Digital identity verification enhances security by using biometric data, government-issued IDs, and AI-powered tools to confirm user identities during banking transactions. Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds a layer of protection by requiring users to provide two different types of credentials, such as a password and a one-time code sent to a mobile device. Discover how these technologies transform banking security and user experience by exploring their key differences and benefits.
Why it is important
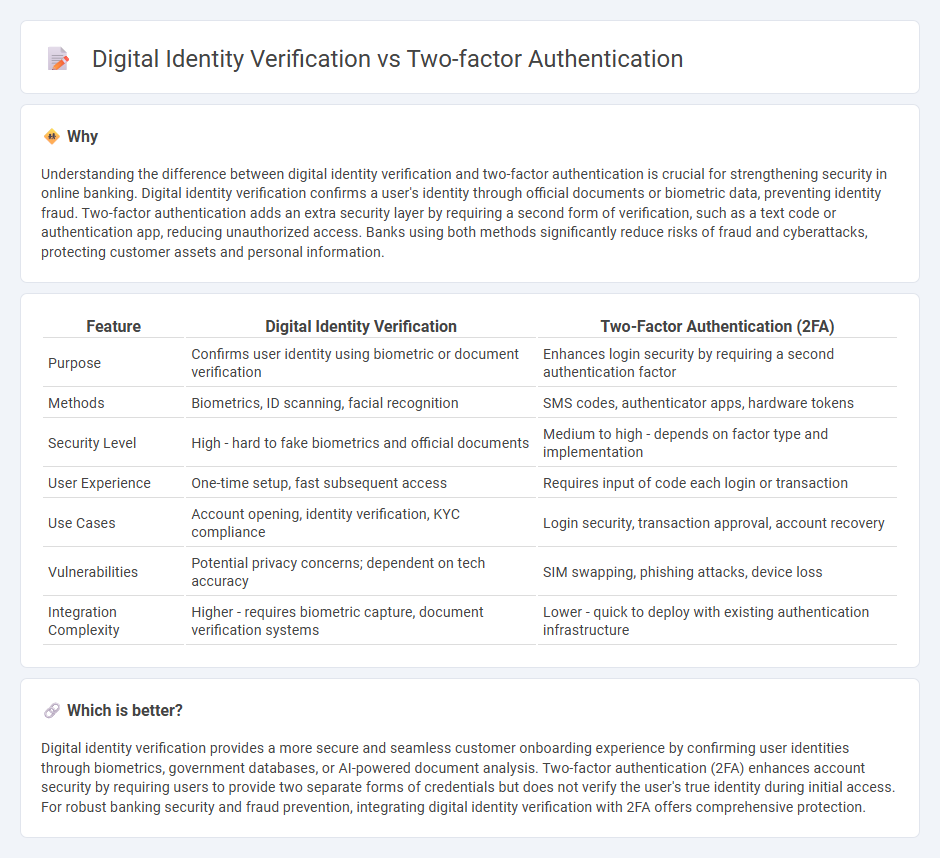
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and two-factor authentication is crucial for strengthening security in online banking. Digital identity verification confirms a user's identity through official documents or biometric data, preventing identity fraud. Two-factor authentication adds an extra security layer by requiring a second form of verification, such as a text code or authentication app, reducing unauthorized access. Banks using both methods significantly reduce risks of fraud and cyberattacks, protecting customer assets and personal information.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Confirms user identity using biometric or document verification | Enhances login security by requiring a second authentication factor |
| Methods | Biometrics, ID scanning, facial recognition | SMS codes, authenticator apps, hardware tokens |
| Security Level | High - hard to fake biometrics and official documents | Medium to high - depends on factor type and implementation |
| User Experience | One-time setup, fast subsequent access | Requires input of code each login or transaction |
| Use Cases | Account opening, identity verification, KYC compliance | Login security, transaction approval, account recovery |
| Vulnerabilities | Potential privacy concerns; dependent on tech accuracy | SIM swapping, phishing attacks, device loss |
| Integration Complexity | Higher - requires biometric capture, document verification systems | Lower - quick to deploy with existing authentication infrastructure |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification provides a more secure and seamless customer onboarding experience by confirming user identities through biometrics, government databases, or AI-powered document analysis. Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances account security by requiring users to provide two separate forms of credentials but does not verify the user's true identity during initial access. For robust banking security and fraud prevention, integrating digital identity verification with 2FA offers comprehensive protection.
Connection
Digital identity verification enhances banking security by accurately confirming a user's identity through biometric data or government-issued IDs, reducing fraud risks. Two-factor authentication (2FA) complements this by requiring a second verification step, such as a one-time code sent to a mobile device, ensuring secure access to accounts. Together, these technologies create a robust defense against unauthorized transactions and identity theft in the banking sector.
Key Terms
One-Time Password (OTP)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring a second verification step, often utilizing One-Time Passwords (OTPs) sent via SMS or generated by authentication apps to confirm user identity. Digital identity verification involves the validation of user credentials and personal data through biometric scans, document uploads, or real-time identity checks, ensuring authenticity beyond just password entry. Explore in-depth how OTP-centric 2FA compares with comprehensive digital identity verification solutions to protect online access.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication, a cornerstone of digital identity verification, leverages unique physiological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans to ensure secure access, offering a higher security level than traditional two-factor authentication (2FA) methods that combine passwords with secondary codes. While 2FA enhances security by requiring multiple verification steps, biometric authentication provides seamless user experience and reduces reliance on passwords vulnerable to phishing or hacking. Explore the advantages of biometric authentication in digital identity verification for a deeper understanding of its role in modern cybersecurity.
Know Your Customer (KYC)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances security in Know Your Customer (KYC) processes by requiring two forms of verification, typically combining something the user knows (password) with something they have (a mobile device). Digital identity verification goes further by using biometric data, document authentication, and AI-driven risk assessments to confirm user identity with higher accuracy and fraud prevention. Explore how integrating these technologies can robustly secure your KYC compliance and customer onboarding.
Source and External Links
What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)? | Definition from TechTarget - Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process where users provide two different authentication factors, such as a password and a biometric factor, to better protect credentials and prevent unauthorized access to accounts and resources.
What is two-factor authentication? | 2-step verification explained - 2FA requires users to prove their identity through two distinct factors, for example by entering a password followed by a code sent to their mobile device, strengthening security beyond password-only methods.
Use Two-Factor Authentication To Protect Your Accounts - Two-factor authentication enhances account security by requiring two types of credentials from categories like something you know (password), something you have (verification code), or something you are (biometrics).
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com