Digital identity verification uses a combination of biometric data, document authentication, and machine learning to securely confirm a customer's identity in banking transactions. Facial recognition technology enhances this process by analyzing unique facial features to prevent fraud and streamline user access. Discover how these innovations are transforming security and convenience in modern banking.
Why it is important
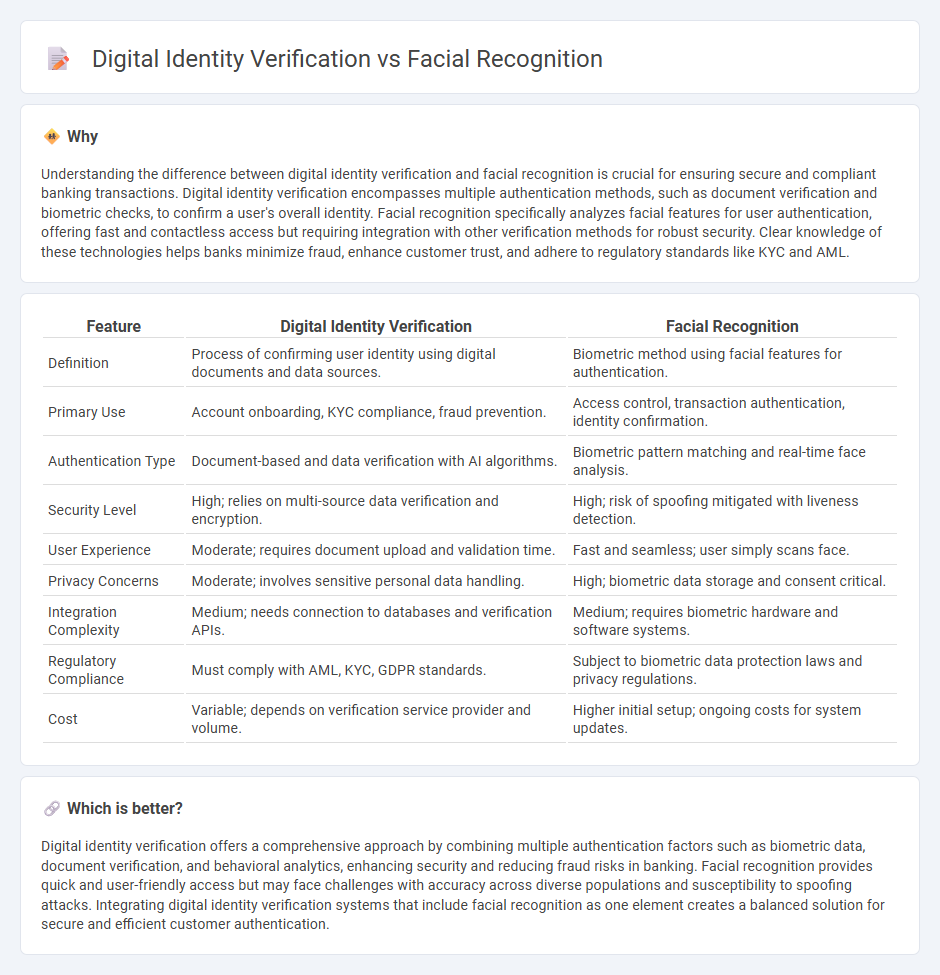
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and facial recognition is crucial for ensuring secure and compliant banking transactions. Digital identity verification encompasses multiple authentication methods, such as document verification and biometric checks, to confirm a user's overall identity. Facial recognition specifically analyzes facial features for user authentication, offering fast and contactless access but requiring integration with other verification methods for robust security. Clear knowledge of these technologies helps banks minimize fraud, enhance customer trust, and adhere to regulatory standards like KYC and AML.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | Facial Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of confirming user identity using digital documents and data sources. | Biometric method using facial features for authentication. |
| Primary Use | Account onboarding, KYC compliance, fraud prevention. | Access control, transaction authentication, identity confirmation. |
| Authentication Type | Document-based and data verification with AI algorithms. | Biometric pattern matching and real-time face analysis. |
| Security Level | High; relies on multi-source data verification and encryption. | High; risk of spoofing mitigated with liveness detection. |
| User Experience | Moderate; requires document upload and validation time. | Fast and seamless; user simply scans face. |
| Privacy Concerns | Moderate; involves sensitive personal data handling. | High; biometric data storage and consent critical. |
| Integration Complexity | Medium; needs connection to databases and verification APIs. | Medium; requires biometric hardware and software systems. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Must comply with AML, KYC, GDPR standards. | Subject to biometric data protection laws and privacy regulations. |
| Cost | Variable; depends on verification service provider and volume. | Higher initial setup; ongoing costs for system updates. |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification offers a comprehensive approach by combining multiple authentication factors such as biometric data, document verification, and behavioral analytics, enhancing security and reducing fraud risks in banking. Facial recognition provides quick and user-friendly access but may face challenges with accuracy across diverse populations and susceptibility to spoofing attacks. Integrating digital identity verification systems that include facial recognition as one element creates a balanced solution for secure and efficient customer authentication.
Connection
Digital identity verification in banking leverages facial recognition technology to enhance security and streamline customer authentication processes. Facial recognition analyzes biometric data by comparing live facial scans with stored digital identities, reducing fraud and enabling seamless access to financial services. This integration supports regulatory compliance such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) standards while improving user experience.
Key Terms
Biometric Authentication
Facial recognition technology captures unique facial features to authenticate individuals, enhancing security by accurately matching live images with stored biometric data. Digital identity verification incorporates facial recognition alongside multi-factor authentication methods, providing a robust framework for verifying user identities and preventing fraud. Explore how integrating biometric authentication elevates security standards in digital identity verification systems.
KYC (Know Your Customer)
Facial recognition technology compared to digital identity verification plays a critical role in enhancing KYC processes by providing rapid and accurate biometric authentication to prevent fraud and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Digital identity verification combines multiple data sources, including government-issued IDs and biometric data, to establish a comprehensive customer profile that strengthens security and reduces onboarding time. Explore how leveraging these technologies transforms customer validation in financial services and other regulated industries.
Liveness Detection
Liveness detection enhances facial recognition by distinguishing real human faces from photos or masks, reducing fraud in digital identity verification processes. Advanced biometric systems integrate liveness checks such as blinking and 3D depth analysis to ensure authenticity and secure user access. Discover how cutting-edge liveness detection technologies are transforming identity verification standards worldwide.
Source and External Links
What is facial recognition and how does it work? - Norton - Facial recognition identifies human faces using AI and biometrics by mapping facial features from images or videos and comparing them to databases, enabling identification or verification while raising privacy concerns.
What Is Face Recognition? | Microsoft Azure - Facial recognition technology analyzes facial geometry in images to create unique templates that can be verified or used for identification against a database.
What is Facial Recognition & How does it work? - Kaspersky - Facial recognition works by detecting faces, capturing facial images, and analyzing key features like inter-eye distance to match or recognize individuals, commonly used in devices like FaceID and surveillance systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com