Composable banking empowers financial institutions to customize their services by integrating modular components, enabling rapid innovation and scalability. Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into non-bank platforms, enhancing customer experience by offering seamless transactions within everyday applications. Explore how these banking models transform financial ecosystems and unlock new business opportunities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between composable banking and embedded banking is crucial for financial institutions aiming to enhance agility and customer experience. Composable banking allows banks to build customized, modular services by integrating best-of-breed components, improving innovation speed and operational flexibility. Embedded banking seamlessly integrates financial services into non-banking platforms, expanding reach and creating new revenue streams. Distinguishing these models enables strategic decisions that align with technological capabilities and market demands.
Comparison Table
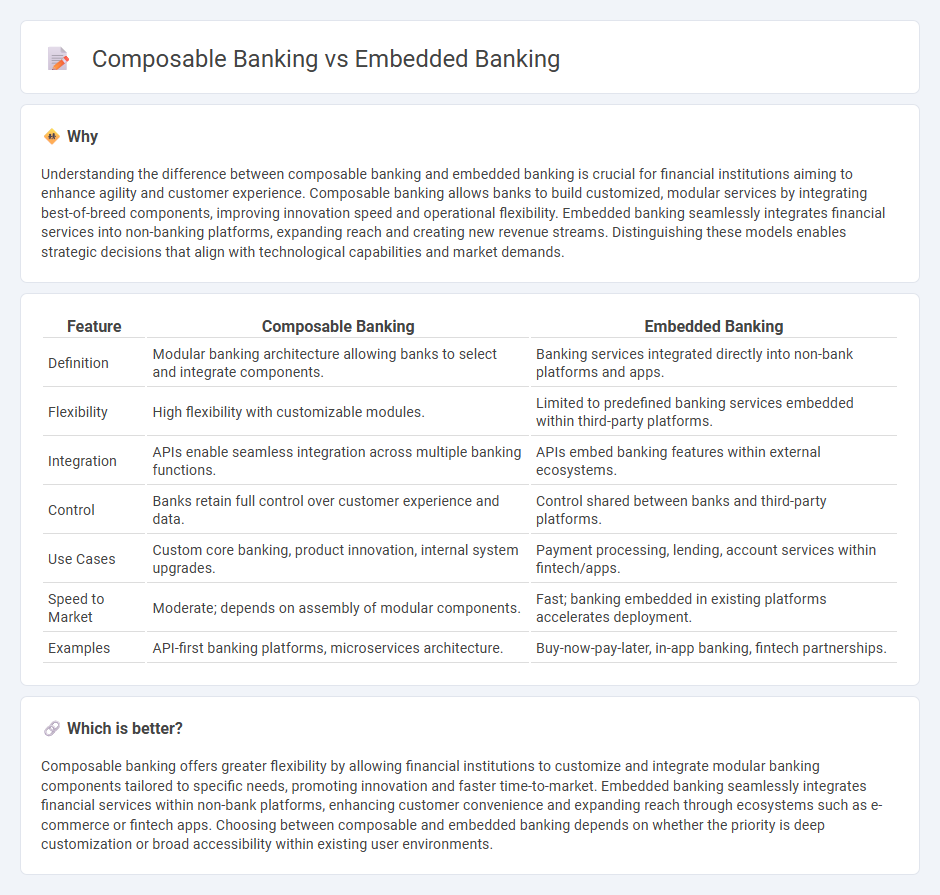
| Feature | Composable Banking | Embedded Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modular banking architecture allowing banks to select and integrate components. | Banking services integrated directly into non-bank platforms and apps. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with customizable modules. | Limited to predefined banking services embedded within third-party platforms. |
| Integration | APIs enable seamless integration across multiple banking functions. | APIs embed banking features within external ecosystems. |
| Control | Banks retain full control over customer experience and data. | Control shared between banks and third-party platforms. |
| Use Cases | Custom core banking, product innovation, internal system upgrades. | Payment processing, lending, account services within fintech/apps. |
| Speed to Market | Moderate; depends on assembly of modular components. | Fast; banking embedded in existing platforms accelerates deployment. |
| Examples | API-first banking platforms, microservices architecture. | Buy-now-pay-later, in-app banking, fintech partnerships. |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers greater flexibility by allowing financial institutions to customize and integrate modular banking components tailored to specific needs, promoting innovation and faster time-to-market. Embedded banking seamlessly integrates financial services within non-bank platforms, enhancing customer convenience and expanding reach through ecosystems such as e-commerce or fintech apps. Choosing between composable and embedded banking depends on whether the priority is deep customization or broad accessibility within existing user environments.
Connection
Composable banking leverages modular APIs to enable financial institutions to integrate diverse banking services rapidly, creating customized solutions. Embedded banking seamlessly incorporates these modular financial services directly into non-bank platforms like e-commerce or fintech apps. This integration allows composable banking components to power embedded banking experiences, enhancing flexibility and user-centric financial offerings.
Key Terms
API Integration
Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into non-bank platforms using pre-built APIs, enabling seamless transactions within apps like e-commerce or ride-sharing. Composable banking leverages modular APIs to allow banks or fintechs to build customizable financial products by combining distinct components, enhancing flexibility and innovation. Explore how API integration strategies differ to optimize customer experience and operational efficiency.
Modularity
Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into non-bank platforms, streamlining user experience and enhancing convenience by leveraging APIs. Composable banking emphasizes modularity, allowing financial institutions to customize and deploy discrete components tailored to specific business needs, driving flexibility and innovation. Explore more to understand how modularity transforms banking ecosystems and accelerates digital transformation.
Customer Experience
Embedded banking integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enhancing customer experience by providing seamless access to banking features within familiar apps. Composable banking leverages modular, API-driven components to customize financial products, enabling personalized and flexible customer journeys. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches revolutionize customer engagement in banking.
Source and External Links
What Is Embedded Banking? - Embedded banking integrates banking services directly into nonfinancial platforms, enabling users to perform banking tasks like paying invoices without leaving familiar apps or systems, thereby saving time and reducing hassle for consumers and businesses alike.
What is embedded banking? What businesses need to know - Embedded banking allows businesses to embed financial services like payments and lending within their own platforms, enabling seamless transactions and financing options such as loans or buy now, pay later directly in their apps or websites.
A complete guide to embedded banking - It involves offering bank accounts, payment methods, credit products, and lending services inside non-financial apps to provide customers with convenient, integrated financial products without redirecting them to traditional banks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com