Composable banking offers a modular approach by allowing financial institutions to customize and integrate best-of-breed components, enhancing agility and innovation compared to traditional digital banking platforms. Digital banking encompasses online and mobile services that provide convenient access to banking products, yet often relies on monolithic systems with limited flexibility. Discover how composable banking transforms financial services with tailored, scalable solutions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between composable banking and digital banking is crucial for financial institutions to design flexible, scalable, and customer-centric solutions. Composable banking enables banks to assemble modular, API-driven components for tailored services, whereas digital banking focuses on delivering traditional banking services through digital channels. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize technology investments and accelerates innovation in the financial sector. Banks that leverage composable architectures can rapidly adapt to market demands and regulatory changes more efficiently than solely digital banking platforms.
Comparison Table
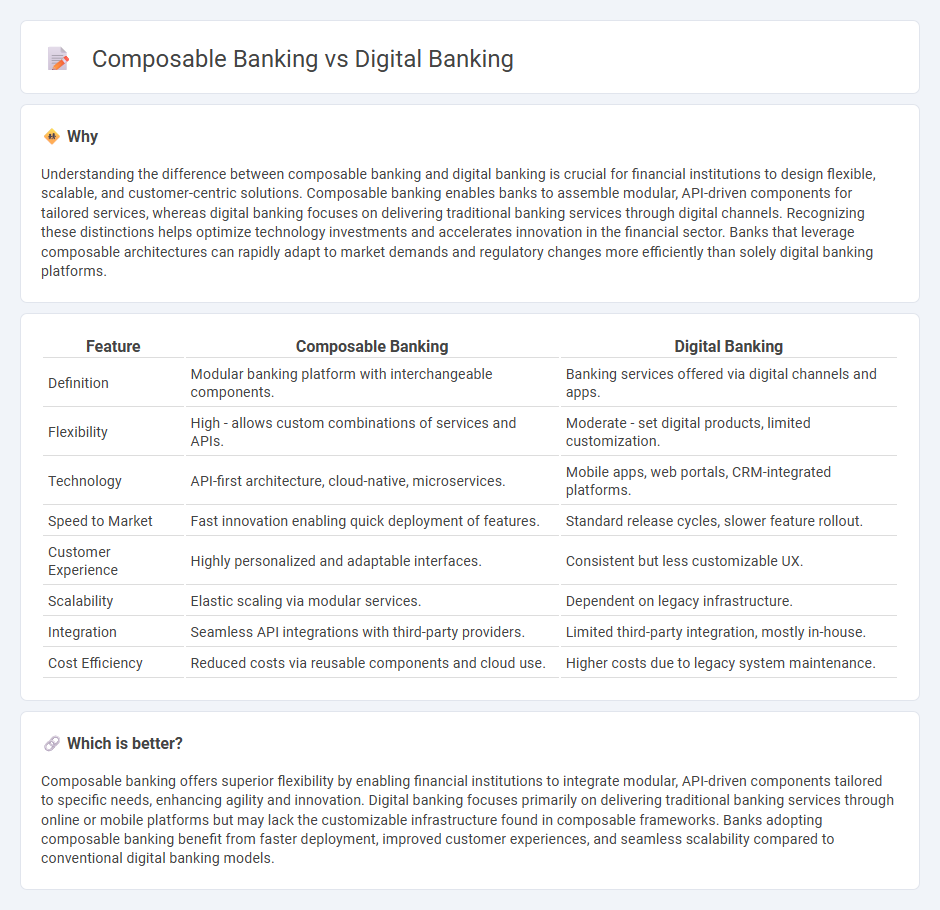
| Feature | Composable Banking | Digital Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modular banking platform with interchangeable components. | Banking services offered via digital channels and apps. |
| Flexibility | High - allows custom combinations of services and APIs. | Moderate - set digital products, limited customization. |
| Technology | API-first architecture, cloud-native, microservices. | Mobile apps, web portals, CRM-integrated platforms. |
| Speed to Market | Fast innovation enabling quick deployment of features. | Standard release cycles, slower feature rollout. |
| Customer Experience | Highly personalized and adaptable interfaces. | Consistent but less customizable UX. |
| Scalability | Elastic scaling via modular services. | Dependent on legacy infrastructure. |
| Integration | Seamless API integrations with third-party providers. | Limited third-party integration, mostly in-house. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced costs via reusable components and cloud use. | Higher costs due to legacy system maintenance. |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers superior flexibility by enabling financial institutions to integrate modular, API-driven components tailored to specific needs, enhancing agility and innovation. Digital banking focuses primarily on delivering traditional banking services through online or mobile platforms but may lack the customizable infrastructure found in composable frameworks. Banks adopting composable banking benefit from faster deployment, improved customer experiences, and seamless scalability compared to conventional digital banking models.
Connection
Composable banking leverages modular APIs and microservices to create flexible, customizable financial solutions that enhance digital banking platforms. Digital banking integrates these composable components to deliver seamless, personalized user experiences, faster product innovation, and improved operational efficiency. This synergy enables banks to quickly adapt to market changes and meet evolving customer expectations.
Key Terms
Core Banking Systems
Core banking systems in digital banking often rely on monolithic architectures offering standardized functionalities, which can limit flexibility and slow down innovation. Composable banking leverages modular components and APIs, enabling financial institutions to quickly customize and scale services tailored to specific customer needs. Explore the advantages of composable banking to understand how it transforms core banking with agility and personalization.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
APIs play a crucial role in both digital banking and composable banking, enabling seamless integration of services and enhancing customer experience through real-time data exchange. Digital banking relies on APIs primarily to extend traditional banking functions into online platforms, while composable banking leverages APIs to build modular, customizable systems that can rapidly adapt to market changes. Explore how the strategic use of APIs shapes the future of banking by unlocking flexibility and innovation.
Modular Architecture
Digital banking leverages monolithic systems to deliver standardized financial services, often limiting flexibility and rapid innovation. Composable banking employs modular architecture, enabling financial institutions to integrate best-of-breed APIs and microservices for tailored, scalable solutions that enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. Discover how modular architecture reshapes banking innovation and agility by exploring its core principles and industry applications.
Source and External Links
Digital Banking: 2025 Market Overview, Trends & Insights - Digital banking digitizes all traditional banking products and processes to serve customers online, with key trends including mobile banking growth, digital-only banks, AI integration for personalized services, and expansion of digital payments.
Digital banking - Wikipedia - Digital banking encompasses online, mobile, and integrated middleware services to provide comprehensive banking functions accessible via various platforms, incorporating automation and security compliance.
Digital Banking - UNFCU - Digital banking allows secure access and management of accounts globally through web and mobile platforms, offering features like account opening, global transfers, loans application, card control, and strong security.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com