Open banking revolutionizes financial services by allowing third-party providers secure access to customer banking data through APIs, enhancing personalization and innovation. Traditional banking relies on proprietary systems with limited data sharing, often resulting in less flexibility and slower service delivery. Explore the differences to understand how open banking reshapes the future of finance.
Why it is important
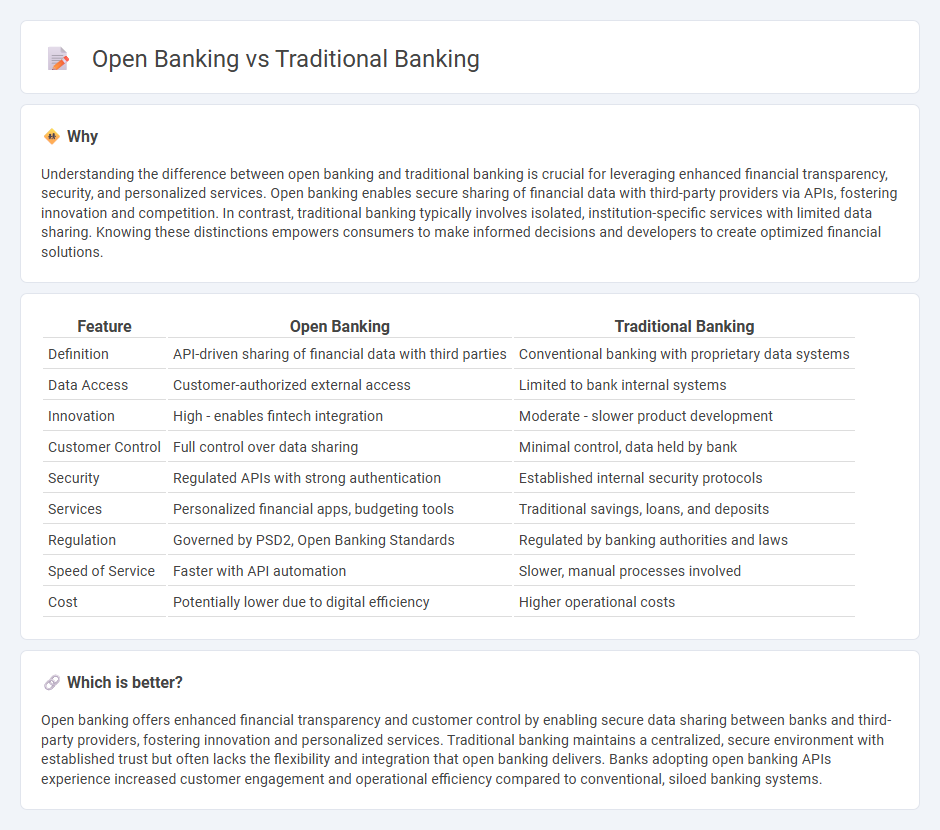
Understanding the difference between open banking and traditional banking is crucial for leveraging enhanced financial transparency, security, and personalized services. Open banking enables secure sharing of financial data with third-party providers via APIs, fostering innovation and competition. In contrast, traditional banking typically involves isolated, institution-specific services with limited data sharing. Knowing these distinctions empowers consumers to make informed decisions and developers to create optimized financial solutions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Open Banking | Traditional Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | API-driven sharing of financial data with third parties | Conventional banking with proprietary data systems |
| Data Access | Customer-authorized external access | Limited to bank internal systems |
| Innovation | High - enables fintech integration | Moderate - slower product development |
| Customer Control | Full control over data sharing | Minimal control, data held by bank |
| Security | Regulated APIs with strong authentication | Established internal security protocols |
| Services | Personalized financial apps, budgeting tools | Traditional savings, loans, and deposits |
| Regulation | Governed by PSD2, Open Banking Standards | Regulated by banking authorities and laws |
| Speed of Service | Faster with API automation | Slower, manual processes involved |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to digital efficiency | Higher operational costs |
Which is better?
Open banking offers enhanced financial transparency and customer control by enabling secure data sharing between banks and third-party providers, fostering innovation and personalized services. Traditional banking maintains a centralized, secure environment with established trust but often lacks the flexibility and integration that open banking delivers. Banks adopting open banking APIs experience increased customer engagement and operational efficiency compared to conventional, siloed banking systems.
Connection
Open banking and traditional banking are interconnected through secure data sharing frameworks that enable banks to grant third-party providers access to customer financial information with consent. This integration fosters innovation in financial services, allowing traditional banks to offer enhanced digital products and personalized customer experiences. By leveraging APIs, traditional banks maintain regulatory compliance while expanding their service ecosystem within the open banking landscape.
Key Terms
Intermediation
Traditional banking relies on direct intermediation where banks act as the sole mediators between depositors and borrowers, controlling funds flow and access to financial services. Open banking shifts this model by enabling third-party providers to access banking data through APIs, fostering competition and innovation while enhancing customer choice and service personalization. Explore the benefits and challenges of intermediation in open banking to better understand its impact on the financial landscape.
API (Application Programming Interface)
Traditional banking relies on closed systems with limited API access, restricting seamless data sharing and interoperability between financial institutions and third-party providers. Open banking utilizes standardized APIs to enable secure, real-time data exchange, fostering innovation and personalized financial services through enhanced connectivity. Explore how API-driven open banking transforms financial ecosystems for greater customer empowerment and efficiency.
Data Portability
Traditional banking typically restricts data portability by confining customer financial information within proprietary systems, limiting easy data transfer between institutions. Open banking leverages APIs to enable seamless and secure sharing of financial data across platforms, empowering customers with greater control and facilitating innovative financial services. Discover how enhanced data portability transforms user experience and drives financial inclusivity.
Source and External Links
Online vs. Traditional Banking: Differences, Pros, and Cons - Traditional banking refers to financial institutions with physical branches and ATMs offering face-to-face service along with digital options, valued for personal relationships, cash handling, a broad range of services, and established security and reputation.
Traditional Banking and Mobile Banking: Differences, Pros, ... - Traditional banking is characterized by physical bank locations where customers can access financial services and interact in person, requiring government licensing and including commercial banks and credit unions.
Online Banking vs. Traditional Banking - Traditional banks typically offer a wide range of financial services, in-person customer support, extensive ATM networks, and relationship banking, though they require some in-person visits which might be less convenient than online-only options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com