Banking as a Service (BaaS) integrates traditional banking capabilities into third-party platforms via APIs, enabling fintech companies to offer banking products without acquiring a full banking license. Cloud banking leverages cloud computing infrastructure to enhance scalability, security, and cost-efficiency for financial institutions, facilitating faster innovation and data management. Explore the evolving landscape to understand how these technologies reshape the future of financial services.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Banking as a Service (BaaS) and cloud banking is crucial for financial institutions aiming to innovate and scale efficiently. BaaS enables third-party providers to offer banking services via APIs, fostering fintech partnerships and digital expansion. Cloud banking leverages cloud infrastructure to enhance agility, reduce costs, and improve security in banking operations. Recognizing these distinctions helps organizations optimize technology investments and deliver superior customer experiences.
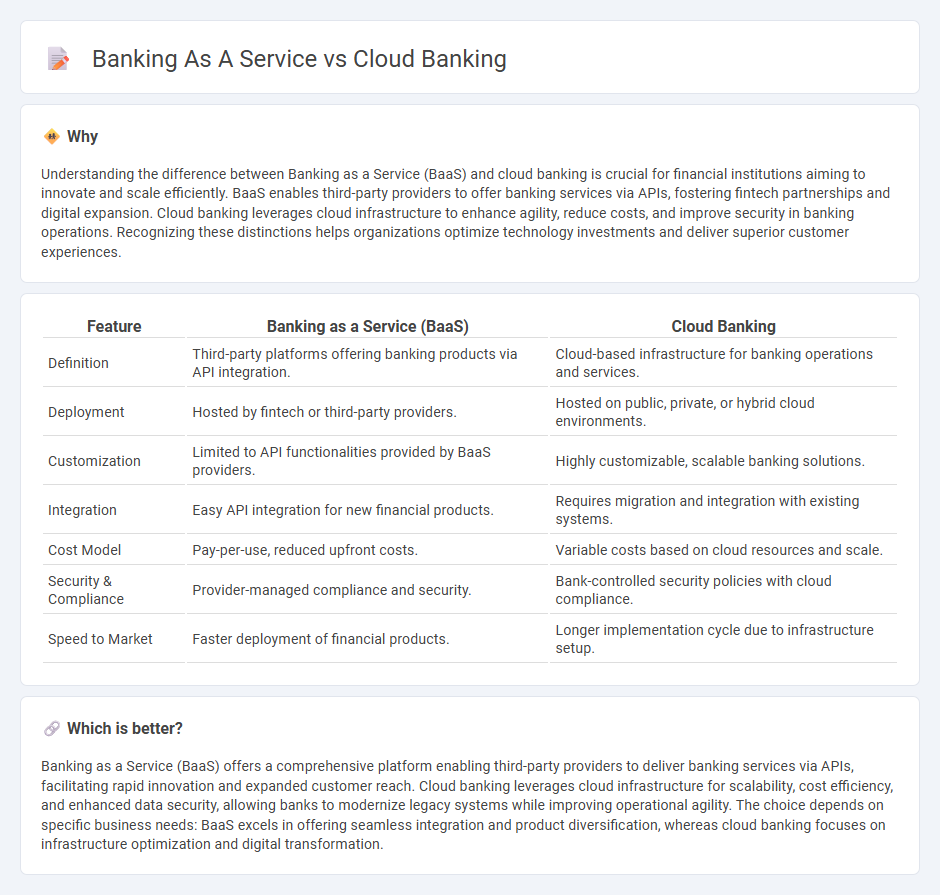
Comparison Table
| Feature | Banking as a Service (BaaS) | Cloud Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Third-party platforms offering banking products via API integration. | Cloud-based infrastructure for banking operations and services. |
| Deployment | Hosted by fintech or third-party providers. | Hosted on public, private, or hybrid cloud environments. |
| Customization | Limited to API functionalities provided by BaaS providers. | Highly customizable, scalable banking solutions. |
| Integration | Easy API integration for new financial products. | Requires migration and integration with existing systems. |
| Cost Model | Pay-per-use, reduced upfront costs. | Variable costs based on cloud resources and scale. |
| Security & Compliance | Provider-managed compliance and security. | Bank-controlled security policies with cloud compliance. |
| Speed to Market | Faster deployment of financial products. | Longer implementation cycle due to infrastructure setup. |
Which is better?
Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers a comprehensive platform enabling third-party providers to deliver banking services via APIs, facilitating rapid innovation and expanded customer reach. Cloud banking leverages cloud infrastructure for scalability, cost efficiency, and enhanced data security, allowing banks to modernize legacy systems while improving operational agility. The choice depends on specific business needs: BaaS excels in offering seamless integration and product diversification, whereas cloud banking focuses on infrastructure optimization and digital transformation.
Connection
Banking as a Service (BaaS) relies heavily on cloud banking infrastructure to enable seamless integration and scalability of financial services. Cloud banking provides the flexible, API-driven platforms that allow BaaS providers to offer customized banking products directly to businesses and third-party developers. This connection facilitates rapid innovation, improved customer experiences, and reduced operational costs in the financial ecosystem.
Key Terms
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
Cloud banking leverages Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) to provide scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient backend systems, enabling financial institutions to deploy applications without managing physical hardware. Banking as a Service (BaaS) integrates with IaaS platforms to offer modular banking capabilities, such as payment processing and compliance tools, through APIs that streamline the delivery of digital financial services. Explore how IaaS powers cloud banking and BaaS to revolutionize core banking infrastructure and accelerate innovation.
API Integration
Cloud banking leverages scalable cloud infrastructure to enhance core banking services, enabling seamless API integration for real-time data exchange, improved security, and faster innovation. Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers modular APIs that allow third-party providers to embed financial services into their platforms, driving customized customer experiences and expanding fintech ecosystems. Explore how API integration transforms financial technology by delving deeper into cloud banking and BaaS solutions.
Regulatory Compliance
Cloud banking leverages cloud infrastructure to enhance scalability, security, and regulatory compliance through automated monitoring and real-time reporting tools that align with standards like GDPR, PSD2, and SOC 2. Banking as a Service (BaaS) platforms integrate third-party banking services via APIs while ensuring compliance by embedding regulatory frameworks within their service layers, enabling fintech firms to offer financial products without direct licensing. Explore how these innovations transform compliance landscapes and mitigate regulatory risks in digital finance.
Source and External Links
What is cloud banking? | IBM - Cloud banking is the on-demand delivery of banking services by financial institutions through the internet, enabling scalable and flexible access to banking functions.
Cloud Banking: A Comprehensive Guide to Selection, Pros & Cons ... - Cloud banking uses cloud computing technology to deliver banking services including core banking, payments, risk management, and analytics, allowing banks to improve operational efficiency, innovate digitally, and enhance customer experience with AI and automation.
A Complete Guide to Cloud Banking - Crassula.io - Cloud banking platforms operate primarily on services from providers like Microsoft Azure, offering models such as BPaaS, IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS to support various banking operations, from infrastructure to software applications, all with flexibility and rapid scalability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com