Debt recycling strategically converts non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment debt, enhancing long-term wealth accumulation. Principal and interest loans require consistent repayments covering both the loan principal and accrued interest, ensuring eventual full ownership of the property. Discover how choosing between debt recycling and principal and interest loans can impact your financial goals.
Why it is important
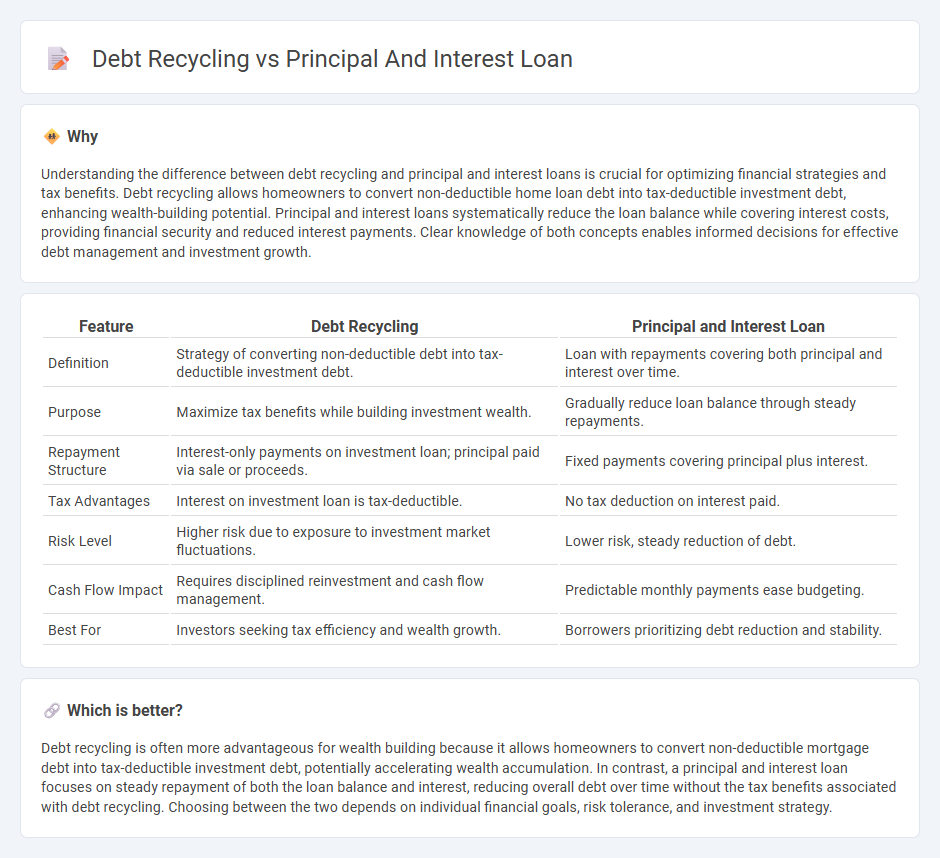
Understanding the difference between debt recycling and principal and interest loans is crucial for optimizing financial strategies and tax benefits. Debt recycling allows homeowners to convert non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment debt, enhancing wealth-building potential. Principal and interest loans systematically reduce the loan balance while covering interest costs, providing financial security and reduced interest payments. Clear knowledge of both concepts enables informed decisions for effective debt management and investment growth.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Debt Recycling | Principal and Interest Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy of converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt. | Loan with repayments covering both principal and interest over time. |
| Purpose | Maximize tax benefits while building investment wealth. | Gradually reduce loan balance through steady repayments. |
| Repayment Structure | Interest-only payments on investment loan; principal paid via sale or proceeds. | Fixed payments covering principal plus interest. |
| Tax Advantages | Interest on investment loan is tax-deductible. | No tax deduction on interest paid. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to exposure to investment market fluctuations. | Lower risk, steady reduction of debt. |
| Cash Flow Impact | Requires disciplined reinvestment and cash flow management. | Predictable monthly payments ease budgeting. |
| Best For | Investors seeking tax efficiency and wealth growth. | Borrowers prioritizing debt reduction and stability. |
Which is better?
Debt recycling is often more advantageous for wealth building because it allows homeowners to convert non-deductible mortgage debt into tax-deductible investment debt, potentially accelerating wealth accumulation. In contrast, a principal and interest loan focuses on steady repayment of both the loan balance and interest, reducing overall debt over time without the tax benefits associated with debt recycling. Choosing between the two depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy.
Connection
Debt recycling involves using a principal and interest loan to strategically convert non-deductible mortgage debt into tax-deductible investment debt. By making regular principal and interest repayments, borrowers gradually reduce their home loan while simultaneously increasing their investment loan balance. This connection optimizes cash flow management and leverages tax benefits to build wealth over time.
Key Terms
Amortization
Principal and interest loans involve fixed amortization schedules combining repayments of both the loan's principal and the accrued interest, reducing the outstanding balance over time. Debt recycling strategically uses equity, often from an investment loan, to convert non-deductible debt into tax-deductible debt while maintaining or increasing investment value. Explore how amortization impacts your financial strategy by understanding the nuances between these loan structures.
Equity
Principal and interest loans steadily reduce the outstanding balance while building equity in your property through regular repayments comprising both principal and interest components. Debt recycling leverages existing equity by converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment loans, aiming to accelerate wealth creation while managing tax efficiency. Discover how strategically using equity can optimize your financial growth and explore tailored solutions for your investment goals.
Leverage
Leverage in principal and interest loans involves regular repayments that reduce both loan principal and interest, directly decreasing overall debt. Debt recycling leverages existing equity to invest while converting nondeductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt, potentially enhancing wealth accumulation efficiency. Discover how strategic leverage through these methods can optimize your financial growth and tax benefits.
Source and External Links
What is a non-blended loan? Principal + Interest payments - In a principal + interest loan, the original amount borrowed (principal) is divided into equal monthly amounts, and interest is calculated on the outstanding principal balance each month, resulting in declining interest payments over time and less overall interest paid compared to blended payment loans.
What Are Principal and Interest for a Loan? - Principal is the amount you borrow, and interest is the added charge you pay on borrowing, calculated as a percentage (interest rate) of the loan balance, both working together to determine the total amount you repay.
Is it better to pay off the interest or principal on my auto loan? - Paying down the principal faster reduces the total interest you pay because interest is charged on the outstanding principal balance, so prioritizing principal payments shortens the loan term and lowers interest costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com