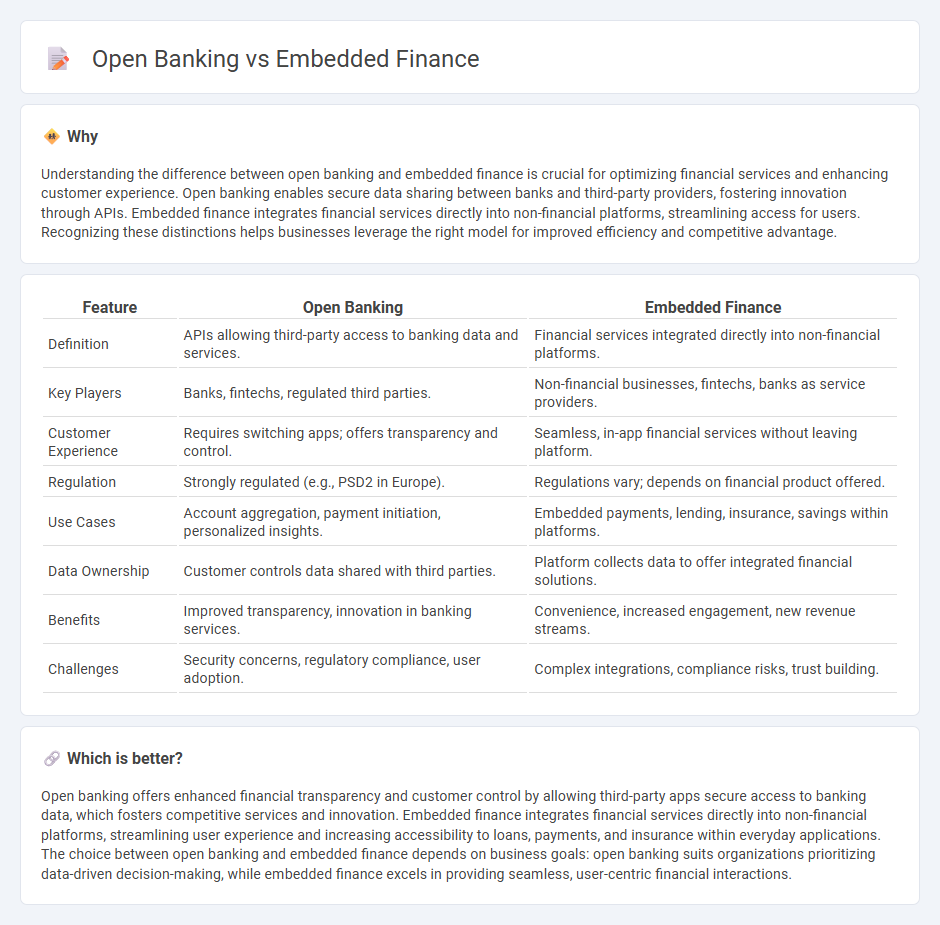
| Feature | Open Banking | Embedded Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | APIs allowing third-party access to banking data and services. | Financial services integrated directly into non-financial platforms. |
| Key Players | Banks, fintechs, regulated third parties. | Non-financial businesses, fintechs, banks as service providers. |
| Customer Experience | Requires switching apps; offers transparency and control. | Seamless, in-app financial services without leaving platform. |
| Regulation | Strongly regulated (e.g., PSD2 in Europe). | Regulations vary; depends on financial product offered. |
| Use Cases | Account aggregation, payment initiation, personalized insights. | Embedded payments, lending, insurance, savings within platforms. |
| Data Ownership | Customer controls data shared with third parties. | Platform collects data to offer integrated financial solutions. |
| Benefits | Improved transparency, innovation in banking services. | Convenience, increased engagement, new revenue streams. |
| Challenges | Security concerns, regulatory compliance, user adoption. | Complex integrations, compliance risks, trust building. |
Which is better?
Open banking offers enhanced financial transparency and customer control by allowing third-party apps secure access to banking data, which fosters competitive services and innovation. Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, streamlining user experience and increasing accessibility to loans, payments, and insurance within everyday applications. The choice between open banking and embedded finance depends on business goals: open banking suits organizations prioritizing data-driven decision-making, while embedded finance excels in providing seamless, user-centric financial interactions.
Connection
Open banking enables third-party developers to access banking data through APIs, facilitating the integration of financial services into non-bank platforms. Embedded finance leverages this connectivity by incorporating banking products directly within apps and websites, enhancing user experience and expanding financial accessibility. Together, they drive innovation in digital banking by promoting seamless, real-time financial interactions across diverse ecosystems.
Key Terms
**Embedded Finance:**
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enabling seamless transactions within apps like e-commerce, ride-sharing, or accounting software. Key benefits include improved user experience, increased customer engagement, and new revenue streams for businesses by embedding payments, lending, or insurance. Discover how embedded finance transforms traditional banking models and enhances digital ecosystems.
APIs
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms using APIs, allowing seamless transactions without redirecting users to traditional banks. Open banking mandates banks to provide secure API access to customer data for third-party developers, fostering innovation and personalized financial products. Explore how API-driven models transform customer experience and create new opportunities in financial technology.
Non-financial platforms
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms like e-commerce, enabling seamless payment, lending, and insurance without redirecting users to traditional banks. Open banking provides secure data sharing APIs allowing third-party developers to build apps that enhance financial transparency and personalized services on such platforms. Explore how these technologies transform user experience and revenue models in digital ecosystems.
Source and External Links
What is embedded finance? 4 ways it will change fintech - Embedded finance is the integration of financial services such as payments, lending, or banking into non-financial platforms, enabling users to access these services seamlessly within tools they already use, with revenue projected to grow to $291.3 billion by 2033.
What does embedded finance mean for business? - Embedded finance allows nonfinancial companies to integrate digital banking and financial products into their platforms, creating frictionless user experiences that foster loyalty and open new business models and monetization opportunities.
Embedded finance: Who will lead the next payments revolution - Embedded finance places financial products within nonfinancial digital customer experiences like shopping or managing inventory, driven by digitization and open banking innovations, enabling financial services to become natural extensions of everyday digital activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com