Sustainable banking focuses on environmentally and socially responsible financial practices, integrating ESG criteria into lending and investment decisions to promote long-term ecological and community well-being. Central banking, on the other hand, involves regulating monetary policy, controlling inflation, and maintaining financial stability through tools like interest rate adjustments and reserve requirements. Explore more to understand how these distinct banking approaches impact global economies and the future of finance.
Why it is important
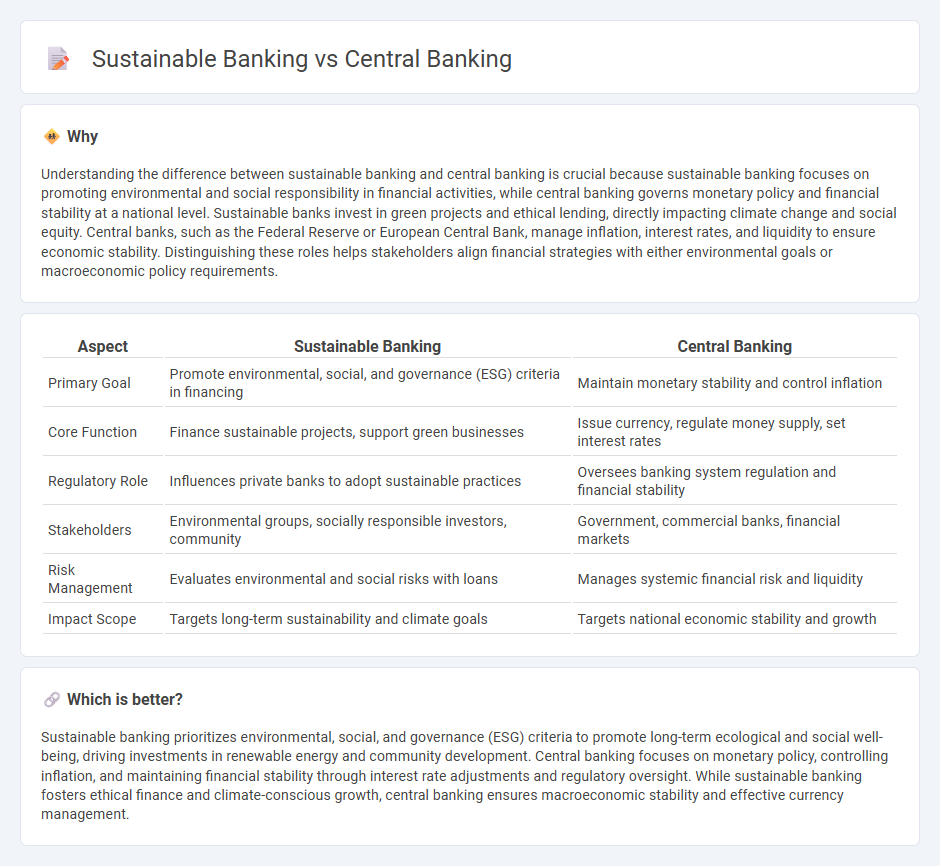
Understanding the difference between sustainable banking and central banking is crucial because sustainable banking focuses on promoting environmental and social responsibility in financial activities, while central banking governs monetary policy and financial stability at a national level. Sustainable banks invest in green projects and ethical lending, directly impacting climate change and social equity. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve or European Central Bank, manage inflation, interest rates, and liquidity to ensure economic stability. Distinguishing these roles helps stakeholders align financial strategies with either environmental goals or macroeconomic policy requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Banking | Central Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Promote environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria in financing | Maintain monetary stability and control inflation |
| Core Function | Finance sustainable projects, support green businesses | Issue currency, regulate money supply, set interest rates |
| Regulatory Role | Influences private banks to adopt sustainable practices | Oversees banking system regulation and financial stability |
| Stakeholders | Environmental groups, socially responsible investors, community | Government, commercial banks, financial markets |
| Risk Management | Evaluates environmental and social risks with loans | Manages systemic financial risk and liquidity |
| Impact Scope | Targets long-term sustainability and climate goals | Targets national economic stability and growth |
Which is better?
Sustainable banking prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term ecological and social well-being, driving investments in renewable energy and community development. Central banking focuses on monetary policy, controlling inflation, and maintaining financial stability through interest rate adjustments and regulatory oversight. While sustainable banking fosters ethical finance and climate-conscious growth, central banking ensures macroeconomic stability and effective currency management.
Connection
Sustainable banking integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial decision-making, influencing central banks to incorporate climate risk assessments and promote green finance policies. Central banking supports sustainable banking by adjusting monetary policies to incentivize investments in renewable energy and low-carbon technologies, enhancing financial stability amid climate change. Collaboration between these institutions drives the transition toward a resilient, low-carbon economy through regulatory frameworks and sustainable investment standards.
Key Terms
**Central Banking:**
Central banking regulates national monetary policy, manages inflation, and ensures financial system stability through interest rate adjustments, reserve requirements, and lender-of-last-resort functions. Key entities include the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, and Bank of England, which influence economic growth and employment levels. Explore more about how central banking shapes global economic frameworks and monetary control.
Monetary Policy
Central banking primarily aims at stabilizing the economy through monetary policy tools such as interest rate adjustments, inflation targeting, and controlling the money supply to ensure financial stability and economic growth. Sustainable banking integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into lending and investment decisions to promote long-term economic resilience and address climate risks. Discover more about how monetary policy intersects with sustainable finance to shape future economic landscapes.
Lender of Last Resort
Central banking serves as the Lender of Last Resort by providing liquidity during financial crises to stabilize the banking system and prevent systemic collapse. Sustainable banking integrates this function by emphasizing long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria alongside financial stability to promote resilient economic growth. Explore the evolving role of central banks in fostering sustainability within financial markets.
Source and External Links
A Brief History of Central Banks - A central bank is the authority responsible for controlling a country's money supply and credit through tools like open market operations, discount window lending, and reserve requirements to achieve price stability, economic stability, and financial stability.
Central bank - Central banks manage a country's monetary policy and typically enjoy institutional, goal, and operational independence to effectively set policy goals and tools without political interference.
Monetary Policy and Central Banking - Central banks use monetary policy to manage economic fluctuations and price stability, employing conventional and unconventional tools, while also overseeing macroprudential policies to ensure financial system stability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com