Neo banking offers fully digital financial services without traditional branch networks, providing seamless mobile-based banking experiences. Direct banks operate exclusively online but are often subsidiaries of established banks, combining digital convenience with regulatory trust. Explore the differences between neo banking and direct banks to find the best fit for your financial needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between neo banking and direct banking is crucial for optimizing financial management and tailoring banking services to individual needs. Neo banks operate exclusively online without physical branches, offering innovative digital experiences and lower fees, while direct banks combine online services with physical branches and often focus on traditional banking products. Recognizing these distinctions aids consumers in selecting the best banking model for convenience, security, and service variety. This knowledge empowers users to leverage technological advancements or personal interaction based on their preferences and financial goals.
Comparison Table
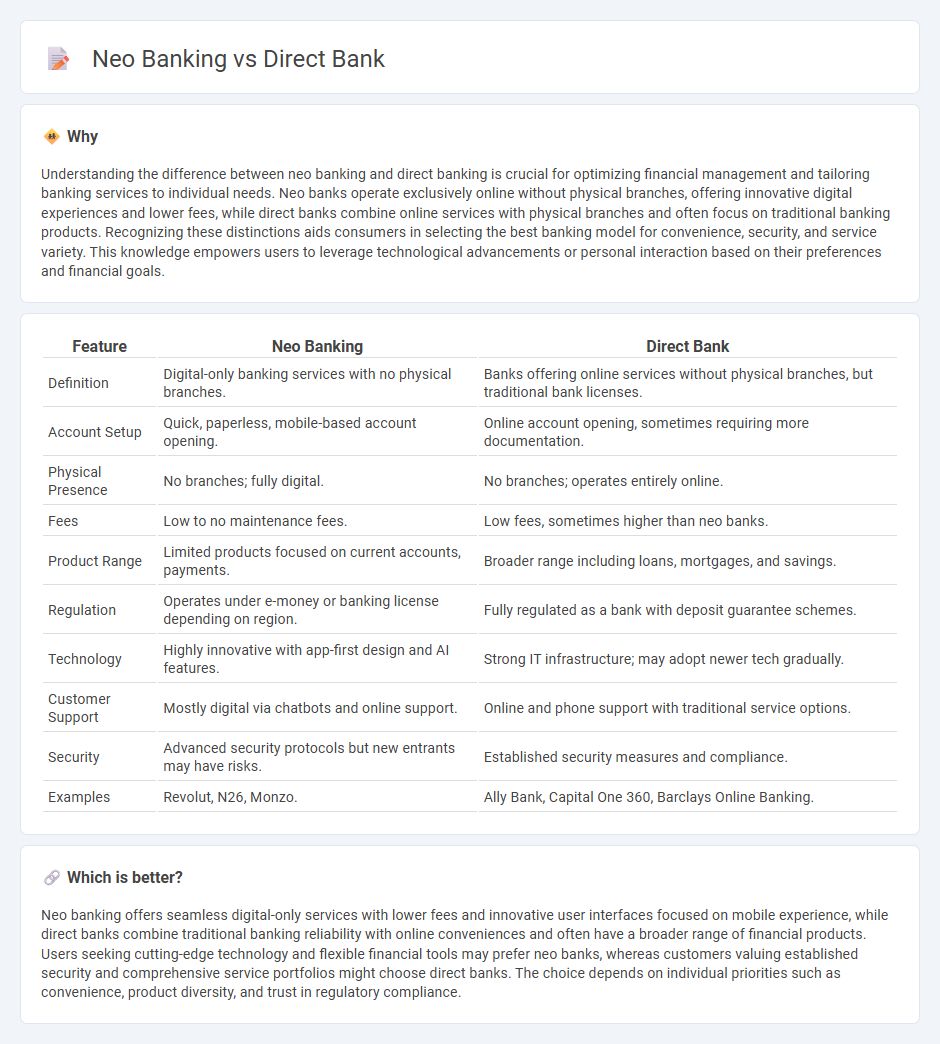
| Feature | Neo Banking | Direct Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital-only banking services with no physical branches. | Banks offering online services without physical branches, but traditional bank licenses. |
| Account Setup | Quick, paperless, mobile-based account opening. | Online account opening, sometimes requiring more documentation. |
| Physical Presence | No branches; fully digital. | No branches; operates entirely online. |
| Fees | Low to no maintenance fees. | Low fees, sometimes higher than neo banks. |
| Product Range | Limited products focused on current accounts, payments. | Broader range including loans, mortgages, and savings. |
| Regulation | Operates under e-money or banking license depending on region. | Fully regulated as a bank with deposit guarantee schemes. |
| Technology | Highly innovative with app-first design and AI features. | Strong IT infrastructure; may adopt newer tech gradually. |
| Customer Support | Mostly digital via chatbots and online support. | Online and phone support with traditional service options. |
| Security | Advanced security protocols but new entrants may have risks. | Established security measures and compliance. |
| Examples | Revolut, N26, Monzo. | Ally Bank, Capital One 360, Barclays Online Banking. |
Which is better?
Neo banking offers seamless digital-only services with lower fees and innovative user interfaces focused on mobile experience, while direct banks combine traditional banking reliability with online conveniences and often have a broader range of financial products. Users seeking cutting-edge technology and flexible financial tools may prefer neo banks, whereas customers valuing established security and comprehensive service portfolios might choose direct banks. The choice depends on individual priorities such as convenience, product diversity, and trust in regulatory compliance.
Connection
Neo banking and direct banking both revolutionize traditional financial services by offering digital-first platforms that eliminate physical branches. Neo banks operate entirely online, providing seamless mobile and web-based banking experiences, while direct banks also function without branches but often belong to established financial institutions. Both models leverage technology to reduce operational costs, enhance convenience, and deliver real-time financial services to tech-savvy customers.
Key Terms
Digital-Only
Direct banks operate without physical branches, offering traditional banking services through digital platforms with established institutions, while neo banks are fintech startups providing innovative, digital-only financial products often without full banking licenses. Both emphasize seamless mobile experiences and lower fees but differ in regulation, service scope, and technology integration. Explore more to understand which digital-only banking model suits your financial needs.
Banking License
Direct banks operate under full banking licenses, allowing them to offer a comprehensive range of regulated financial services including deposits, loans, and payment products. Neo banks, while digitally driven, often partner with licensed banks or operate under limited licenses, restricting their ability to independently provide traditional banking functions. Explore the distinct regulatory frameworks that shape direct banks and neo banks for a deeper understanding.
Third-Party Partnerships
Direct banks operate primarily through their own infrastructure, limiting third-party collaborations to maintain control and security over financial services. Neo banks heavily rely on extensive third-party partnerships, integrating fintech innovations like payment processors, lending platforms, and customer service tools to enhance user experience and scalability. Explore how these differing strategies impact service offerings and customer engagement in the evolving digital banking landscape.
Source and External Links
Direct bank - Wikipedia - A direct bank, also called a branch-less or virtual bank, offers banking services solely via digital channels like the Internet, mobile apps, and email without physical branches, often providing FDIC insured accounts and other traditional banking services online.
My Banking Direct - Secure and Competitive Banking Solutions - My Banking Direct is an online banking service by Flagstar Bank that provides FDIC-insured deposit accounts such as high-yield savings with competitive interest rates, accessible entirely online without branch visits.
DIRECT Home Rewards - DIRECT offers a digital banking platform with FDIC-insured accounts through Pacific West Bank, including prepaid debit cards, mobile app access, and security features like AES 256 encryption and PCI compliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com