Composable banking enables financial institutions to customize and integrate modular services rapidly, enhancing flexibility and innovation compared to traditional core banking systems. Core banking provides centralized, standardized operations essential for managing accounts, transactions, and customer data across branches but often lacks agility. Explore more to understand how composable banking revolutionizes financial service delivery with adaptability and speed.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between composable banking and core banking is crucial for financial institutions seeking agility and innovation in product offerings. Composable banking enables modular, customizable services that can be quickly adapted to market demands, unlike traditional core banking systems that are often rigid and monolithic. This distinction impacts operational efficiency, customer experience, and the ability to integrate emerging technologies such as APIs and cloud services. Knowledge of both systems allows banks to strategically balance stability with flexibility in their digital transformation initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Composable Banking | Core Banking |
|---|---|---|
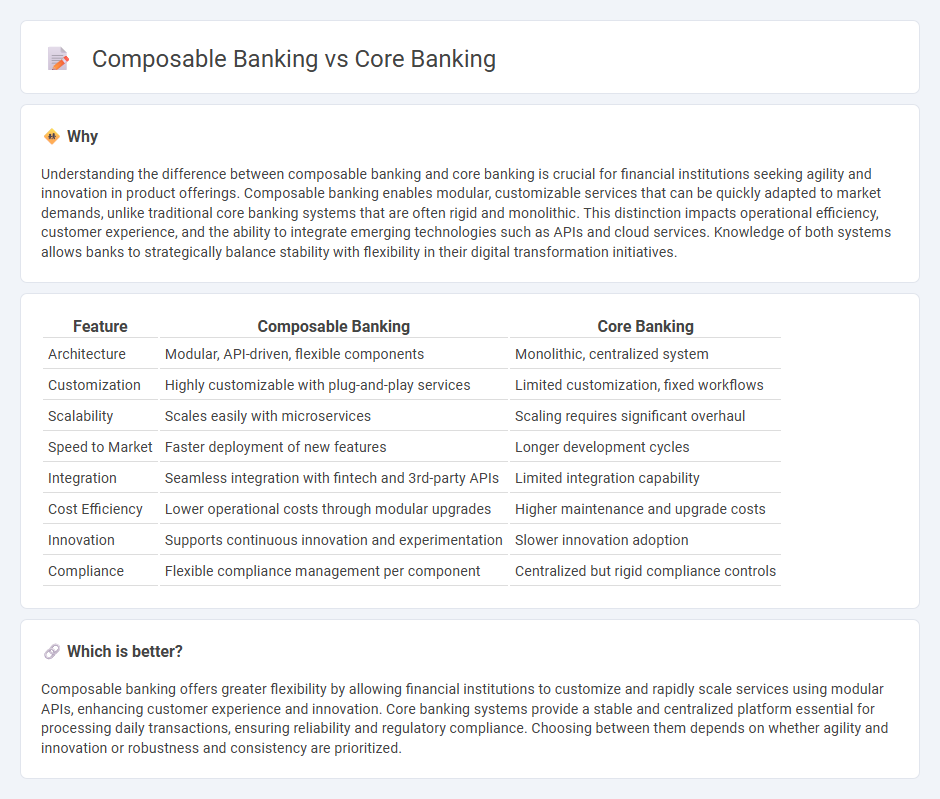
| Architecture | Modular, API-driven, flexible components | Monolithic, centralized system |
| Customization | Highly customizable with plug-and-play services | Limited customization, fixed workflows |
| Scalability | Scales easily with microservices | Scaling requires significant overhaul |
| Speed to Market | Faster deployment of new features | Longer development cycles |
| Integration | Seamless integration with fintech and 3rd-party APIs | Limited integration capability |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs through modular upgrades | Higher maintenance and upgrade costs |
| Innovation | Supports continuous innovation and experimentation | Slower innovation adoption |
| Compliance | Flexible compliance management per component | Centralized but rigid compliance controls |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers greater flexibility by allowing financial institutions to customize and rapidly scale services using modular APIs, enhancing customer experience and innovation. Core banking systems provide a stable and centralized platform essential for processing daily transactions, ensuring reliability and regulatory compliance. Choosing between them depends on whether agility and innovation or robustness and consistency are prioritized.
Connection
Composable banking leverages modular APIs that integrate seamlessly with core banking systems, enabling financial institutions to customize and scale services efficiently. Core banking provides the essential infrastructure for transaction processing, customer account management, and regulatory compliance, serving as the foundation for composable banking layers. This connection allows banks to innovate rapidly while maintaining stability and security in their operations.
Key Terms
Monolithic Architecture (Core Banking)
Monolithic core banking systems consolidate all banking functions into a single, unified platform, which can lead to challenges in scalability and flexibility due to tightly coupled components. This architecture often results in slower innovation cycles and limited customization options compared to modern composable banking frameworks. Discover how composable banking can offer modular solutions for agility and personalized customer experiences.
Modular Architecture (Composable Banking)
Composable banking leverages a modular architecture enabling financial institutions to assemble and customize core banking services through interoperable APIs, enhancing agility and innovation compared to traditional monolithic core banking systems. This approach allows rapid integration of new features, scalability, and tailored customer experiences by combining best-of-breed components from multiple vendors. Discover how modular architecture in composable banking transforms digital banking efficiency and competitiveness.
API Integration
Core banking systems provide a centralized platform for managing financial transactions, customer accounts, and regulatory compliance with limited flexibility in customization. Composable banking leverages modular APIs, enabling banks to integrate diverse fintech solutions rapidly, enhancing innovation and personalized customer experiences. Explore how API integration transforms banking agility and drives efficient service delivery.
Source and External Links
Core banking - Core banking enables customers to access their accounts and perform basic transactions from any branch of a networked bank, with services like deposits, loans, and payments managed centrally through advanced software systems.
What is Core Banking? - Core banking is the centralized back-end system that connects a bank's branches, allowing seamless customer access to account management, loans, deposits, and withdrawals from any location.
What Is Core Banking: Definition, Features, Benefits - Core banking systems automate and streamline daily banking operations, enhancing efficiency, customer experience, and security while enabling banks to rapidly launch new services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com