Sustainable investing focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to generate long-term financial returns and positive societal impact. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) involves companies proactively managing their business processes to produce an overall positive impact on society and the environment. Explore the key differences and complementary roles of sustainable investing and CSR in reshaping modern banking.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and corporate social responsibility (CSR) is crucial for making informed financial decisions that align with ethical and environmental goals. Sustainable investing focuses on funding companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term financial returns and positive impact. Corporate social responsibility refers to a company's internal policies and practices aimed at ethical behavior, community engagement, and environmental stewardship. Knowing these distinctions helps investors identify genuine impact opportunities and avoid misleading claims in the banking sector.
Comparison Table
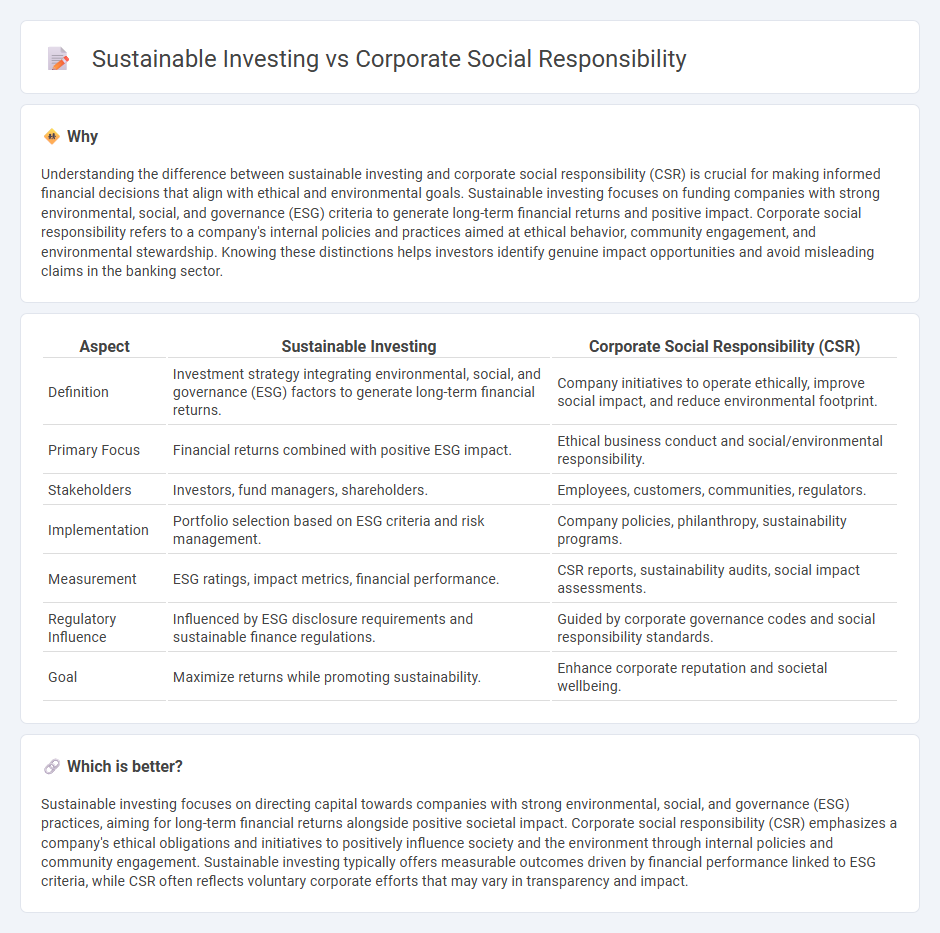
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment strategy integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors to generate long-term financial returns. | Company initiatives to operate ethically, improve social impact, and reduce environmental footprint. |
| Primary Focus | Financial returns combined with positive ESG impact. | Ethical business conduct and social/environmental responsibility. |
| Stakeholders | Investors, fund managers, shareholders. | Employees, customers, communities, regulators. |
| Implementation | Portfolio selection based on ESG criteria and risk management. | Company policies, philanthropy, sustainability programs. |
| Measurement | ESG ratings, impact metrics, financial performance. | CSR reports, sustainability audits, social impact assessments. |
| Regulatory Influence | Influenced by ESG disclosure requirements and sustainable finance regulations. | Guided by corporate governance codes and social responsibility standards. |
| Goal | Maximize returns while promoting sustainability. | Enhance corporate reputation and societal wellbeing. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on directing capital towards companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, aiming for long-term financial returns alongside positive societal impact. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes a company's ethical obligations and initiatives to positively influence society and the environment through internal policies and community engagement. Sustainable investing typically offers measurable outcomes driven by financial performance linked to ESG criteria, while CSR often reflects voluntary corporate efforts that may vary in transparency and impact.
Connection
Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial decision-making, aligning investments with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals focused on ethical practices and community impact. Banks play a crucial role by funding businesses that prioritize sustainability and responsible governance, thereby driving positive social and environmental outcomes. This connection enhances long-term financial performance while fostering accountability and transparency within corporate entities.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) emphasizes a company's ethical obligations and social impact through environmental stewardship, social equity, and transparent governance. Sustainable investing integrates ESG criteria into financial analysis to identify companies that demonstrate long-term environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and strong governance practices. Explore the distinctions and synergies between CSR and sustainable investing to enhance your understanding of ESG strategies.
Impact Investing
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes a company's ethical practices and commitment to social and environmental causes, directly impacting operational processes and stakeholder engagement. Sustainable investing, particularly impact investing, allocates capital to companies and projects generating measurable, positive social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. Discover how impact investing bridges responsible business practices and financial growth to drive meaningful change.
Stakeholder Engagement
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) centers on a company's commitment to ethical practices and positive community impact through direct stakeholder engagement, including employees, customers, and local communities. Sustainable investing prioritizes integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to drive long-term value and address stakeholder concerns at a systemic level. Explore how both strategies enhance stakeholder relationships and create shared value for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Corporate Social Responsibility - Corporate social responsibility (CSR) involves businesses operating with principles that positively impact society and the environment, often surpassing legal obligations.
What is Corporate Social Responsibility? Guide & Examples - This guide describes CSR as a company's efforts to improve society, including actions like donations, volunteer programs, and environmental practices.
Corporate Social Responsibility - CSR is a form of international private business self-regulation that aims to contribute to societal goals through philanthropy, activism, or charitable activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com