Synthetic identity fraud manipulates fabricated personal information to create false identities for fraudulent banking activities, often resulting in significant financial losses for lenders. Loan stacking involves multiple simultaneous loan applications across various institutions, exploiting the system before lenders can detect the overextension of credit. Explore in-depth strategies to identify and prevent these sophisticated banking frauds.
Why it is important
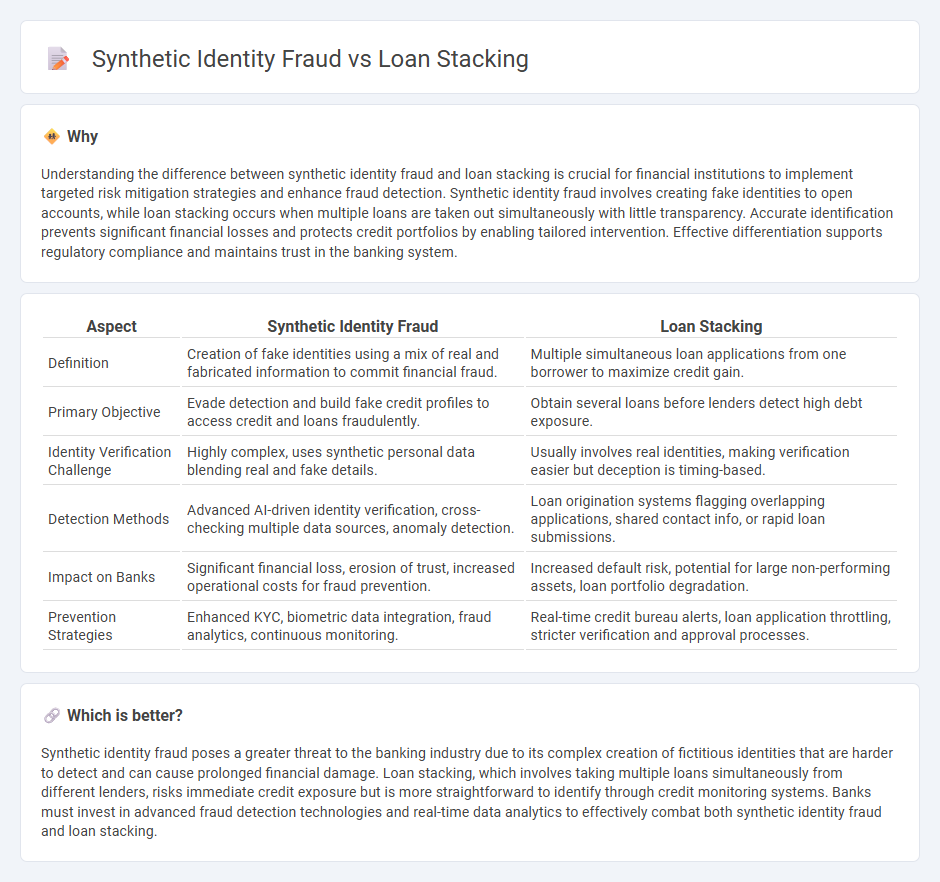
Understanding the difference between synthetic identity fraud and loan stacking is crucial for financial institutions to implement targeted risk mitigation strategies and enhance fraud detection. Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities to open accounts, while loan stacking occurs when multiple loans are taken out simultaneously with little transparency. Accurate identification prevents significant financial losses and protects credit portfolios by enabling tailored intervention. Effective differentiation supports regulatory compliance and maintains trust in the banking system.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Identity Fraud | Loan Stacking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creation of fake identities using a mix of real and fabricated information to commit financial fraud. | Multiple simultaneous loan applications from one borrower to maximize credit gain. |
| Primary Objective | Evade detection and build fake credit profiles to access credit and loans fraudulently. | Obtain several loans before lenders detect high debt exposure. |
| Identity Verification Challenge | Highly complex, uses synthetic personal data blending real and fake details. | Usually involves real identities, making verification easier but deception is timing-based. |
| Detection Methods | Advanced AI-driven identity verification, cross-checking multiple data sources, anomaly detection. | Loan origination systems flagging overlapping applications, shared contact info, or rapid loan submissions. |
| Impact on Banks | Significant financial loss, erosion of trust, increased operational costs for fraud prevention. | Increased default risk, potential for large non-performing assets, loan portfolio degradation. |
| Prevention Strategies | Enhanced KYC, biometric data integration, fraud analytics, continuous monitoring. | Real-time credit bureau alerts, loan application throttling, stricter verification and approval processes. |
Which is better?
Synthetic identity fraud poses a greater threat to the banking industry due to its complex creation of fictitious identities that are harder to detect and can cause prolonged financial damage. Loan stacking, which involves taking multiple loans simultaneously from different lenders, risks immediate credit exposure but is more straightforward to identify through credit monitoring systems. Banks must invest in advanced fraud detection technologies and real-time data analytics to effectively combat both synthetic identity fraud and loan stacking.
Connection
Synthetic identity fraud and loan stacking are interconnected threats in banking where criminals create fabricated identities to obtain multiple loans simultaneously from various lenders. This strategy exploits weaknesses in credit verification systems, enabling fraudsters to amass significant debt without immediate detection. Financial institutions face increased risks of default and revenue loss due to these coordinated fraudulent activities.
Key Terms
Credit Risk
Loan stacking involves multiple lenders issuing loans to a borrower without awareness of the existing debt, significantly increasing credit risk due to overlapping liabilities and potential default. Synthetic identity fraud creates false identities using real and fabricated information, complicating credit risk assessment by blending legitimate credit histories with fraudulent activity. Explore comprehensive strategies to mitigate these emerging credit risks in financial institutions.
Borrower Verification
Loan stacking involves multiple lenders approving loans simultaneously without awareness of each other, exploiting weak borrower verification systems. Synthetic identity fraud fabricates borrower identities using real and fake information, challenging traditional verification methods reliant on static data points. Explore advanced borrower verification techniques and technologies that can effectively combat both loan stacking and synthetic identity fraud.
Fraud Detection
Loan stacking involves multiple simultaneous loan applications by a single borrower, often using real or stolen personal information, which can increase default risk and challenge conventional fraud detection systems. Synthetic identity fraud, on the other hand, fabricates entirely new identities using a mix of real and fake data, making detection difficult through traditional credit checks and requiring advanced AI-driven anomaly detection techniques. Discover more about how innovative fraud detection technologies can mitigate these evolving threats effectively.
Source and External Links
What Is Loan Stacking? - SoFi - Loan stacking is the process of applying for multiple loans in a very short timeframe, typically online, to access large amounts of cash quickly, which can lead to unmanageable debt and credit damage even though it's not technically illegal.
Loan Stacking: Risks and Alternatives - NerdWallet - Loan stacking refers to taking out multiple business loans from different lenders within a short period to increase accessible capital, but it carries significant risks and may violate loan agreements if not disclosed to lenders.
Loan Stacking - DataVisor Digital Fraud Wiki - Loan stacking is the practice of obtaining multiple loans or lines of credit simultaneously in a short time, often online, and while not illegal, it can involve fraud if borrowers have no intention to repay.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com