Super apps integrate multiple financial services like payments, loans, and investments within one platform, enhancing user convenience and engagement. Embedded finance seamlessly incorporates banking services into non-financial apps, allowing businesses to offer tailored financial solutions directly to their customers. Explore how these innovations are transforming the banking landscape and creating new opportunities.
Why it is important
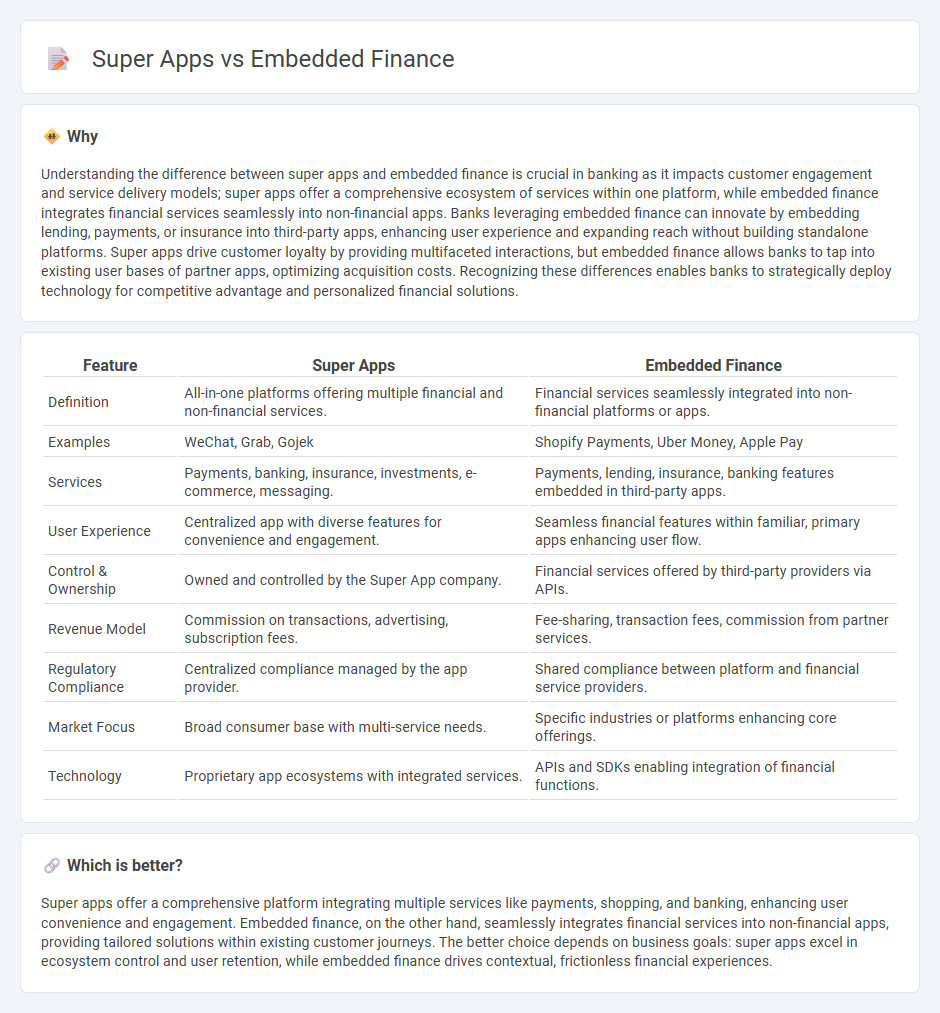
Understanding the difference between super apps and embedded finance is crucial in banking as it impacts customer engagement and service delivery models; super apps offer a comprehensive ecosystem of services within one platform, while embedded finance integrates financial services seamlessly into non-financial apps. Banks leveraging embedded finance can innovate by embedding lending, payments, or insurance into third-party apps, enhancing user experience and expanding reach without building standalone platforms. Super apps drive customer loyalty by providing multifaceted interactions, but embedded finance allows banks to tap into existing user bases of partner apps, optimizing acquisition costs. Recognizing these differences enables banks to strategically deploy technology for competitive advantage and personalized financial solutions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Super Apps | Embedded Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | All-in-one platforms offering multiple financial and non-financial services. | Financial services seamlessly integrated into non-financial platforms or apps. |
| Examples | WeChat, Grab, Gojek | Shopify Payments, Uber Money, Apple Pay |
| Services | Payments, banking, insurance, investments, e-commerce, messaging. | Payments, lending, insurance, banking features embedded in third-party apps. |
| User Experience | Centralized app with diverse features for convenience and engagement. | Seamless financial features within familiar, primary apps enhancing user flow. |
| Control & Ownership | Owned and controlled by the Super App company. | Financial services offered by third-party providers via APIs. |
| Revenue Model | Commission on transactions, advertising, subscription fees. | Fee-sharing, transaction fees, commission from partner services. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Centralized compliance managed by the app provider. | Shared compliance between platform and financial service providers. |
| Market Focus | Broad consumer base with multi-service needs. | Specific industries or platforms enhancing core offerings. |
| Technology | Proprietary app ecosystems with integrated services. | APIs and SDKs enabling integration of financial functions. |
Which is better?
Super apps offer a comprehensive platform integrating multiple services like payments, shopping, and banking, enhancing user convenience and engagement. Embedded finance, on the other hand, seamlessly integrates financial services into non-financial apps, providing tailored solutions within existing customer journeys. The better choice depends on business goals: super apps excel in ecosystem control and user retention, while embedded finance drives contextual, frictionless financial experiences.
Connection
Super apps integrate multiple financial services within a single platform, fostering seamless embedded finance experiences that allow users to access banking, payments, and lending without leaving the app environment. By embedding financial products directly into non-financial apps, these platforms enhance customer engagement and streamline transactions, driving higher adoption rates among digital-savvy consumers. This synergy between super apps and embedded finance accelerates the transformation of traditional banking models toward more inclusive and convenient ecosystem-based financial services.
Key Terms
**Embedded Finance:**
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enhancing user experience by providing seamless access to payments, lending, insurance, and investments without leaving the app. This model drives increased customer engagement, reduces friction, and boosts revenue channels for businesses in retail, e-commerce, and service industries. Explore how embedded finance transforms traditional financial interactions and empowers digital ecosystems.
API Integration
Embedded finance leverages API integration to seamlessly incorporate financial services into non-financial platforms, enabling businesses to offer banking, payments, or lending without leaving their ecosystem. Super apps utilize APIs to connect multiple services--such as messaging, shopping, and financial products--creating an all-in-one user experience and driving greater customer engagement. Explore how mastering API integration can transform your digital strategy and unlock new revenue streams.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Embedded finance integrates banking services directly into non-financial platforms through APIs, enabling seamless financial transactions within apps like e-commerce or ride-sharing. Super apps consolidate multiple services, including embedded finance, social media, and e-commerce, into a single interface, offering users a unified digital ecosystem. Explore the evolving landscape of Banking-as-a-Service to understand how these models transform financial accessibility and customer experience.
Source and External Links
What is embedded finance? 4 ways it will change fintech - Embedded finance integrates financial services like payments, lending, or banking into non-financial platforms, enabling seamless access to finance within apps or websites without redirecting users to banks, and is projected to grow to $291.3 billion by 2033.
What does embedded finance mean for business? - Embedded finance allows non-financial companies to embed digital banking and financial products into their platforms, creating frictionless customer experiences, new monetization paths, and extended financial access especially in emerging markets.
Embedded finance: Who will lead the next payments revolution - Embedded finance places financial products inside non-financial digital experiences and platforms, such as loyalty apps and accounting software, driven by digitization, consumer behavior shifts, and open-banking innovations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com