Crypto custody involves securing digital assets such as cryptocurrencies and private keys using specialized hardware and software solutions to prevent unauthorized access and theft. Data custody focuses on managing and protecting sensitive information like personal data, financial records, and business documents through encryption, access controls, and compliance with data protection regulations. Explore the differences and best practices for safeguarding your assets by learning more about crypto custody versus data custody.
Why it is important
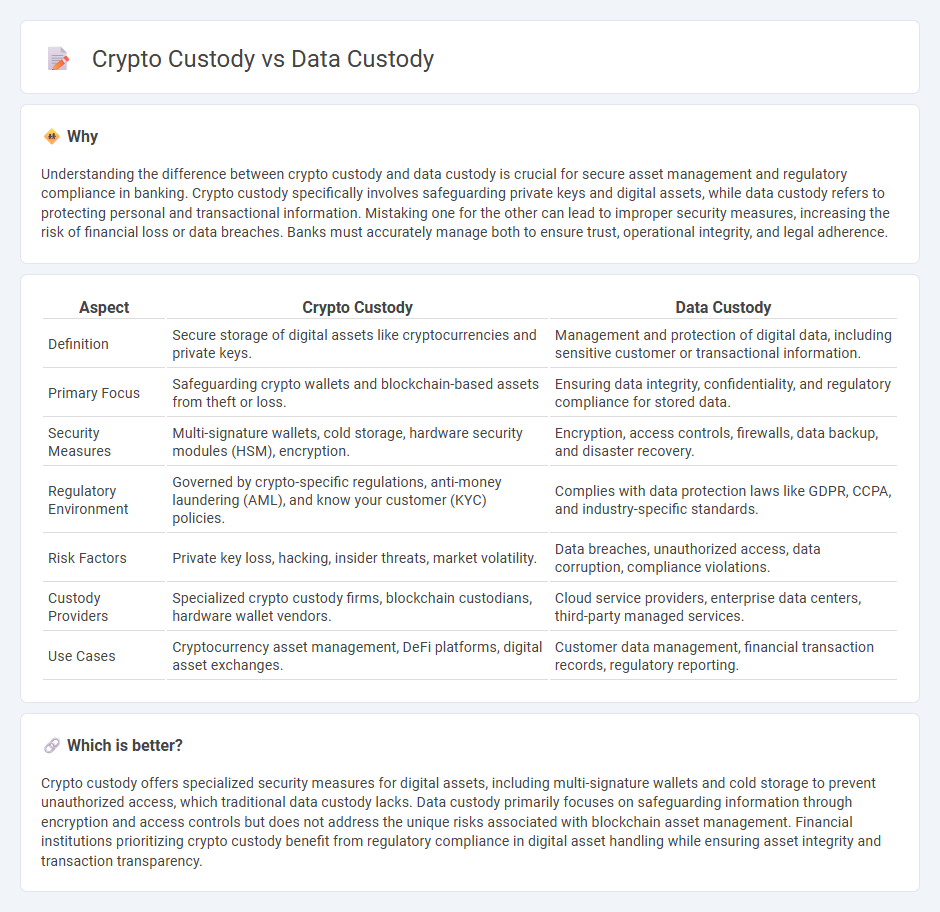
Understanding the difference between crypto custody and data custody is crucial for secure asset management and regulatory compliance in banking. Crypto custody specifically involves safeguarding private keys and digital assets, while data custody refers to protecting personal and transactional information. Mistaking one for the other can lead to improper security measures, increasing the risk of financial loss or data breaches. Banks must accurately manage both to ensure trust, operational integrity, and legal adherence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Crypto Custody | Data Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Secure storage of digital assets like cryptocurrencies and private keys. | Management and protection of digital data, including sensitive customer or transactional information. |
| Primary Focus | Safeguarding crypto wallets and blockchain-based assets from theft or loss. | Ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and regulatory compliance for stored data. |
| Security Measures | Multi-signature wallets, cold storage, hardware security modules (HSM), encryption. | Encryption, access controls, firewalls, data backup, and disaster recovery. |
| Regulatory Environment | Governed by crypto-specific regulations, anti-money laundering (AML), and know your customer (KYC) policies. | Complies with data protection laws like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific standards. |
| Risk Factors | Private key loss, hacking, insider threats, market volatility. | Data breaches, unauthorized access, data corruption, compliance violations. |
| Custody Providers | Specialized crypto custody firms, blockchain custodians, hardware wallet vendors. | Cloud service providers, enterprise data centers, third-party managed services. |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrency asset management, DeFi platforms, digital asset exchanges. | Customer data management, financial transaction records, regulatory reporting. |
Which is better?
Crypto custody offers specialized security measures for digital assets, including multi-signature wallets and cold storage to prevent unauthorized access, which traditional data custody lacks. Data custody primarily focuses on safeguarding information through encryption and access controls but does not address the unique risks associated with blockchain asset management. Financial institutions prioritizing crypto custody benefit from regulatory compliance in digital asset handling while ensuring asset integrity and transaction transparency.
Connection
Crypto custody and data custody intersect critically in banking through the secure management of digital assets and sensitive information. Both require advanced encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication to protect against cyber threats and ensure regulatory compliance. Effective integration of crypto and data custody solutions enhances the integrity and accessibility of financial transactions in modern banking systems.
Key Terms
Ownership
Data custody refers to the responsibility of securely storing and managing digital information without transferring ownership, whereas crypto custody involves the safekeeping of private keys that grant actual ownership and control over cryptocurrency assets. Ownership in crypto custody is intrinsic, as possession of keys directly equates to control over digital assets, unlike data custody where the custodian manages data on behalf of the owner. Discover more about the critical distinctions between data custody and crypto custody to understand their implications on security and control.
Security
Data custody involves the safeguarding of digital information through access controls, encryption, and regular backups to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Crypto custody specifically secures private keys and digital assets using hardware security modules (HSMs), multi-signature wallets, and cold storage solutions to prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats. Explore detailed security measures and best practices in data and crypto custody to strengthen your protection strategies.
Access Control
Data custody involves managing and protecting digital information through established access control mechanisms such as role-based permissions and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access. Crypto custody specifically secures private keys and digital assets using advanced cryptographic techniques, hardware security modules (HSMs), and multi-signature wallets to ensure exclusive control and prevent asset theft. Explore detailed strategies for implementing effective access control in both data and crypto custody to enhance security frameworks.
Source and External Links
Five reasons you need a data custody plan - Data custody refers to how data is protected and safeguarded throughout its lifecycle, defining ownership, usage, storage, and compliance responsibilities to ensure security and clear governance within organizations.
Why Chain Of Custody is Key for Data Security & Business Growth - Chain of custody is a process to track and document every interaction with data, creating audit trails, enforcing access controls, and supporting forensic analysis for security incidents and regulatory compliance.
Chain of custody: do you know where your data is? - Chain of custody provides a fully documented history of where digital assets live, who controls them, and how they are managed or securely destroyed, critical for regulatory compliance and risk mitigation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com