Green financing supports environmentally sustainable projects by providing capital to initiatives focused on renewable energy, energy efficiency, and conservation efforts. Debt financing involves borrowing funds that must be repaid with interest, often used for expansion, capital expenditures, or operational costs. Explore the key differences and benefits of green financing versus traditional debt financing to make informed banking decisions.
Why it is important
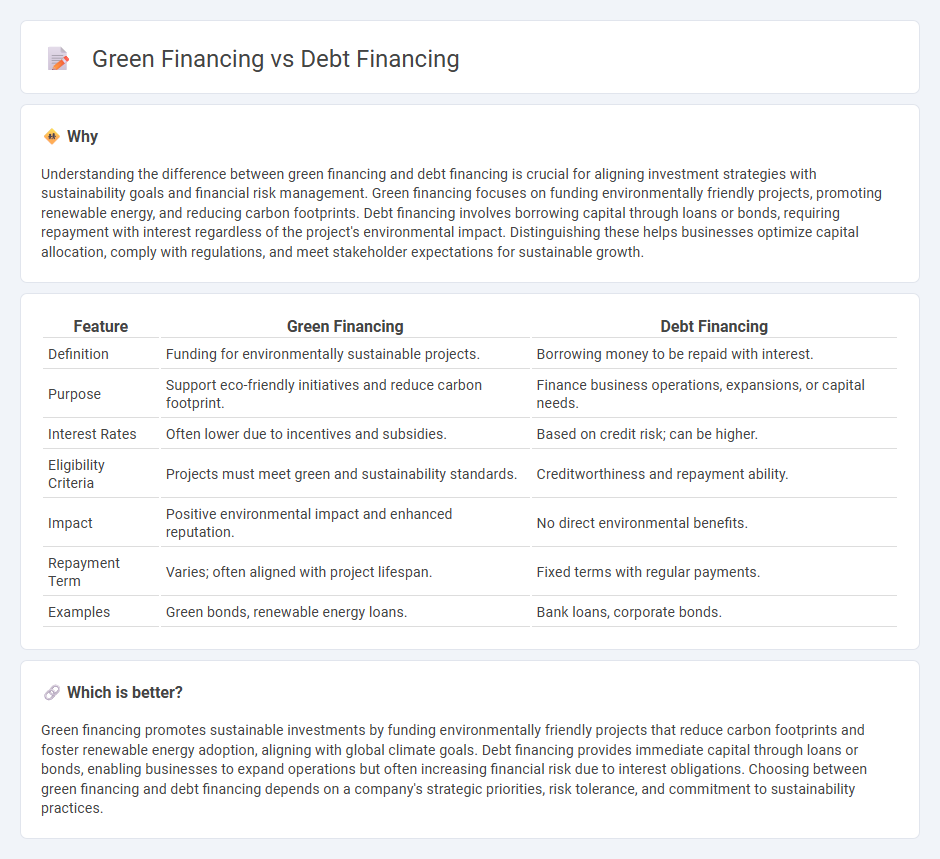
Understanding the difference between green financing and debt financing is crucial for aligning investment strategies with sustainability goals and financial risk management. Green financing focuses on funding environmentally friendly projects, promoting renewable energy, and reducing carbon footprints. Debt financing involves borrowing capital through loans or bonds, requiring repayment with interest regardless of the project's environmental impact. Distinguishing these helps businesses optimize capital allocation, comply with regulations, and meet stakeholder expectations for sustainable growth.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Green Financing | Debt Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funding for environmentally sustainable projects. | Borrowing money to be repaid with interest. |
| Purpose | Support eco-friendly initiatives and reduce carbon footprint. | Finance business operations, expansions, or capital needs. |
| Interest Rates | Often lower due to incentives and subsidies. | Based on credit risk; can be higher. |
| Eligibility Criteria | Projects must meet green and sustainability standards. | Creditworthiness and repayment ability. |
| Impact | Positive environmental impact and enhanced reputation. | No direct environmental benefits. |
| Repayment Term | Varies; often aligned with project lifespan. | Fixed terms with regular payments. |
| Examples | Green bonds, renewable energy loans. | Bank loans, corporate bonds. |
Which is better?
Green financing promotes sustainable investments by funding environmentally friendly projects that reduce carbon footprints and foster renewable energy adoption, aligning with global climate goals. Debt financing provides immediate capital through loans or bonds, enabling businesses to expand operations but often increasing financial risk due to interest obligations. Choosing between green financing and debt financing depends on a company's strategic priorities, risk tolerance, and commitment to sustainability practices.
Connection
Green financing and debt financing are interconnected through the issuance of green bonds, which allow banks and financial institutions to raise capital specifically for environmentally sustainable projects. These debt instruments attract investors focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, aligning financial returns with ecological impact. The integration of green financing within debt financing frameworks promotes sustainable economic growth while mitigating climate risks.
Key Terms
Loan
Debt financing involves borrowing funds with a commitment to repay principal plus interest, typically through traditional loans used by businesses for various capital needs. Green financing specifically targets loans that fund environmentally sustainable projects, such as renewable energy installations or energy efficiency upgrades, often offering favorable terms or incentives to promote eco-friendly investments. Explore how green loans reshape borrowing strategies by supporting both financial growth and environmental impact.
Sustainability Bonds
Sustainability bonds represent a key innovation in financing that combines debt financing principles with environmental and social objectives, channeling capital towards projects that promote sustainable development. These bonds are critical for organizations aiming to balance financial returns with measurable positive impacts on climate action, renewable energy, and social infrastructure. Discover how sustainability bonds can integrate responsible investment goals with effective capital allocation strategies.
Interest Rate
Debt financing typically involves borrowing funds at fixed or variable interest rates, which directly impact the overall cost of capital for businesses or projects. Green financing, often supported by government incentives or subsidies, tends to offer lower interest rates to encourage investment in environmentally sustainable initiatives. Explore more insights on how interest rates influence financial strategies for sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
Debt Financing - Overview, Options, Pros and Cons - This webpage provides an overview of debt financing, including its definition, common forms like bank loans and bonds, and the benefits and drawbacks for businesses.
Debt Financing: Definition & How It Works - This resource explains debt financing, including types such as SBA loans, credit lines, and bonds, and how it works for businesses and startups.
Debt Financing 101: The Basics, Benefits & Drawbacks - This article covers the basics of debt financing, including how it works, the benefits and drawbacks, and considerations for businesses looking to borrow money.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com