Pay by Bank enables direct payments from a customer's bank account without the need for card details, offering faster settlement and enhanced security. ACH payments are electronic bank transfers processed through the Automated Clearing House network, often associated with slower processing times and higher fraud risks. Explore the differences between Pay by Bank and ACH payments to optimize your transaction methods.
Why it is important
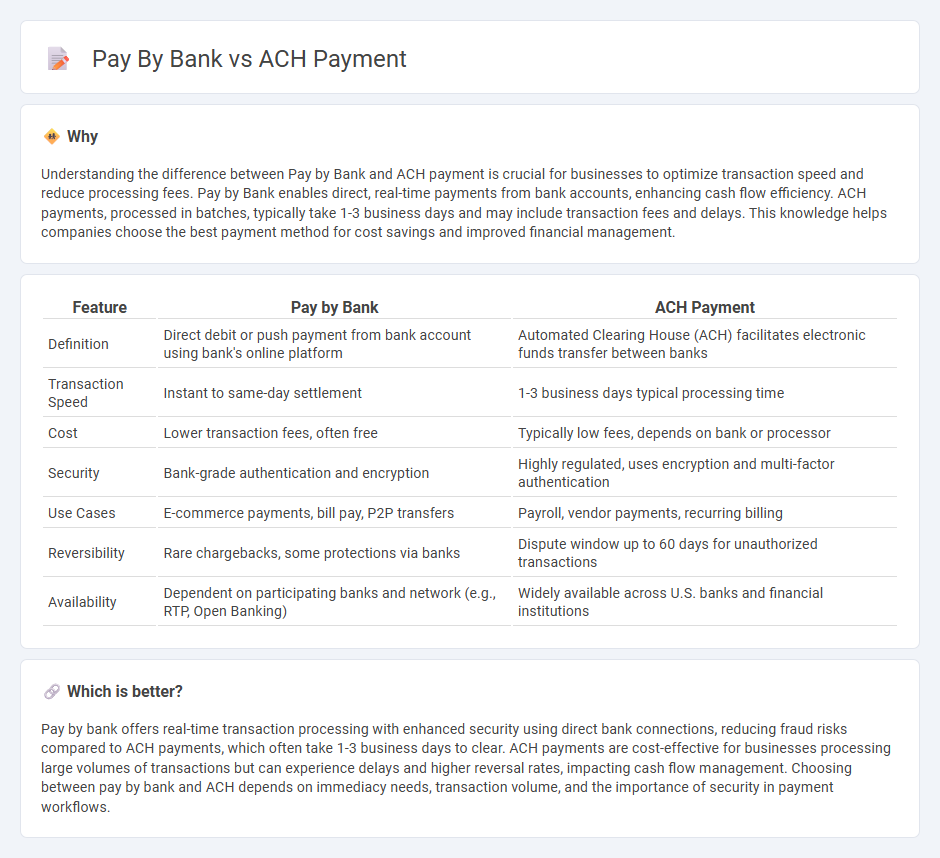
Understanding the difference between Pay by Bank and ACH payment is crucial for businesses to optimize transaction speed and reduce processing fees. Pay by Bank enables direct, real-time payments from bank accounts, enhancing cash flow efficiency. ACH payments, processed in batches, typically take 1-3 business days and may include transaction fees and delays. This knowledge helps companies choose the best payment method for cost savings and improved financial management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Pay by Bank | ACH Payment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct debit or push payment from bank account using bank's online platform | Automated Clearing House (ACH) facilitates electronic funds transfer between banks |
| Transaction Speed | Instant to same-day settlement | 1-3 business days typical processing time |
| Cost | Lower transaction fees, often free | Typically low fees, depends on bank or processor |
| Security | Bank-grade authentication and encryption | Highly regulated, uses encryption and multi-factor authentication |
| Use Cases | E-commerce payments, bill pay, P2P transfers | Payroll, vendor payments, recurring billing |
| Reversibility | Rare chargebacks, some protections via banks | Dispute window up to 60 days for unauthorized transactions |
| Availability | Dependent on participating banks and network (e.g., RTP, Open Banking) | Widely available across U.S. banks and financial institutions |
Which is better?
Pay by bank offers real-time transaction processing with enhanced security using direct bank connections, reducing fraud risks compared to ACH payments, which often take 1-3 business days to clear. ACH payments are cost-effective for businesses processing large volumes of transactions but can experience delays and higher reversal rates, impacting cash flow management. Choosing between pay by bank and ACH depends on immediacy needs, transaction volume, and the importance of security in payment workflows.
Connection
Pay by Bank and ACH payment are connected through their use of the Automated Clearing House network to facilitate secure, electronic funds transfers directly between bank accounts. Pay by Bank leverages ACH payments to enable real-time or near-real-time transactions without the need for credit cards or cash, improving transaction speed and reducing processing fees. Both methods rely on robust banking protocols to ensure secure authorization and settlement of payments within the U.S. financial system.
Key Terms
Clearing House
ACH payments use the Automated Clearing House network to electronically transfer funds between bank accounts, enabling secure, low-cost transactions for payroll, bill payments, and direct deposits. Pay by bank services leverage real-time bank-to-bank transfers, often facilitated by clearing houses or payment gateways, to provide faster settlement and enhanced transparency. Explore how clearing houses optimize these processes to improve payment efficiency and reliability.
Account-to-Account Transfer
ACH payment and pay by bank both enable seamless Account-to-Account Transfers, with ACH leveraging the Automated Clearing House network for batch processing and delayed settlement, while pay by bank offers real-time direct debits or credits through open banking APIs. Pay by bank reduces transaction fees and enhances security by removing intermediaries compared to traditional ACH methods, making it a preferred choice for instant payments and improved cash flow management. Explore the benefits and technical differences to determine the optimal payment solution for your financial operations.
Authorization
ACH payment authorization involves granting permission to debit or credit funds electronically through the Automated Clearing House network, ensuring secure and regulated transactions between bank accounts in the U.S. Pay by bank authorization leverages real-time consent and authentication directly with the user's bank, often via open banking APIs, enhancing security and reducing fraud risk. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which authorization method best suits your payment processing needs.
Source and External Links
What an ACH payment is and how an ACH transfer works - ACH payments are electronic fund transfers between accounts at different U.S. financial institutions, processed in batches via the Automated Clearing House network and typically settled within several business hours on business days.
What's an ACH payment? - An ACH payment is an electronic transfer of money from one U.S. bank account to another through the ACH network, commonly used for online transactions and often taking up to 2 business days to complete.
What is an ACH transaction? - ACH transactions include a wide range of electronic money transfers between banks and credit unions, such as direct deposit of paychecks and recurring bill payments, with processing times that can vary from same-day to several days depending on the transaction and institution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com