Instant settlement processes financial transactions immediately, enhancing liquidity and reducing counterparty risk by confirming transfers in real time. End-of-day settlement consolidates multiple transactions for batch processing, improving operational efficiency but increasing exposure to credit risk until settlement completes. Discover how these settlement methods impact cash flow and risk management in modern banking.
Why it is important
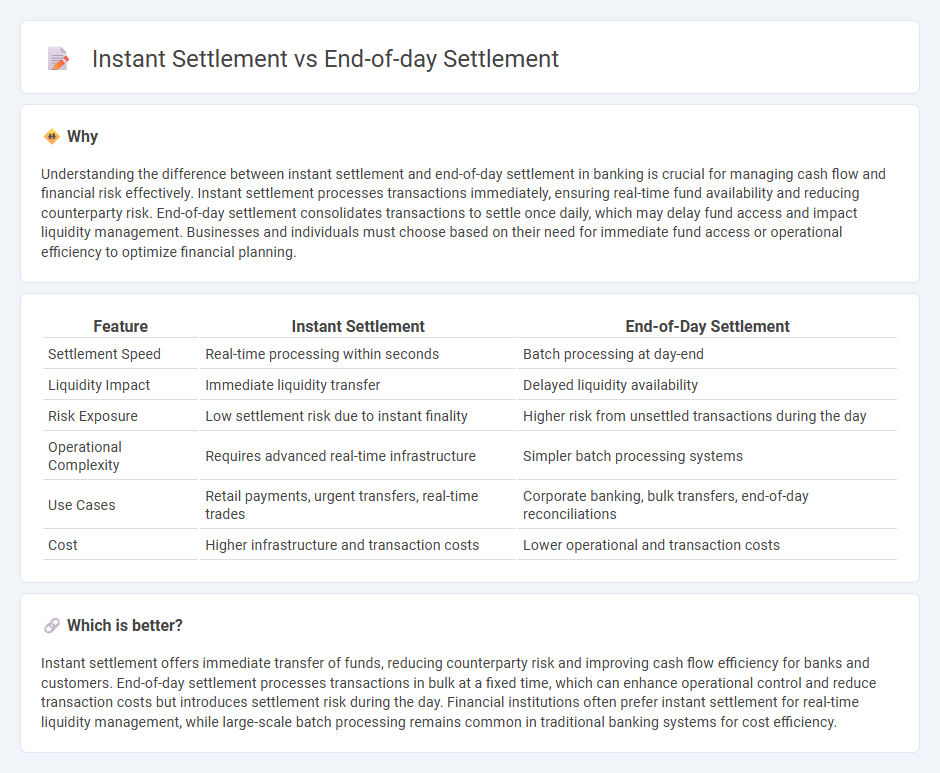
Understanding the difference between instant settlement and end-of-day settlement in banking is crucial for managing cash flow and financial risk effectively. Instant settlement processes transactions immediately, ensuring real-time fund availability and reducing counterparty risk. End-of-day settlement consolidates transactions to settle once daily, which may delay fund access and impact liquidity management. Businesses and individuals must choose based on their need for immediate fund access or operational efficiency to optimize financial planning.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Instant Settlement | End-of-Day Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Settlement Speed | Real-time processing within seconds | Batch processing at day-end |
| Liquidity Impact | Immediate liquidity transfer | Delayed liquidity availability |
| Risk Exposure | Low settlement risk due to instant finality | Higher risk from unsettled transactions during the day |
| Operational Complexity | Requires advanced real-time infrastructure | Simpler batch processing systems |
| Use Cases | Retail payments, urgent transfers, real-time trades | Corporate banking, bulk transfers, end-of-day reconciliations |
| Cost | Higher infrastructure and transaction costs | Lower operational and transaction costs |
Which is better?
Instant settlement offers immediate transfer of funds, reducing counterparty risk and improving cash flow efficiency for banks and customers. End-of-day settlement processes transactions in bulk at a fixed time, which can enhance operational control and reduce transaction costs but introduces settlement risk during the day. Financial institutions often prefer instant settlement for real-time liquidity management, while large-scale batch processing remains common in traditional banking systems for cost efficiency.
Connection
Instant settlement processes enable real-time transfer of funds, improving liquidity and reducing credit risk by immediately finalizing transactions. End-of-day settlement consolidates all transactions processed throughout the day, ensuring accurate reconciliation and compliance with regulatory requirements. Both settlement types complement each other by balancing the need for immediate fund availability and comprehensive financial reporting in banking operations.
Key Terms
Clearing
End-of-day settlement consolidates transactions to be cleared and settled once daily, reducing operational costs and counterparty risk by netting trades before finalizing payments. Instant settlement processes transactions in real-time, improving liquidity and reducing settlement risk but requiring robust clearing infrastructure to handle immediate fund transfers. Discover how clearing mechanisms differ between these settlement types to enhance your financial operations.
Settlement cycle
The end-of-day settlement process involves transactions being aggregated and settled collectively at the close of the trading day, typically following a T+1 or T+2 settlement cycle, ensuring batch processing efficiency but delaying fund availability. Instant settlement, leveraging advanced payment technologies and blockchain, facilitates immediate transaction finality, drastically reducing the settlement cycle to seconds or minutes, which enhances liquidity and minimizes counterparty risk. Explore how these settlement cycles impact financial operations and risk management strategies in modern markets.
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems enable immediate, irrevocable transfer of funds, contrasting with end-of-day settlement where transactions accumulate and clear collectively at a set time. RTGS enhances liquidity management by providing real-time updates and reducing settlement risk for high-value interbank payments. Discover how RTGS transforms financial operations with faster, secure payment settlements.
Source and External Links
End of Day Consolidated Settlement - DTCC - End-of-day net funds settlement provides same-day finality, reduces settlement risk, and involves settling banks aggregating net balances for multiple participants via a single Fedwire instruction.
Understanding Settlement Cycles: What Does T+1 Mean for You? - FINRA - As of May 28, 2024, most U.S. securities transactions settle on the next business day after the trade date (T+1), meaning end-of-day settlement activity reflects trades executed the previous business day.
Money Settlement - DTCC Learning Center - Settlement at DTCC occurs each business day around 4:15 p.m. ET, with cash moved via the Federal Reserve Bank of New York through settling banks, and final settlement figures posted around 3:45 p.m. ET.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com