Stablecoin rails offer faster transaction settlement and enhanced transparency compared to traditional ACH systems, leveraging blockchain technology for near-instantaneous cross-border payments. ACH transfers, while reliable and widely adopted, often involve longer processing times and intermediary fees that can slow down liquidity movement. Explore the evolving landscape of payment infrastructures to understand how these innovations impact financial operations.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between stablecoin rails and ACH is crucial for optimizing transaction speed and cost in banking; stablecoin rails provide near-instant, low-fee cross-border payments using blockchain technology. ACH (Automated Clearing House) offers reliable, regulated, but slower and often costlier bank transfer services within the U.S. Banks leveraging stablecoin rails can enhance liquidity management and offer real-time settlement, whereas ACH remains the backbone for traditional domestic financial transactions. Knowledge of these systems enables financial institutions to select the most efficient payment method based on use case and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
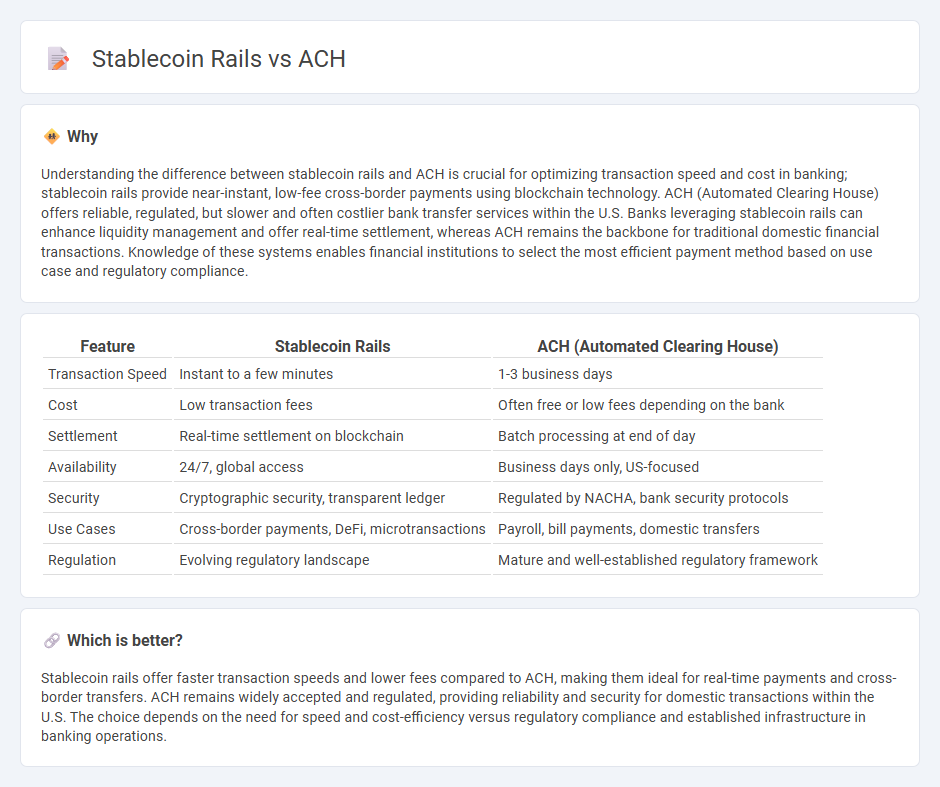
| Feature | Stablecoin Rails | ACH (Automated Clearing House) |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Instant to a few minutes | 1-3 business days |
| Cost | Low transaction fees | Often free or low fees depending on the bank |
| Settlement | Real-time settlement on blockchain | Batch processing at end of day |
| Availability | 24/7, global access | Business days only, US-focused |
| Security | Cryptographic security, transparent ledger | Regulated by NACHA, bank security protocols |
| Use Cases | Cross-border payments, DeFi, microtransactions | Payroll, bill payments, domestic transfers |
| Regulation | Evolving regulatory landscape | Mature and well-established regulatory framework |
Which is better?
Stablecoin rails offer faster transaction speeds and lower fees compared to ACH, making them ideal for real-time payments and cross-border transfers. ACH remains widely accepted and regulated, providing reliability and security for domestic transactions within the U.S. The choice depends on the need for speed and cost-efficiency versus regulatory compliance and established infrastructure in banking operations.
Connection
Stablecoin rails leverage blockchain technology to enable faster, transparent, and cost-effective cross-border payments compared to traditional ACH (Automated Clearing House) transactions, which rely on batch processing and banking intermediaries. While ACH processes handle domestic electronic fund transfers with delays of one to two business days, stablecoin rails offer near-instant settlement by recording transactions on decentralized ledgers. Integrating stablecoin rails with ACH systems can enhance liquidity management and streamline payment reconciliation for banks and financial institutions.
Key Terms
Settlement Speed
ACH transfers typically settle within 1-3 business days, reflecting traditional banking system constraints and operational hours. Stablecoin rails operate on blockchain technology, offering near-instant settlement times that can occur 24/7, independent of banking hours. Explore the advantages of stablecoin settlement speeds and how they transform digital transactions.
Counterparty Risk
ACH payments rely on traditional banking networks, exposing transactions to counterparty risk from banks and intermediaries handling funds. Stablecoin rails utilize blockchain technology, reducing reliance on central authorities and offering increased transparency and security against counterparty failures. Explore the differences between ACH and stablecoin rails to understand how counterparty risk influences payment reliability.
Regulatory Compliance
ACH payment rails are governed by strict federal regulations such as the Electronic Fund Transfer Act (EFTA) and overseen by NACHA, ensuring thorough compliance protocols and consumer protection measures. Stablecoin rails operate under emerging regulatory frameworks that vary by jurisdiction, often requiring adherence to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) guidelines to prevent illicit activities. Explore the evolving regulatory landscape to understand how ACH and stablecoins address compliance challenges in the digital payments ecosystem.
Source and External Links
What is an ACH Payment? | HR & Payroll Glossary - The Automated Clearing House (ACH) is an electronic network that facilitates secure fund transfers between individuals, businesses, and financial institutions in the US, handling billions of transactions annually.
What is an ACH transaction? - An ACH transaction is an electronic money transfer between banks and credit unions, commonly used for direct deposits, bill payments, and routine debits, with processing times that can range from same-day to several business days.
Automated Clearinghouse Services - The ACH system is a nationwide US network where depository institutions send batches of electronic credit and debit transfers, supporting services like payroll direct deposit, social security benefits, and bill payments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com