Neobanks operate exclusively online, offering digital-first banking solutions with streamlined user experiences and reduced fees. Cooperative banks prioritize member ownership and community-focused services, providing personalized banking tied to local needs and economic development. Explore the distinct features of neobanks and cooperative banks to determine which banking model suits your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between neobanks and cooperative banks is crucial for selecting the right financial services tailored to your needs. Neobanks operate exclusively online, offering streamlined digital experiences, while cooperative banks emphasize member ownership and localized community support. Choosing between these institutions impacts access to personalized services, loan options, and regulatory protections. In-depth knowledge enables consumers to optimize banking benefits, including fee structures, interest rates, and customer service channels.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobank | Cooperative Bank |
|---|---|---|
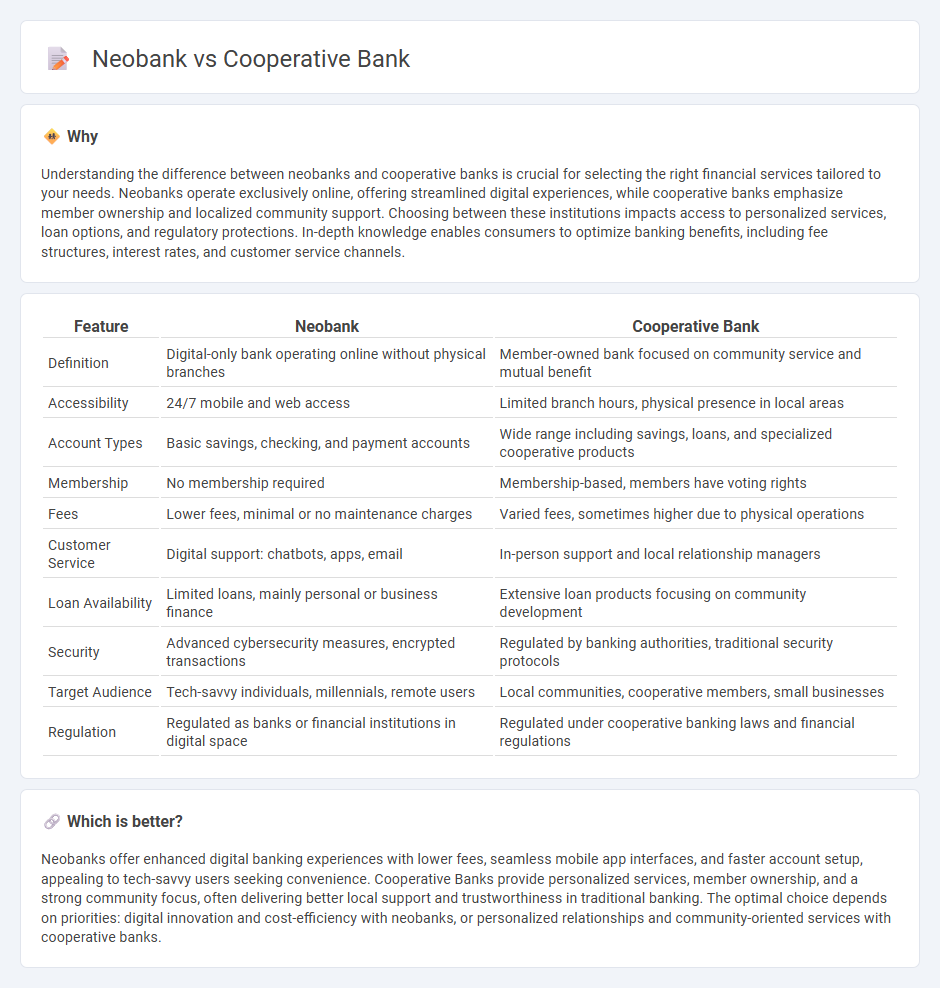
| Definition | Digital-only bank operating online without physical branches | Member-owned bank focused on community service and mutual benefit |
| Accessibility | 24/7 mobile and web access | Limited branch hours, physical presence in local areas |
| Account Types | Basic savings, checking, and payment accounts | Wide range including savings, loans, and specialized cooperative products |
| Membership | No membership required | Membership-based, members have voting rights |
| Fees | Lower fees, minimal or no maintenance charges | Varied fees, sometimes higher due to physical operations |
| Customer Service | Digital support: chatbots, apps, email | In-person support and local relationship managers |
| Loan Availability | Limited loans, mainly personal or business finance | Extensive loan products focusing on community development |
| Security | Advanced cybersecurity measures, encrypted transactions | Regulated by banking authorities, traditional security protocols |
| Target Audience | Tech-savvy individuals, millennials, remote users | Local communities, cooperative members, small businesses |
| Regulation | Regulated as banks or financial institutions in digital space | Regulated under cooperative banking laws and financial regulations |
Which is better?
Neobanks offer enhanced digital banking experiences with lower fees, seamless mobile app interfaces, and faster account setup, appealing to tech-savvy users seeking convenience. Cooperative Banks provide personalized services, member ownership, and a strong community focus, often delivering better local support and trustworthiness in traditional banking. The optimal choice depends on priorities: digital innovation and cost-efficiency with neobanks, or personalized relationships and community-oriented services with cooperative banks.
Connection
Neobanks and cooperative banks are connected through their emphasis on customer-centric banking models that leverage technology to enhance user experience. Both prioritize community engagement--cooperative banks through member ownership and local focus, and neobanks by offering digital-first services tailored to modern consumers. Their convergence highlights a shift towards accessible, transparent, and inclusive financial services in the evolving banking industry.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Cooperative banks operate under a member-owned structure, where each member has equal voting rights, fostering a democratic decision-making process that benefits local communities. Neobanks are typically owned by private investors or venture capital firms, prioritizing rapid growth and technology-driven services without member governance. Explore more to understand how these ownership models impact customer experience and financial services.
Regulatory Framework
Cooperative banks operate under strict regulatory frameworks that emphasize member ownership, local community service, and adherence to national banking laws, ensuring stability and consumer protection. Neobanks, as digital-only financial institutions, often function under different regulatory models, leveraging partnerships with traditional banks or obtaining fintech licenses that allow them to innovate while navigating evolving compliance standards. Explore the detailed regulatory distinctions and implications for consumer trust to better understand their operational landscapes.
Digital Operations
Cooperative banks integrate traditional banking values with robust digital operations, offering secure online banking, mobile apps, and personalized member services that emphasize community trust. Neobanks operate exclusively online, providing streamlined, user-friendly interfaces, rapid account setup, and innovative financial tools without physical branches to reduce costs. Discover the distinctive advantages of digital operations in cooperative banks and neobanks to choose the best fit for your banking needs.
Source and External Links
Cooperative banking - Wikipedia - Cooperative banks are financial institutions owned by their customers, operating under the cooperative principle of one person, one vote, providing retail and commercial banking services with a focus on member control, though some banks dilute this by raising capital publicly.
What is a Cooperative Bank? - Cooperative Banks, like Greenfield Cooperative Bank founded in 1905, focus on serving community financial interests by prioritizing depositor benefits and are governed by elected corporators who represent depositors' interests.
National Cooperative Bank - The National Cooperative Bank in the U.S. is dedicated exclusively to providing banking products and solutions nationwide specifically for cooperatives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com