Neobanking represents a digital-first approach to banking, offering seamless mobile and online financial services without traditional brick-and-mortar branches, while direct banking combines both online and telephone banking, often provided by established banks without physical branches. Neobanks focus on user-friendly interfaces, lower fees, and innovative features, whereas direct banks emphasize competitive interest rates and comprehensive regulatory protections. Explore how these banking models can transform your financial experience and meet your unique needs.
Why it is important
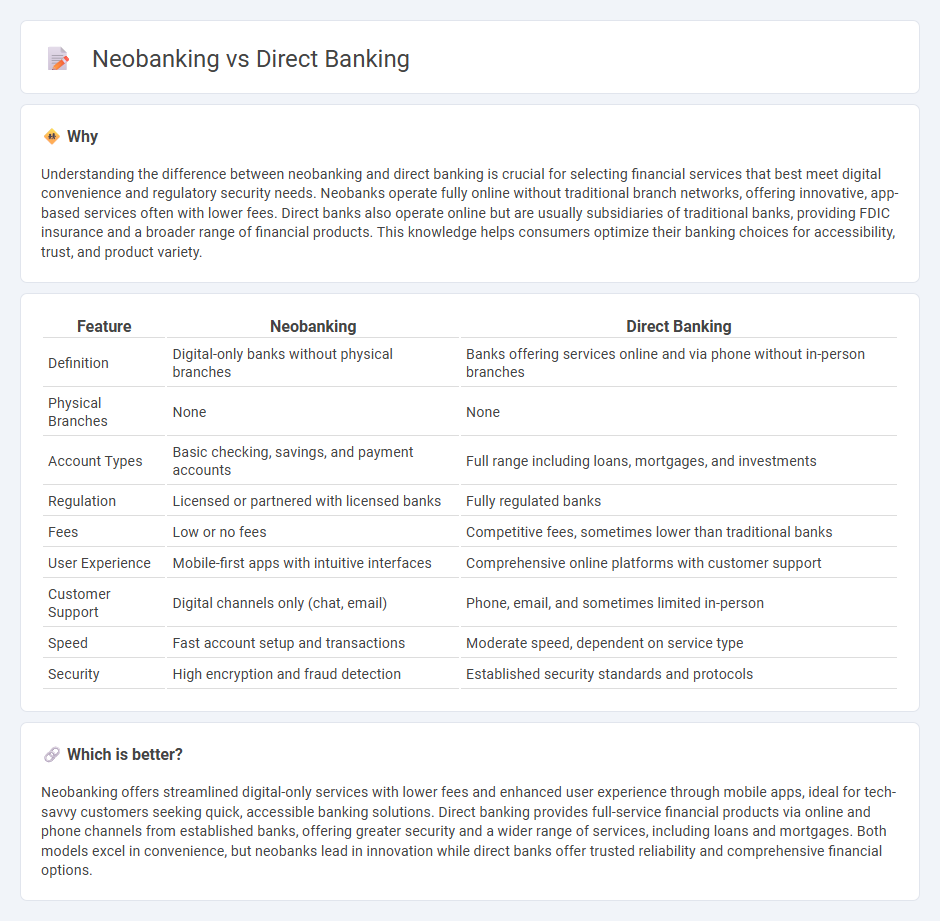
Understanding the difference between neobanking and direct banking is crucial for selecting financial services that best meet digital convenience and regulatory security needs. Neobanks operate fully online without traditional branch networks, offering innovative, app-based services often with lower fees. Direct banks also operate online but are usually subsidiaries of traditional banks, providing FDIC insurance and a broader range of financial products. This knowledge helps consumers optimize their banking choices for accessibility, trust, and product variety.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobanking | Direct Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital-only banks without physical branches | Banks offering services online and via phone without in-person branches |
| Physical Branches | None | None |
| Account Types | Basic checking, savings, and payment accounts | Full range including loans, mortgages, and investments |
| Regulation | Licensed or partnered with licensed banks | Fully regulated banks |
| Fees | Low or no fees | Competitive fees, sometimes lower than traditional banks |
| User Experience | Mobile-first apps with intuitive interfaces | Comprehensive online platforms with customer support |
| Customer Support | Digital channels only (chat, email) | Phone, email, and sometimes limited in-person |
| Speed | Fast account setup and transactions | Moderate speed, dependent on service type |
| Security | High encryption and fraud detection | Established security standards and protocols |
Which is better?
Neobanking offers streamlined digital-only services with lower fees and enhanced user experience through mobile apps, ideal for tech-savvy customers seeking quick, accessible banking solutions. Direct banking provides full-service financial products via online and phone channels from established banks, offering greater security and a wider range of services, including loans and mortgages. Both models excel in convenience, but neobanks lead in innovation while direct banks offer trusted reliability and comprehensive financial options.
Connection
Neobanking and direct banking are connected through their digital-first approach, eliminating the need for physical branches and enabling customers to perform all banking activities online. Both models leverage advanced technology platforms to offer seamless, real-time financial services, including account management, payments, and loans, enhancing customer convenience and reducing operational costs for banks. The integration of mobile apps, APIs, and cloud computing underpins their shared infrastructure, driving innovation and personalized banking experiences.
Key Terms
Digital-Only Platform
Direct banking operates through established banks offering digital-only platforms without physical branches, emphasizing cost savings and comprehensive services. Neobanking involves fintech companies providing exclusively digital financial services with a focus on user-friendly interfaces and niche banking solutions. Explore further to understand how these digital-only platforms reshape modern banking.
Regulatory Licensing
Direct banking institutions operate under traditional banking licenses regulated by national financial authorities, ensuring compliance with established banking laws and customer protection standards. Neobanks typically partner with licensed banks or obtain specialized financial licenses to offer digital-only services, often facing evolving regulatory frameworks tailored to fintech innovations. Explore the detailed regulatory distinctions to understand how licensing impacts service security and customer trust in direct banking and neobanking models.
Customer Self-Service
Direct banking enables customers to access financial services through traditional banks' online platforms, prioritizing convenience and security in self-service options. Neobanking offers a fully digital experience with innovative interfaces and real-time customer support, enhancing usability and personalization in financial management. Explore the key features and benefits of self-service in both banking models to find the best fit for your needs.
Source and External Links
Direct bank - A direct bank is a financial institution offering services exclusively online without branch networks, providing convenience and cost-efficiency through digital platforms and often FDIC insurance, distinct from online banking offered by traditional banks and from neobanks which lack federal charters.
My Banking Direct - An online financial service of Flagstar Bank offering FDIC-insured high-yield savings accounts with competitive rates, operating as a direct bank with secure digital access.
FNBO Direct: High-Yield Savings & Money Market Accounts - An FDIC-insured direct bank providing secure online and mobile banking tools for managing savings and payments digitally 24/7, with easy account opening for U.S. residents.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com