Cloud migration in banking involves transferring core banking systems and data to a single cloud environment to enhance scalability and security, while multi-cloud strategies deploy workloads across multiple cloud platforms to optimize performance and reduce vendor risk. Financial institutions leverage these approaches to improve operational resilience, comply with regulatory requirements, and drive innovation through real-time data analytics and AI integration. Explore the advantages and challenges of cloud migration versus multi-cloud solutions to determine the best strategy for your banking organization.
Why it is important
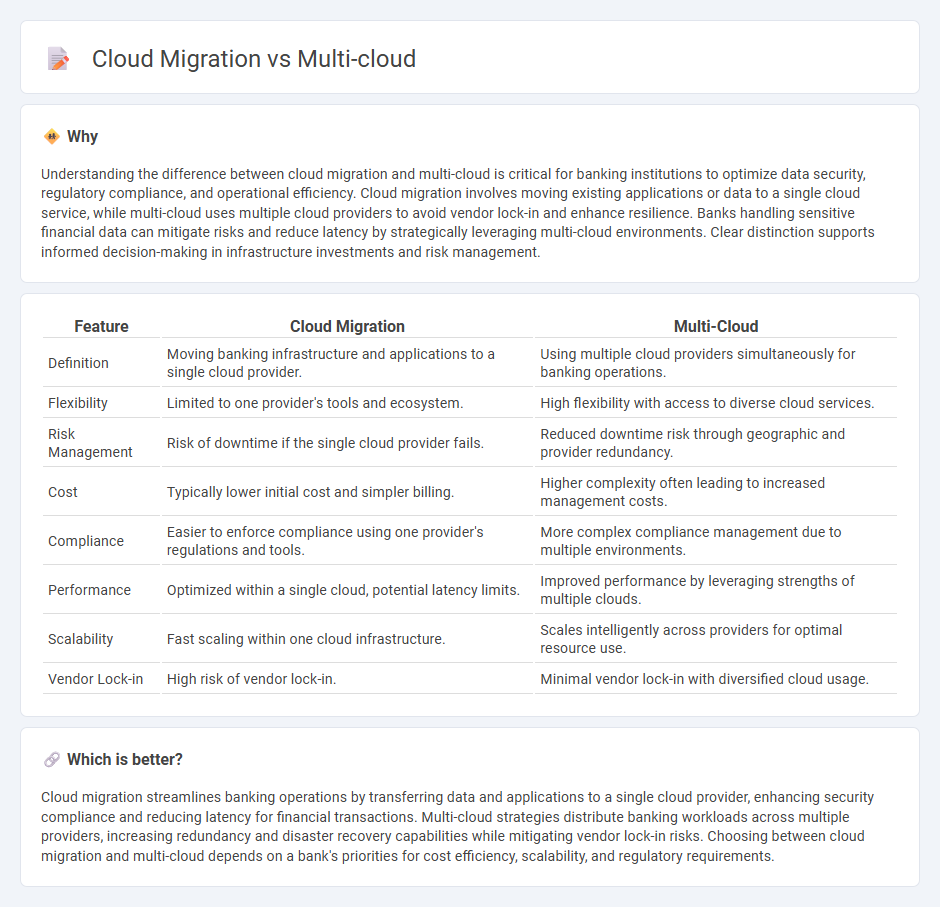
Understanding the difference between cloud migration and multi-cloud is critical for banking institutions to optimize data security, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. Cloud migration involves moving existing applications or data to a single cloud service, while multi-cloud uses multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance resilience. Banks handling sensitive financial data can mitigate risks and reduce latency by strategically leveraging multi-cloud environments. Clear distinction supports informed decision-making in infrastructure investments and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cloud Migration | Multi-Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moving banking infrastructure and applications to a single cloud provider. | Using multiple cloud providers simultaneously for banking operations. |
| Flexibility | Limited to one provider's tools and ecosystem. | High flexibility with access to diverse cloud services. |
| Risk Management | Risk of downtime if the single cloud provider fails. | Reduced downtime risk through geographic and provider redundancy. |
| Cost | Typically lower initial cost and simpler billing. | Higher complexity often leading to increased management costs. |
| Compliance | Easier to enforce compliance using one provider's regulations and tools. | More complex compliance management due to multiple environments. |
| Performance | Optimized within a single cloud, potential latency limits. | Improved performance by leveraging strengths of multiple clouds. |
| Scalability | Fast scaling within one cloud infrastructure. | Scales intelligently across providers for optimal resource use. |
| Vendor Lock-in | High risk of vendor lock-in. | Minimal vendor lock-in with diversified cloud usage. |
Which is better?
Cloud migration streamlines banking operations by transferring data and applications to a single cloud provider, enhancing security compliance and reducing latency for financial transactions. Multi-cloud strategies distribute banking workloads across multiple providers, increasing redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities while mitigating vendor lock-in risks. Choosing between cloud migration and multi-cloud depends on a bank's priorities for cost efficiency, scalability, and regulatory requirements.
Connection
Cloud migration in banking enables seamless data and application transfers from on-premises systems to cloud environments, facilitating enhanced scalability and operational agility. Multi-cloud strategies distribute banking workloads across multiple cloud providers, reducing dependency risks and improving disaster recovery capabilities. This interconnected approach allows banks to optimize resources, ensure data security, and comply with regulatory standards through diversified cloud infrastructures.
Key Terms
Interoperability
Multi-cloud strategies emphasize interoperability by enabling organizations to run workloads seamlessly across multiple cloud providers, reducing vendor lock-in and enhancing flexibility. Cloud migration focuses on transferring existing applications and data from on-premises or single-cloud environments to a new cloud infrastructure, often prioritizing compatibility and integration during the transition. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how interoperability impacts your cloud adoption strategy.
Data Sovereignty
Multi-cloud strategies distribute data and applications across multiple cloud providers to enhance redundancy and compliance with regional data sovereignty laws, ensuring data remains within specific geographic boundaries. In contrast, cloud migration involves moving existing workloads from on-premises or legacy systems to a single cloud environment, which may pose challenges in adhering to diverse local data protection regulations. Explore how aligning your cloud approach with data sovereignty requirements can mitigate risks and optimize governance in your enterprise.
Vendor Lock-in
Multi-cloud strategies leverage multiple cloud providers to reduce vendor lock-in risks by distributing workloads and data across diverse platforms, enhancing flexibility and negotiating power. In contrast, cloud migration typically involves moving resources from on-premises to a single cloud provider, which can increase dependency on that vendor's services and pricing structures. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how these approaches impact vendor lock-in and business agility.
Source and External Links
Multicloud - Wikipedia - Multicloud refers to a cloud deployment model where services are provided by two or more cloud providers, enhancing flexibility and resilience.
What is Multicloud? | IBM - Multicloud offers flexibility, cost control, and avoids vendor lock-in by using services from multiple cloud vendors.
What Is Multicloud? | Microsoft Azure - Multicloud involves using multiple cloud providers to optimize performance, increase flexibility, and mitigate risks of single-vendor reliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com