Composable banking enables financial institutions to create customized, flexible banking solutions by integrating modular components through APIs, enhancing agility and innovation. Platform banking offers a centralized ecosystem where banks provide a suite of core services and third-party applications on a single digital platform, facilitating seamless customer experiences and operational efficiency. Explore the differences and benefits of composable versus platform banking to understand which approach can best transform your financial services.
Why it is important
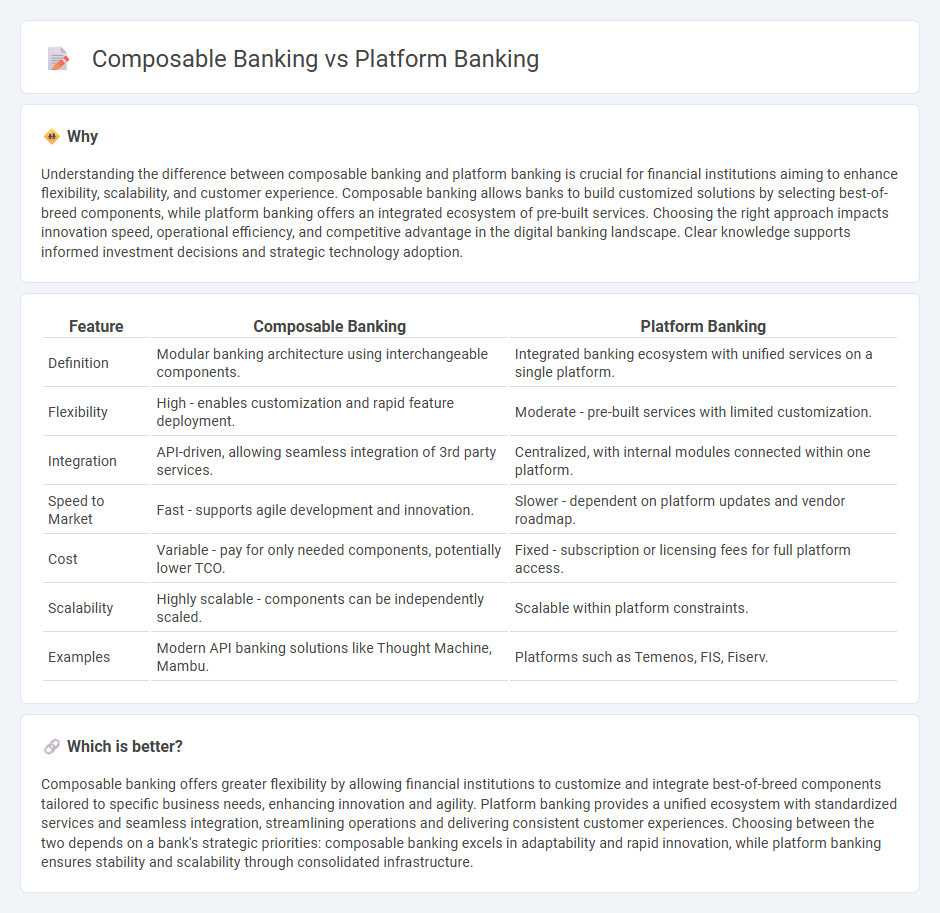
Understanding the difference between composable banking and platform banking is crucial for financial institutions aiming to enhance flexibility, scalability, and customer experience. Composable banking allows banks to build customized solutions by selecting best-of-breed components, while platform banking offers an integrated ecosystem of pre-built services. Choosing the right approach impacts innovation speed, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage in the digital banking landscape. Clear knowledge supports informed investment decisions and strategic technology adoption.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Composable Banking | Platform Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modular banking architecture using interchangeable components. | Integrated banking ecosystem with unified services on a single platform. |
| Flexibility | High - enables customization and rapid feature deployment. | Moderate - pre-built services with limited customization. |
| Integration | API-driven, allowing seamless integration of 3rd party services. | Centralized, with internal modules connected within one platform. |
| Speed to Market | Fast - supports agile development and innovation. | Slower - dependent on platform updates and vendor roadmap. |
| Cost | Variable - pay for only needed components, potentially lower TCO. | Fixed - subscription or licensing fees for full platform access. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable - components can be independently scaled. | Scalable within platform constraints. |
| Examples | Modern API banking solutions like Thought Machine, Mambu. | Platforms such as Temenos, FIS, Fiserv. |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers greater flexibility by allowing financial institutions to customize and integrate best-of-breed components tailored to specific business needs, enhancing innovation and agility. Platform banking provides a unified ecosystem with standardized services and seamless integration, streamlining operations and delivering consistent customer experiences. Choosing between the two depends on a bank's strategic priorities: composable banking excels in adaptability and rapid innovation, while platform banking ensures stability and scalability through consolidated infrastructure.
Connection
Composable banking leverages modular APIs and microservices to enable flexible financial product development, while platform banking uses these core components to create integrated ecosystems connecting banks, fintechs, and third-party service providers. The connection lies in composable banking's ability to provide the foundational infrastructure that platform banking utilizes for seamless interoperability and customer-centric service delivery. This synergy drives innovation, faster time-to-market, and enhanced personalization in digital banking experiences.
Key Terms
API Integration
Platform banking relies on standardized API integration to connect various third-party services within a unified ecosystem, enhancing scalability and customer customization. Composable banking uses modular APIs to assemble personalized banking solutions by selecting best-of-breed components, allowing greater flexibility and faster innovation cycles. Discover how API integration shapes the future of banking by exploring detailed comparisons of platform and composable approaches.
Modular Architecture
Platform banking utilizes a unified digital infrastructure enabling third-party integrations through APIs, promoting scalability and streamlined service delivery. Composable banking emphasizes modular architecture, allowing financial institutions to assemble and customize their tech stack by selecting best-of-breed components for agility and innovation. Explore the advantages of modular design and how it transforms banking strategies for enhanced customer experience.
Ecosystem Partnerships
Platform banking integrates diverse financial services through APIs, enabling seamless ecosystem partnerships that enhance customer experiences and operational efficiency. Composable banking offers modular, customizable components allowing banks to rapidly adapt and innovate within their ecosystems by selecting best-of-breed services. Discover how these approaches reshape financial ecosystems and drive strategic collaborations.
Source and External Links
Platform banking...and how it enhances financial services - Platform banking is when banks integrate fintech services into their own platforms via APIs to offer customers a broader, more specialized range of financial services beyond traditional banking products.
Platform Banking: Revolutionizing Financial Services in Digital Age - Platform banking transforms banks into digital marketplaces that offer a unified interface connecting various financial products through open APIs and partnerships with fintechs, enabling seamless, integrated customer experiences.
What Is a Banking Platform and Why Is It the Key to SME Growth in ... - Platform banking creates a digital ecosystem linking banks, third-party fintechs, and customers, allowing tailored, personalized services through cloud technologies and open APIs, especially benefiting small and medium enterprises by improving flexibility and client experience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com