Income streaming in banking involves diversifying revenue sources through multiple financial products like loans, fees, and interest income, providing stable cash flow. Dividend income, on the other hand, is the profit distribution paid to shareholders, reflecting company performance and impacting personal or institutional investment returns. Explore the nuances and benefits of these income strategies to optimize your banking and investment decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between income streaming and dividend income is crucial for effective banking and investment strategies, as income streaming involves regularly scheduled payments from various sources, while dividend income specifically refers to earnings distributed by corporations to shareholders. Income streaming provides financial stability through diverse revenue channels, aiding in risk management and cash flow planning. Dividend income signals a company's profitability and can impact tax obligations differently than income streaming. Clear knowledge of both helps optimize portfolio returns and tax efficiency in banking.
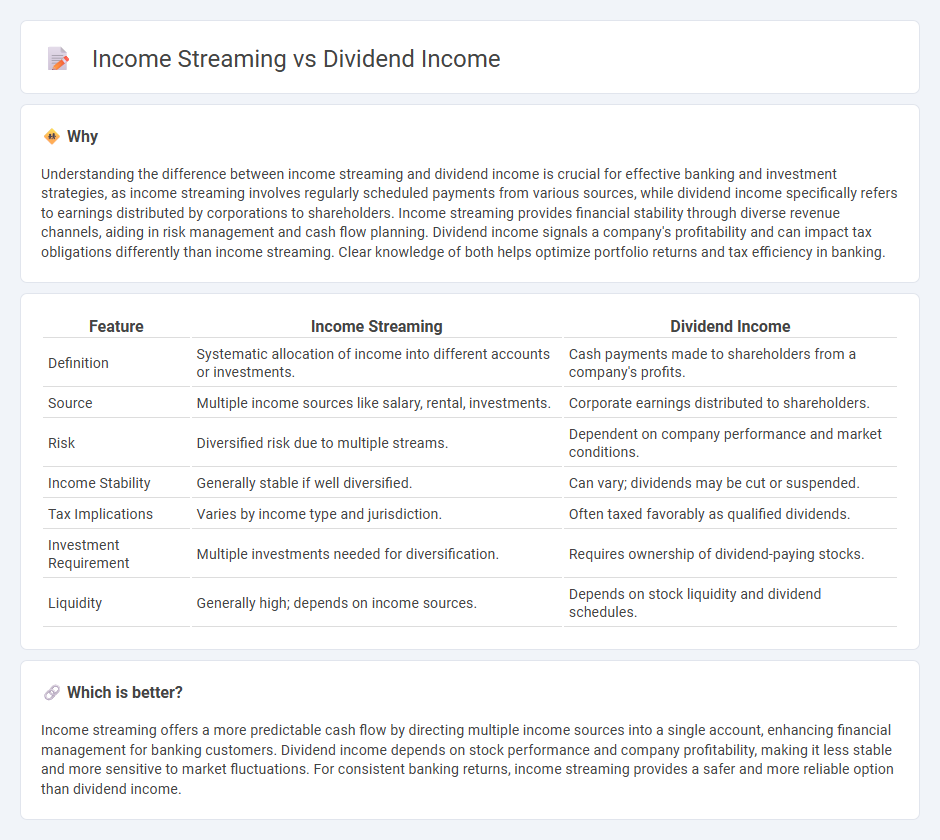
Comparison Table
| Feature | Income Streaming | Dividend Income |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic allocation of income into different accounts or investments. | Cash payments made to shareholders from a company's profits. |
| Source | Multiple income sources like salary, rental, investments. | Corporate earnings distributed to shareholders. |
| Risk | Diversified risk due to multiple streams. | Dependent on company performance and market conditions. |
| Income Stability | Generally stable if well diversified. | Can vary; dividends may be cut or suspended. |
| Tax Implications | Varies by income type and jurisdiction. | Often taxed favorably as qualified dividends. |
| Investment Requirement | Multiple investments needed for diversification. | Requires ownership of dividend-paying stocks. |
| Liquidity | Generally high; depends on income sources. | Depends on stock liquidity and dividend schedules. |
Which is better?
Income streaming offers a more predictable cash flow by directing multiple income sources into a single account, enhancing financial management for banking customers. Dividend income depends on stock performance and company profitability, making it less stable and more sensitive to market fluctuations. For consistent banking returns, income streaming provides a safer and more reliable option than dividend income.
Connection
Income streaming in banking involves diversifying revenue sources, with dividend income serving as a key component by providing consistent cash flow from investments in dividend-paying stocks or financial instruments. This strategy enhances financial stability and profitability by balancing interest income with regular dividend payouts. Banks leverage dividend income to support sustainable operations and investor returns, integrating it into broader income management practices.
Key Terms
Passive Income
Dividend income provides passive income through regular payouts from company profits, offering investors a steady cash flow without active management. Income streaming, on the other hand, encompasses diverse passive income sources like rental properties, royalties, and online businesses, creating multiple revenue streams that enhance financial stability. Explore more strategies to maximize passive income and diversify your financial portfolio effectively.
Yield
Dividend income offers investors a stream of earnings derived from corporate profits, typically providing a consistent yield based on company performance and payout ratios. Income streaming, by contrast, involves multiple revenue streams such as rental income, royalties, or interest payments, often diversifying yield sources for enhanced stability. Explore deeper insights into optimizing yield through dividend income and income streaming strategies.
Capital Distribution
Dividend income represents periodic payments made to shareholders from a company's profits, offering a steady cash flow often favored by income investors. Income streaming through capital distribution involves return of investors' original capital rather than profit earnings, impacting the investment's cost basis and potential tax treatment. Explore further to understand how capital distribution influences your investment income strategy and tax implications.
Source and External Links
How are dividends taxed? - Vanguard - Dividends are payments from companies to shareholders, often quarterly, and are taxed either as ordinary income or at the lower qualified dividend rate depending on how long you've held the shares.
Is There a Dividend Tax? Your Guide to Taxes on Dividends - Ordinary dividends are taxed at your regular income tax rate, while qualified dividends benefit from capital gains tax rates, which can be 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on your income and filing status.
Dividends | Department of Revenue | Commonwealth of Pennsylvania - Pennsylvania taxes capital gain distributions from funds as dividend income and requires residents to report any excess return of capital distributions over basis as taxable gain.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com