Digital identity verification streamlines customer onboarding by using encrypted data to confirm user identities remotely, reducing fraud and enhancing security in banking transactions. Biometric authentication relies on unique physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans to provide a secure, seamless access method for account protection. Discover how these technologies revolutionize banking security and customer experience.
Why it is important
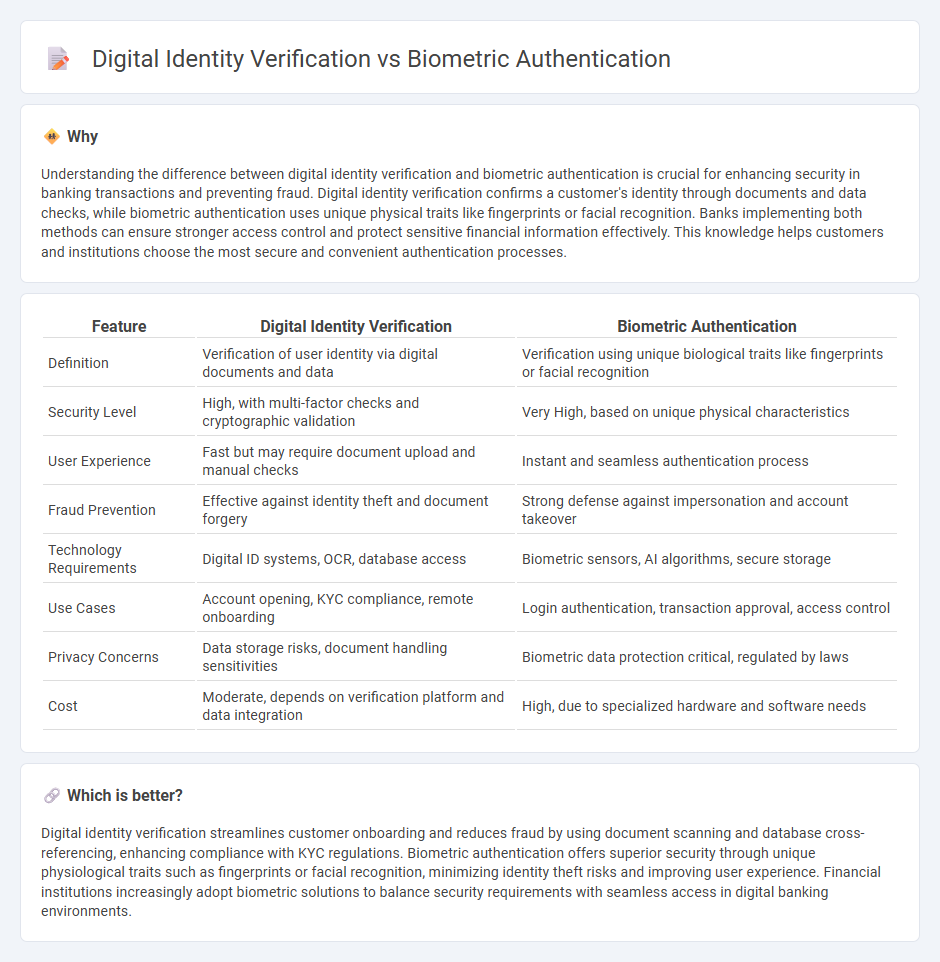
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and biometric authentication is crucial for enhancing security in banking transactions and preventing fraud. Digital identity verification confirms a customer's identity through documents and data checks, while biometric authentication uses unique physical traits like fingerprints or facial recognition. Banks implementing both methods can ensure stronger access control and protect sensitive financial information effectively. This knowledge helps customers and institutions choose the most secure and convenient authentication processes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | Biometric Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verification of user identity via digital documents and data | Verification using unique biological traits like fingerprints or facial recognition |
| Security Level | High, with multi-factor checks and cryptographic validation | Very High, based on unique physical characteristics |
| User Experience | Fast but may require document upload and manual checks | Instant and seamless authentication process |
| Fraud Prevention | Effective against identity theft and document forgery | Strong defense against impersonation and account takeover |
| Technology Requirements | Digital ID systems, OCR, database access | Biometric sensors, AI algorithms, secure storage |
| Use Cases | Account opening, KYC compliance, remote onboarding | Login authentication, transaction approval, access control |
| Privacy Concerns | Data storage risks, document handling sensitivities | Biometric data protection critical, regulated by laws |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on verification platform and data integration | High, due to specialized hardware and software needs |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification streamlines customer onboarding and reduces fraud by using document scanning and database cross-referencing, enhancing compliance with KYC regulations. Biometric authentication offers superior security through unique physiological traits such as fingerprints or facial recognition, minimizing identity theft risks and improving user experience. Financial institutions increasingly adopt biometric solutions to balance security requirements with seamless access in digital banking environments.
Connection
Digital identity verification and biometric authentication are interconnected as biometric authentication uses unique physical characteristics like fingerprints or facial recognition to confirm a person's identity digitally. Banks employ these technologies to enhance security, reduce fraud, and streamline customer onboarding processes. The integration of biometric data within digital identity frameworks ensures accurate, real-time verification, minimizing identity theft and unauthorized access.
Key Terms
**Biometric Authentication:**
Biometric authentication leverages unique physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans to verify individual identities with high accuracy and security. This technology reduces the risk of fraud by relying on traits that are difficult to replicate or steal compared to traditional passwords or tokens. Explore more about how biometric authentication enhances security frameworks and user experience.
Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition, a leading biometric authentication method, uses unique patterns of ridges and valleys on fingers to verify identity with high accuracy and speed. Digital identity verification integrates multiple data points, including fingerprint scans, to confirm an individual's identity across online platforms and services, enhancing security against fraud. Explore how fingerprint recognition transforms digital identity verification to ensure robust protection and seamless user experience.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology plays a crucial role in biometric authentication by analyzing unique facial features to grant secure access, whereas digital identity verification uses facial recognition combined with other data points to prove an individual's identity online. Biometric authentication focuses primarily on access control through physical traits, while digital identity verification integrates multiple verification layers for enhanced fraud prevention. Explore deeper insights into how facial recognition transforms security protocols and user experience.
Source and External Links
What is Biometric Authentication and How Does It Work? - Biometric authentication verifies a user's identity using unique biological traits like fingerprints, faces, or iris patterns and is generally more secure than traditional authentication methods.
What is Biometric Authentication? - It safeguards sensitive information by confirming identity through unique physical features such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or voice recognition, making it harder to hack than passwords.
What is Biometric Authentication? Use Cases, Pros & Cons - Biometric authentication creates a unique data model from physical or behavioral traits to authenticate access, offering stronger security and convenience compared to username and password systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com