Blockchain remittance transforms cross-border payments by leveraging decentralized ledger technology to enable faster, cheaper, and more transparent transactions compared to traditional correspondent banking, which relies on intermediaries and multiple banks to process transfers. With blockchain, transaction fees are significantly lower and settlement times reduce from days to minutes, enhancing efficiency and reducing fraud risk. Explore deeper insights into how blockchain technology is revolutionizing global remittance and reshaping international banking.
Why it is important
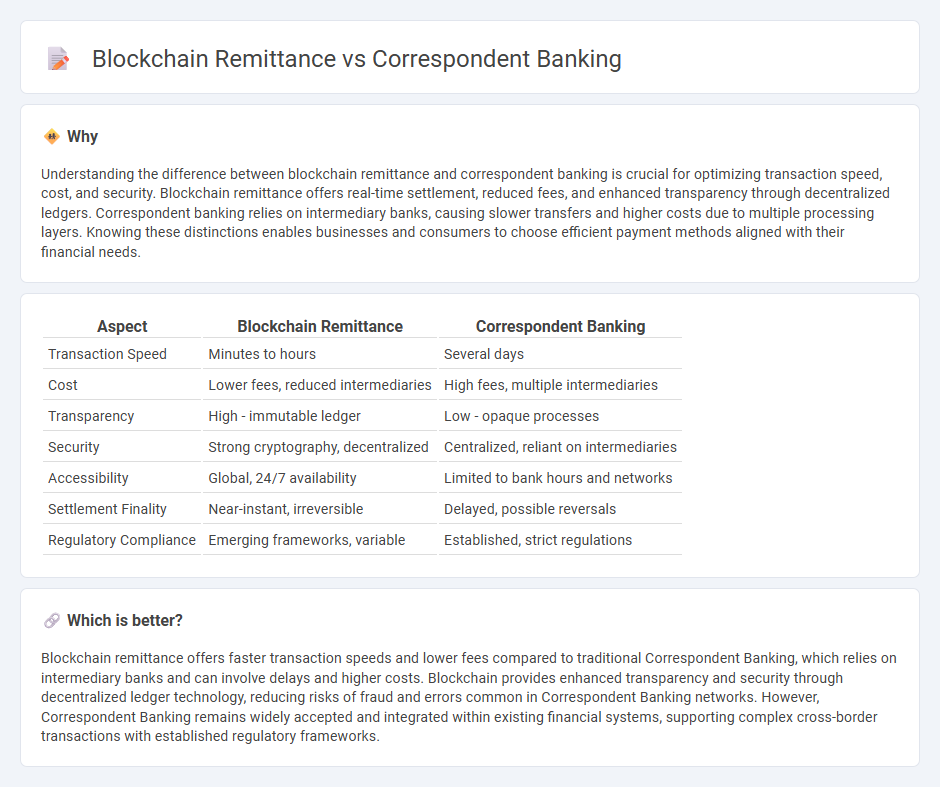
Understanding the difference between blockchain remittance and correspondent banking is crucial for optimizing transaction speed, cost, and security. Blockchain remittance offers real-time settlement, reduced fees, and enhanced transparency through decentralized ledgers. Correspondent banking relies on intermediary banks, causing slower transfers and higher costs due to multiple processing layers. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses and consumers to choose efficient payment methods aligned with their financial needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blockchain Remittance | Correspondent Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to hours | Several days |
| Cost | Lower fees, reduced intermediaries | High fees, multiple intermediaries |
| Transparency | High - immutable ledger | Low - opaque processes |
| Security | Strong cryptography, decentralized | Centralized, reliant on intermediaries |
| Accessibility | Global, 24/7 availability | Limited to bank hours and networks |
| Settlement Finality | Near-instant, irreversible | Delayed, possible reversals |
| Regulatory Compliance | Emerging frameworks, variable | Established, strict regulations |
Which is better?
Blockchain remittance offers faster transaction speeds and lower fees compared to traditional Correspondent Banking, which relies on intermediary banks and can involve delays and higher costs. Blockchain provides enhanced transparency and security through decentralized ledger technology, reducing risks of fraud and errors common in Correspondent Banking networks. However, Correspondent Banking remains widely accepted and integrated within existing financial systems, supporting complex cross-border transactions with established regulatory frameworks.
Connection
Blockchain remittance enhances the efficiency of correspondent banking by enabling faster, more transparent cross-border payments with reduced reliance on intermediary banks. Correspondent banking traditionally involves complex networks and higher costs, while blockchain technology streamlines transaction settlement through decentralized ledgers and smart contracts. Integrating blockchain into correspondent banking networks improves liquidity management, lowers settlement risks, and accelerates fund transfers globally.
Key Terms
Nostro/Vostro Accounts
Correspondent banking relies heavily on Nostro and Vostro accounts to facilitate cross-border payments by holding foreign currencies within intermediary banks, leading to higher costs and slower transaction times. Blockchain remittance utilizes distributed ledger technology to enable direct peer-to-peer transfers without the need for these intermediary accounts, resulting in faster settlements and reduced fees. Explore how blockchain technology is revolutionizing traditional correspondent banking processes and enhancing global remittance efficiency.
Decentralized Ledger
Correspondent banking relies on a network of intermediary banks to facilitate cross-border payments, often resulting in slower transaction times and higher fees. Blockchain remittance utilizes decentralized ledger technology to enable secure, transparent, and near-instant transfers without intermediaries. Discover how decentralized ledgers transform global remittance by enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
SWIFT Messaging
Correspondent banking relies heavily on the SWIFT messaging network for secure, standardized communication between banks in cross-border transactions, often leading to slower processing times and higher costs due to multiple intermediaries. Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledger technology to eliminate intermediaries, allowing near-instantaneous, transparent transfers with reduced fees and enhanced security. Explore the evolving impact of SWIFT messaging on global payments and the transformative potential of blockchain remittance solutions.
Source and External Links
Introduction to Correspondent Banking - Correspondent banking is a relationship where one bank (correspondent) provides services like international payments and currency transactions to another bank (respondent), enabling access to foreign markets and cross-border transactions.
Correspondent account - A correspondent account is a bank account established to handle deposits, payments, and other financial transactions for another financial institution, typically to facilitate operations in foreign currencies or jurisdictions.
Correspondent Banking Risk - AML Compliance - Correspondent banking involves a correspondent bank providing international transaction services for a respondent bank, often from another country, and requires risk assessments to address potential money laundering and financial crime risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com