Personal financial management tools empower individuals to track expenses, create budgets, and set savings goals by providing intuitive dashboards and real-time analytics. Core banking systems serve as the backbone for financial institutions, handling transactions, customer information, and regulatory compliance with high security and scalability. Explore the differences and benefits of these technologies to optimize your financial strategy.
Why it is important
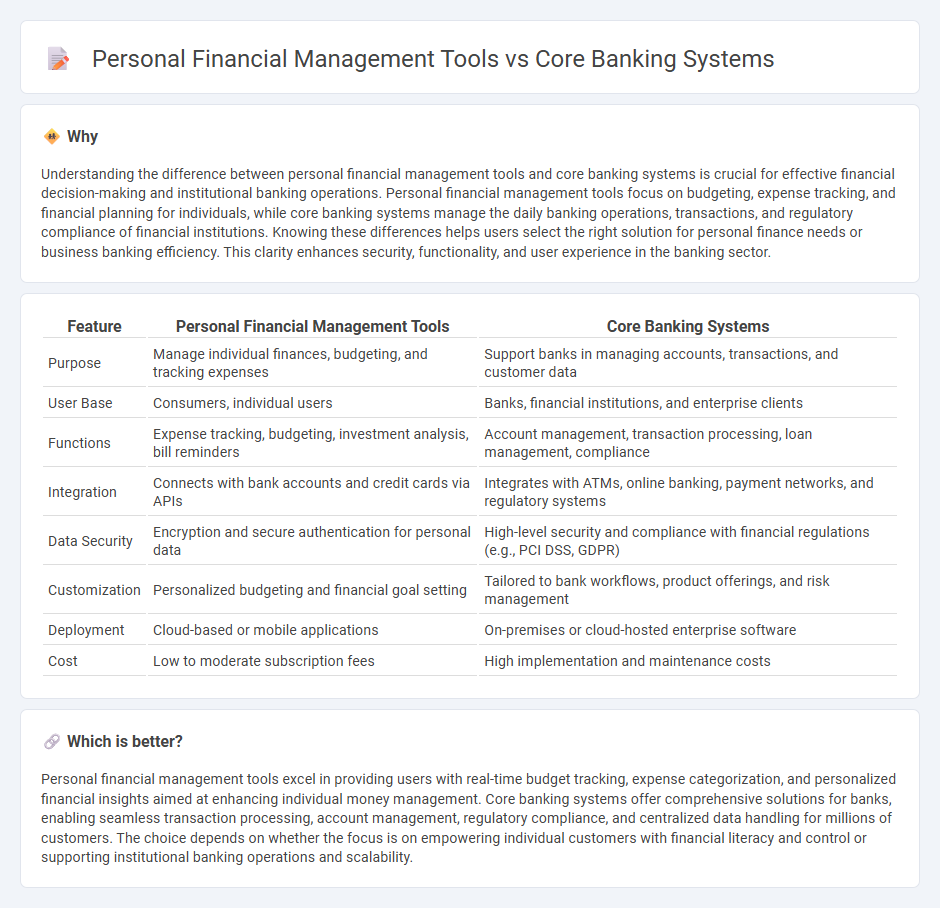
Understanding the difference between personal financial management tools and core banking systems is crucial for effective financial decision-making and institutional banking operations. Personal financial management tools focus on budgeting, expense tracking, and financial planning for individuals, while core banking systems manage the daily banking operations, transactions, and regulatory compliance of financial institutions. Knowing these differences helps users select the right solution for personal finance needs or business banking efficiency. This clarity enhances security, functionality, and user experience in the banking sector.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Personal Financial Management Tools | Core Banking Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manage individual finances, budgeting, and tracking expenses | Support banks in managing accounts, transactions, and customer data |
| User Base | Consumers, individual users | Banks, financial institutions, and enterprise clients |
| Functions | Expense tracking, budgeting, investment analysis, bill reminders | Account management, transaction processing, loan management, compliance |
| Integration | Connects with bank accounts and credit cards via APIs | Integrates with ATMs, online banking, payment networks, and regulatory systems |
| Data Security | Encryption and secure authentication for personal data | High-level security and compliance with financial regulations (e.g., PCI DSS, GDPR) |
| Customization | Personalized budgeting and financial goal setting | Tailored to bank workflows, product offerings, and risk management |
| Deployment | Cloud-based or mobile applications | On-premises or cloud-hosted enterprise software |
| Cost | Low to moderate subscription fees | High implementation and maintenance costs |
Which is better?
Personal financial management tools excel in providing users with real-time budget tracking, expense categorization, and personalized financial insights aimed at enhancing individual money management. Core banking systems offer comprehensive solutions for banks, enabling seamless transaction processing, account management, regulatory compliance, and centralized data handling for millions of customers. The choice depends on whether the focus is on empowering individual customers with financial literacy and control or supporting institutional banking operations and scalability.
Connection
Personal financial management tools integrate with core banking systems by accessing real-time transaction data and account balances through secure APIs, enabling users to monitor, budget, and manage their finances efficiently. Core banking systems provide the foundational infrastructure for processing deposits, withdrawals, and payments, while personal financial management tools offer analytical insights and personalized recommendations based on this transactional data. This seamless connection enhances customer experience by delivering accurate financial snapshots and facilitating informed decision-making within the banking ecosystem.
Key Terms
**Core Banking Systems:**
Core banking systems serve as the central backbone for financial institutions, managing essential operations such as transaction processing, account management, and regulatory compliance across multiple branches. These systems offer robust security, real-time data processing, and seamless integration with payment gateways, ensuring stability and reliability for large-scale banking activities. Explore how core banking systems revolutionize banking efficiency and customer experience by learning more about their key features and benefits.
Centralized Database
Core banking systems rely on a centralized database to streamline real-time transaction processing, account management, and regulatory compliance across multiple channels. Personal financial management tools utilize centralized data aggregation from various financial accounts to provide users with a unified view of their finances, budgeting insights, and spending analysis. Explore the differences in data management and functionality between these technologies to optimize your financial infrastructure.
Transaction Processing
Core banking systems excel in transaction processing by handling high volumes of real-time financial transactions across multiple channels, ensuring accuracy, security, and regulatory compliance. Personal financial management (PFM) tools, while capable of categorizing and tracking user transactions, primarily focus on providing insights and budgeting assistance rather than processing transactions directly. Explore how integrating both systems can optimize financial operations and user experience.
Source and External Links
What is Core Banking? - IBM - Core banking systems are centralized platforms that connect all a bank's branches, enabling real-time processing of transactions like deposits, withdrawals, loans, and new accounts while ensuring security and seamless customer access from any location.
Core banking - Wikipedia - Core banking allows customers to access their accounts and perform basic transactions at any networked branch, supported by software that centralizes record-keeping and integrates services across multiple channels including ATMs, internet, and mobile banking.
Top Core Banking Software Companies List [2025] - SDK.finance - Leading core banking platforms such as Temenos, Mambu, Finacle, and Oracle FLEXCUBE provide comprehensive, customizable solutions that automate and streamline banking operations, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences, whether deployed on-premises or in the cloud.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com